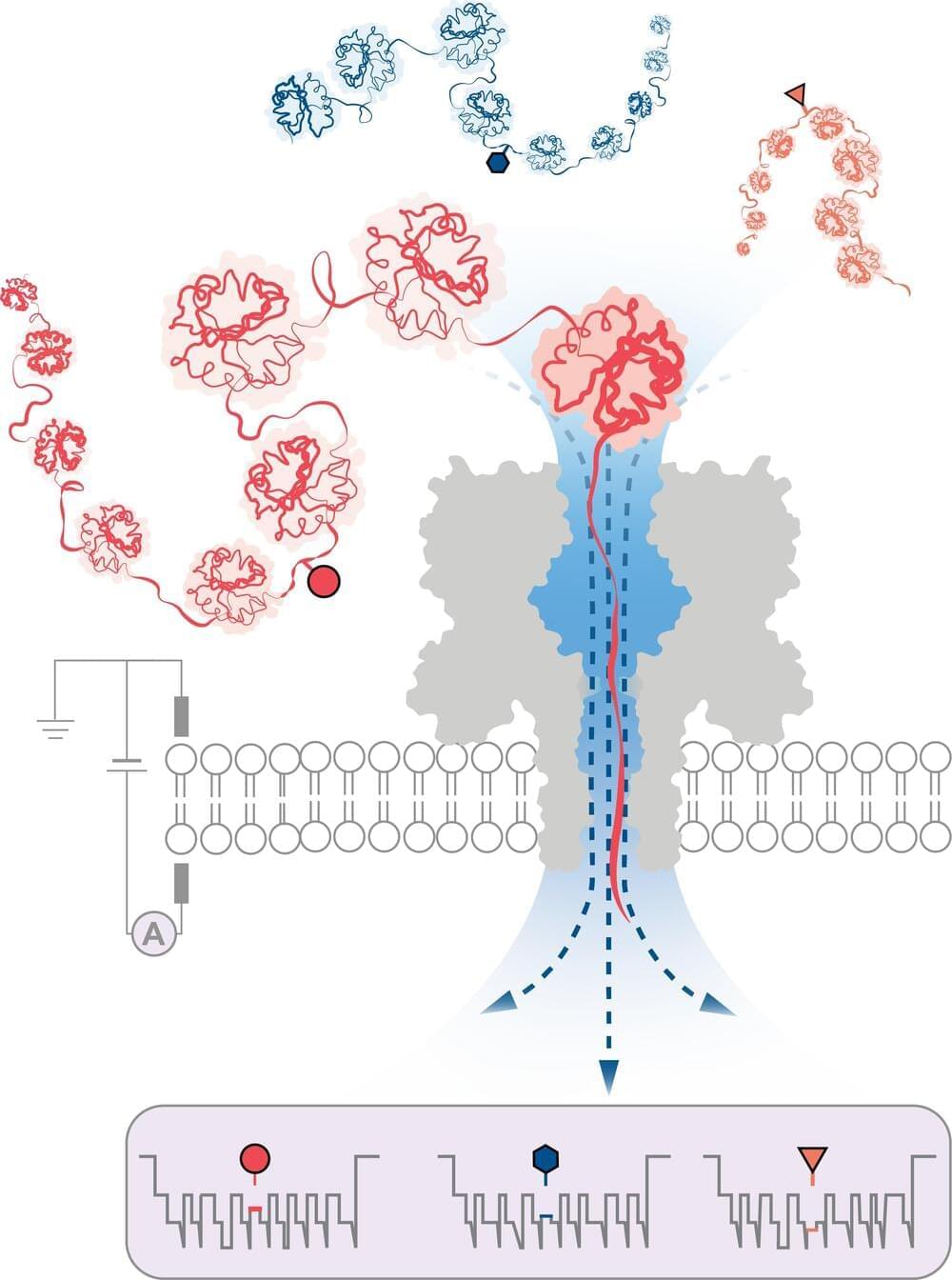
The researchers were successful in showing the relationship between activin A and bone erosion in cholesteatoma. “Our study showed that targeting activin A is a potential treatment in the management of cholesteatomas,” says senior author Masaru Ishii, MD, PhD, professor.
Currently in clinical settings, the only effective treatment for cholesteatomas is complete surgical removal. However, the discovery of how a cholesteatoma can cause bone erosion in this study offers new hope for developing novel medical treatments as first-line management for cholesteatomas.
“A cholesteatoma can still return or happen again even after its surgical removal, so it is important to know what is actually causing it,” notes lead author Kotaro Shimizu.