Though drug developers have achieved some progress in treating Alzheimer’s disease with medicines that reduce amyloid-beta protein, other problems of the disease, including inflammation, continue unchecked. In a new study, scientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT describe a candidate drug that in human cell cultures and Alzheimer’s mouse models reduced inflammation and improved memory.
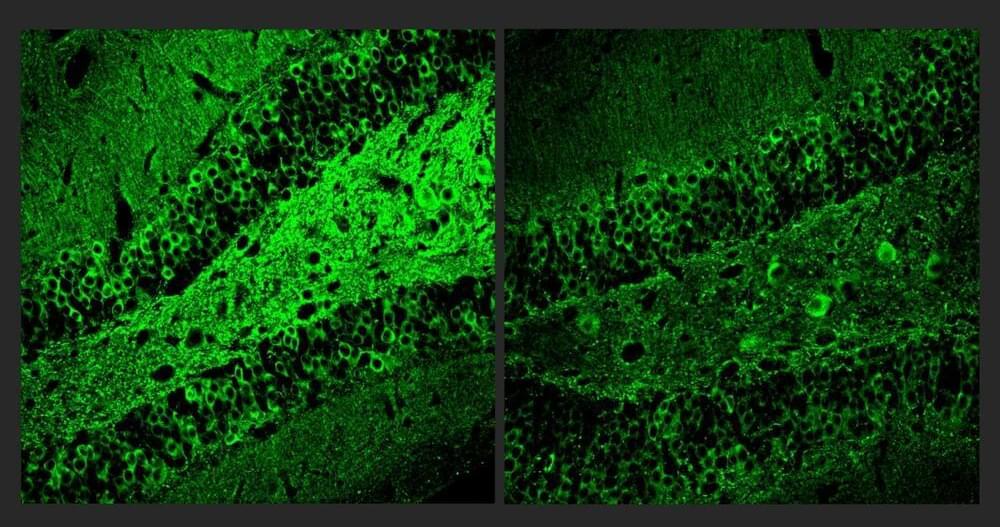
The target of the new “A11” molecule is a genetic transcription factor called PU.1. Prior research has shown that amid Alzheimer’s disease, PU.1 becomes an overzealous director of inflammatory gene expression in the brain’s microglia immune cells. A11 suppresses this problematic PU.1 activity, the new research shows, by recruiting other proteins that repress the inflammatory genes PU.1 works to express. But because A11 concentrates mostly in the brain and does not reduce PU.1 levels, it does not appear to disrupt PU.1’s other job, which is to ensure the production of a wide variety of blood cells.
“Inflammation is a major component of Alzheimer’s disease pathology that has been especially hard to treat,” says study senior author Li-Huei Tsai, Picower Professor of Neuroscience at MIT and director of The Picower Institute and MIT’s Aging Brain Initiative. “This preclinical study demonstrates that A11 reduces inflammation in human microglia-like cells, as well as in multiple mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, and significantly improves cognition in the mice. We believe A11 therefore merits further development and testing.”