In a groundbreaking clinical trial, two patients suffering from severe heart failure experienced improvements in their symptoms through an innovative procedure. The clinical trial was conducted by Heartseed, a medical venture associated with Keio University in Tokyo’s Shinjuku Ward.
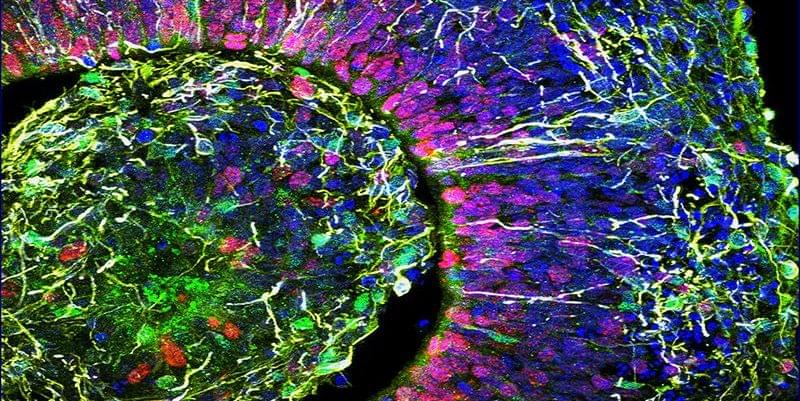
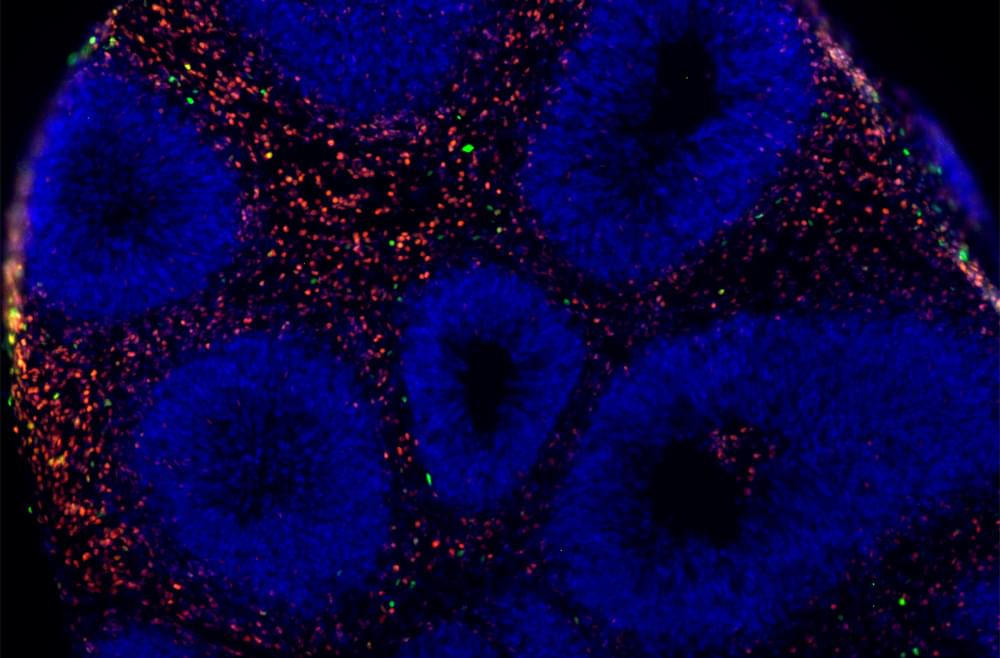
The procedure involves the transplantation of “cardiomyocyte spheroids” (CM spheroids), spherical clusters of heart muscle cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). This development represents a significant step forward in the treatment of heart failure using iPSCs, with plans for practical implementation set for around 2025.
Japanese venture Heartseed has found that treating heart failure with iPSC-derived cardiomyocyte spheroids could achieve sustained tissue regeneration.