http://www.blogtalkradio.com/lifelessonsnetwork/2017/12/08/g…io-hacking




The SRF Summer Scholars Program offers undergraduate students the opportunity to conduct biomedical research to combat diseases of aging, such as cancer, atherosclerosis, and Parkinson’s Disease. Under the guidance of a scientific mentor, each Summer Scholar is responsible for his or her own research project in such areas as genetic engineering and stem cell research. The Summer Scholars Program emphasizes development of both laboratory and communication skills to develop well-rounded future scientists, healthcare professionals, and policy makers.
In a bold first-of-its-kind experiment, scientists have edited a person’s genes directly inside living tissue in an ambitious bid to cure a man of a rare, crippling genetic disorder.
While CRISPR has broken ground in things like editing human embryos and injecting patients with genetically edited cells, this alternative technique pioneers a new real-time approach to infusing a person’s blood with a gene-editing virus.
“For the first time, a patient has received a therapy intended to precisely edit the DNA of cells directly inside the body,” says CEO of Sangamo Therapeutics, Sandy Macrae, whose company is testing the experimental procedure.
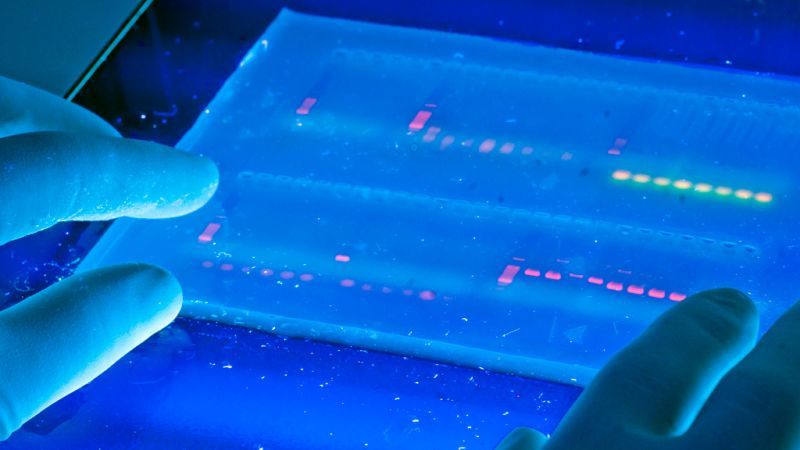
It worked. Working with mice, they were able to reverse the disease symptoms of kidney disease, type 1 diabetes, and a form of muscular dystrophy. In the mouse with kidney disease, for example, they turned on two genes associated with kidney function and saw the kidney function improved.
The unassumingly named CRISPR/Cas9 is a technology that stands to remake the world as we know it. By allowing scientists to more easily than ever cut and paste all those As, Cs, Ts, and Gs that encode all the world’s living things, for one thing, it could one day cure many devastating diseases.
All that power, though, comes with one pretty sizable caveat: Sometimes CRISPR doesn’t work quite like we expect it to. While the scientific establishment is still embroiled in a debate over just how serious the problem is, CRISPR sometimes causes off-target effects. And for scientists doing gene editing on human patients, those mutations could wind up inadvertently causing problems like tumors or genetic disease. Yikes.

‘UN diplomats confirmed that the new email release would worsen the “bad name” of gene drives in some circles. “Many countries [will] have concerns when this technology comes from DARPA, a US military science agency,” one said.‘.
Cutting-edge gene editing tools such as Crispr-Cas9 work by using a synthetic ribonucleic acid (RNA) to cut into DNA strands and then insert, alter or remove targeted traits. These might, for example, distort the sex-ratio of mosquitoes to effectively wipe out malarial populations.
Some UN experts, though, worry about unintended consequences. One told the Guardian: “You may be able to remove viruses or the entire mosquito population, but that may also have downstream ecological effects on species that depend on them.”
“My main worry,” he added, “is that we do something irreversible to the environment, despite our good intentions, before we fully appreciate the way that this technology will work.”
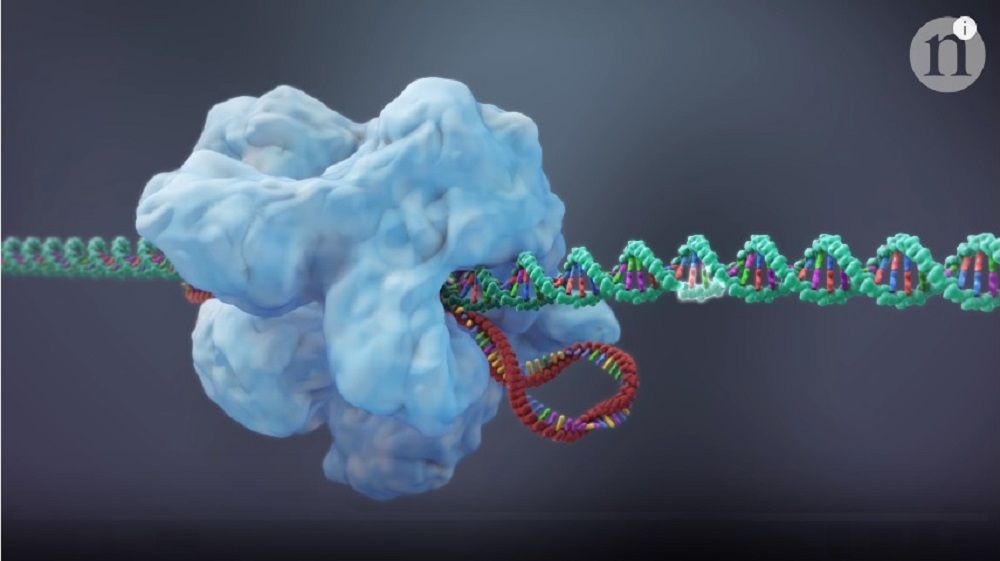
Summary: (Video) A short animation from the journal Nature demonstrates revolutionary new additions to the CRISPR toolbox some call CRISPR 2.0. Scroll down for video. [This article first appeared on LongevityFacts. Follow us on Reddit | Google+ | Facebook. Author: Brady Hartman.]
Techniques to modify DNA in the genome have existed for several decades, and the original CRISPR-Cas9, called CRISPR 1.0, brought an era of faster, cheaper, and more efficient gene editing tools. A short video from the journal Nature shows you how scientists have revolutionized the original CRISPR-Cas9 system, significantly expanded its toolbox, creating a more powerful set of tools some call CRISPR 2.0. Genetic engineers have discovered how to make CRISPR perform new tricks such as improved gene editing, turning genes on and off, and making genes glow for research.
What are gene editing and crispr-cas9?
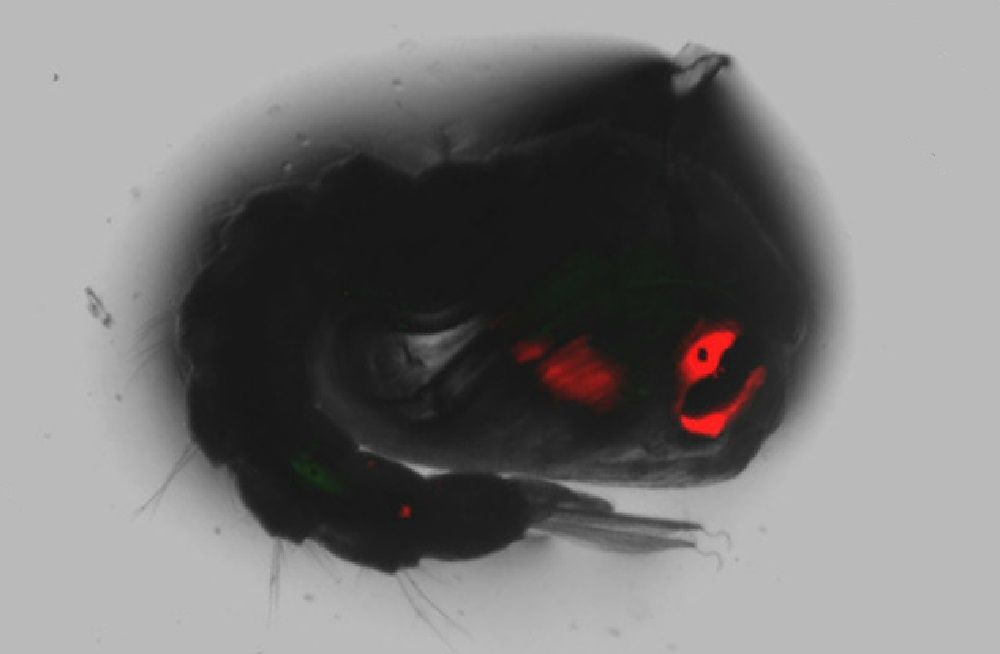
Summary: Will gene drive wipe out malaria-causing mosquitoes, or will the genetic technology that ‘spreads like wildfire’ cause a catastrophe? Gene drive raises hopes and fears as a team of scientists funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation are using it to wipe out the mosquitoes that carry malaria, to eradicate the disease. [This article first appeared on LongevityFacts. Follow us on Reddit | Google+ | Facebook. Author: Brady Hartman.]
In a basement lab at the Imperial College London (ICL), a group of researchers led by Andrew Hammond are on a mission to wipe out malaria. The scientists are funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and are using a technology called gene drive – a souped-up form of genetic engineering designed to wipe out the mosquitoes that carry the disease.
The lab contains cages of mosquitoes modified with the gene drive, along with an additional gene that makes their eyes and other body parts glow red under laser light.