COVID-19 News:


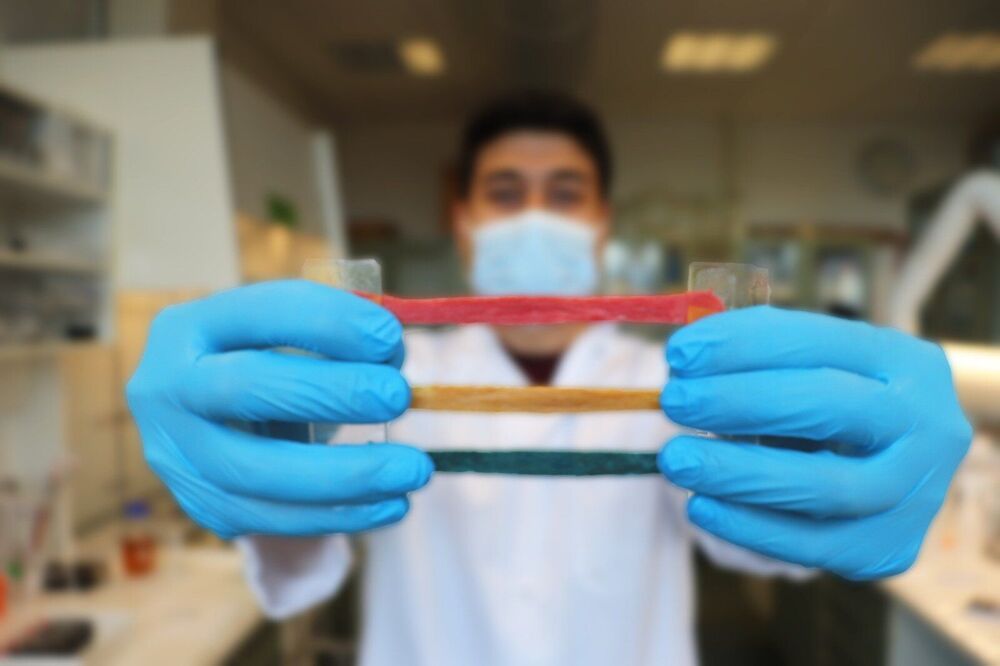
Researchers at DTU Health Tech have developed a new material that can facilitate a near-perfect merger between machines and the human body for diagnostics and treatment.
A DTU research team consisting of Malgorzata Gosia Pierchala, Firoz Babu Kadumundi, and Mehdi Mehrali from #TeamBioEngine headed by Alireza Dolatshahi-Pirouz, have developed a new material—CareGum—that among other things has potential for monitoring motor impairment associated with neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s.
Don’t worry you haven’t stumbled onto that strange part of the internet again, but it is true that we never truly did sequence the entire Human genome. For you see what was completed in June 2000 was the so called ‘first draft’, which constituted roughly 92% of genome. The problem with the remaining 8% was that these were genomic ‘dead zones’, made up of vast regions of repeating patterns of nucleotide bases that made studying these regions of the genome effectively impossible with the technology that was available at the time.
However, recent breakthroughs in high throughput nanopore sequencing technology have allowed for these so call dead zones to be sequences. Analysing these zone revealed 80 different genes which had been missed during the initial draft of the Human genome. Admittedly this is not many considering that the other 92% of the genome contain 19889 genes, but it may turn out that these genes hold great significance, as there are still many biological pathways which we do not fully understand. It is likely that many of these genes will soon be linked with what are known as orphan enzymes, which are proteins that are created from an unidentified gene, which is turn opens up the door to studying these enzymes more closely via controlling their expression.
So how does this discovery effect the field of regenerative medicine? Well the discovery of these hidden genes is potentially very significant for our general understand of Human biology, which in turn is important for our understanding of how we might go about fixing issues which arise. Possibly more important that the discovery of these hidden genes, is the milestone this sequencing represents in our ability to study our genomes quickly and efficiently with an all-inclusive approach. The vast amount of data that will soon be produced via full genome analysis will go a long way towards understanding the role that genetics play in keeping our bodies healthy, which in turn will allow us to replicate and improve upon natural regenerative and repair mechanisms. It might even allow us to come up with some novel approaches which have no basis in nature.

When attacked by chemotherapy, all cancer cells have the ability to start hibernating in order to wait out the threat, finds new research.
Researchers discover that cancer cells go into hibernation to avoid chemotherapy effects.
Papers referenced in the video:
Sirtuins, Healthspan, and Longevity in Mammals.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124115965000034
Sirt1 extends life span and delays aging in mice through the regulation of Nk2 homeobox 1 in the DMH and LH
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24011076/
Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17086191/
Rapamycin, But Not Resveratrol or Simvastatin, Extends Life Span of Genetically Heterogeneous Mice.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20974732/
Sirt1 improves healthy ageing and protects from metabolic syndrome-associated cancer.

The Moon will get between us and the Sun next week, creating a fiery halo.
During the annular eclipse, the Sun is at its nearest point to Earth, while the Moon is at its greatest distance away from Earth, so it is not large enough to cover up the entirety of the Sun from our view from Earth.
When is the annular solar eclipse?
The annular solar eclipse will take place on Thursday, June 10, and the exact times are dependent on your location. The eclipse will begin at sunrise for many in North America and last a little less than an hour.
