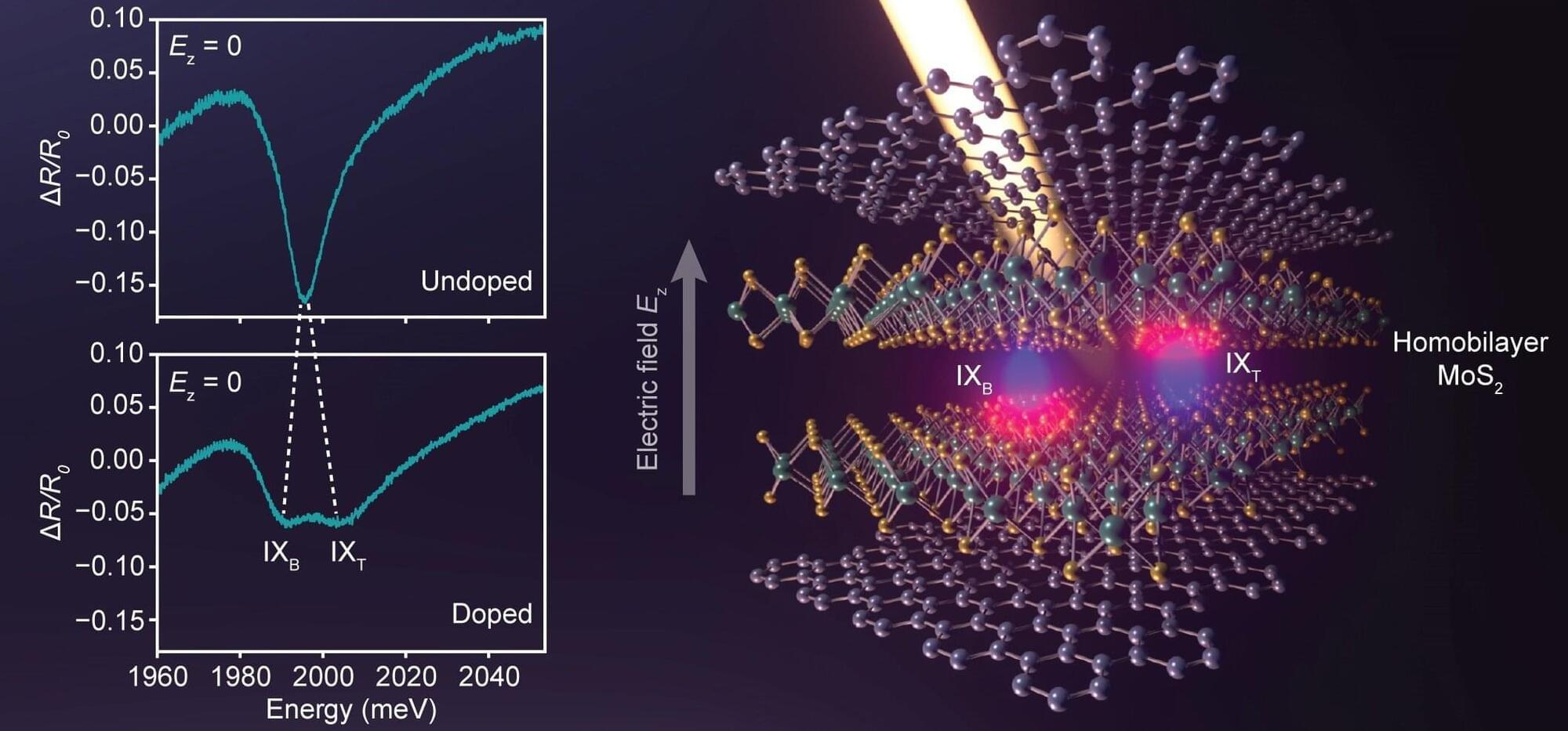
Quantum technologies are systems that can compute data, sense their surrounding environment or perform other functions leveraging quantum mechanical effects. Connecting these technologies over long distances has so far proved challenging, as quantum information can easily become scrambled or destroyed following decoherence resulting from the systems’ interactions with their surrounding environment.
Over the past few years, quantum physicists and engineers have been trying to devise effective techniques to reliably establish quantum networks, infrastructures that allow quantum information to travel between different devices.
The realization of these networks requires so-called quantum relays, intermediate stations that can forward and redistribute entangled states, extending the distances across which devices can communicate.