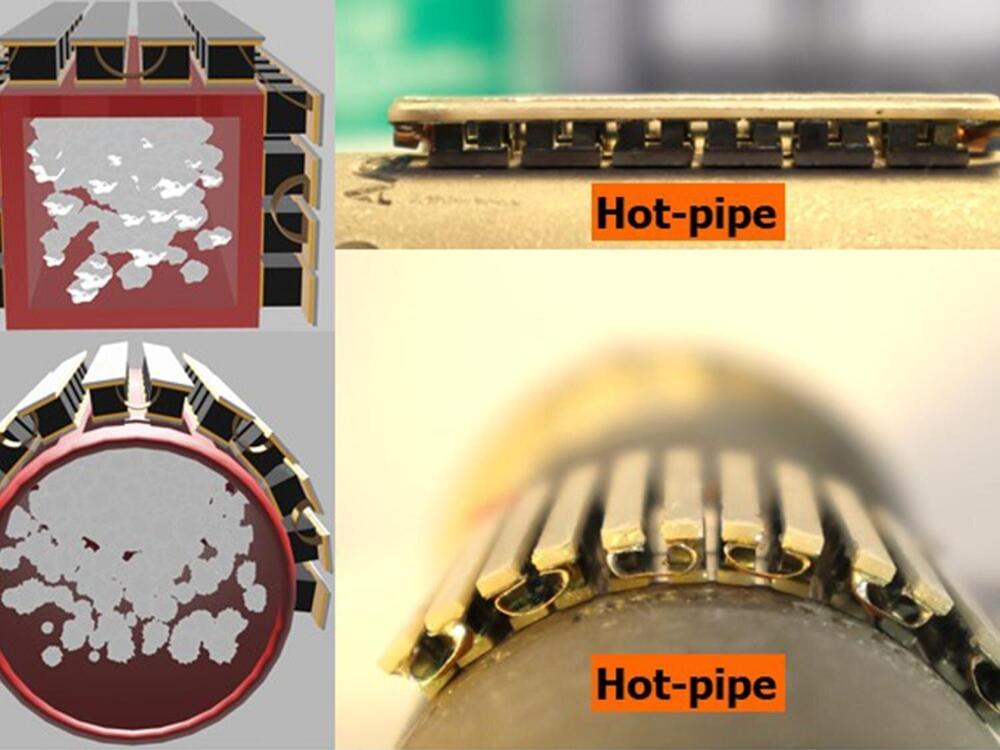
The energy systems that power our lives also produce wasted heat—like heat that radiates off hot water pipes in buildings and exhaust pipes on vehicles. A new flexible thermoelectric generator can wrap around pipes and other hot surfaces and convert wasted heat into electricity more efficiently than previously possible, according to scientists at Penn State and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
“A large amount of heat from the energy we consume is essentially being thrown away, often dispersed right into the atmosphere,” said Shashank Priya, associate vice president for research and professor of materials science and engineering at Penn State. “We haven’t had cost-effective ways with conformal shapes to trap and convert that heat to useable energy. This research opens that door.”
Penn State researchers have been working to improve the performance of thermoelectric generators—devices that can convert differences in temperature to electricity. When the devices are placed near a heat source, electrons moving from the hot side to the cold side produce an electric current, the scientists said.