An intriguing new artificial intelligence project called “The Simulation” is exploring the possibility of autonomously creating new episodes of the hit animated series South Park. Researchers from Fable Studios have published a paper detailing their approach, which combines multi-agent simulations, large language models, and custom visual generation systems.
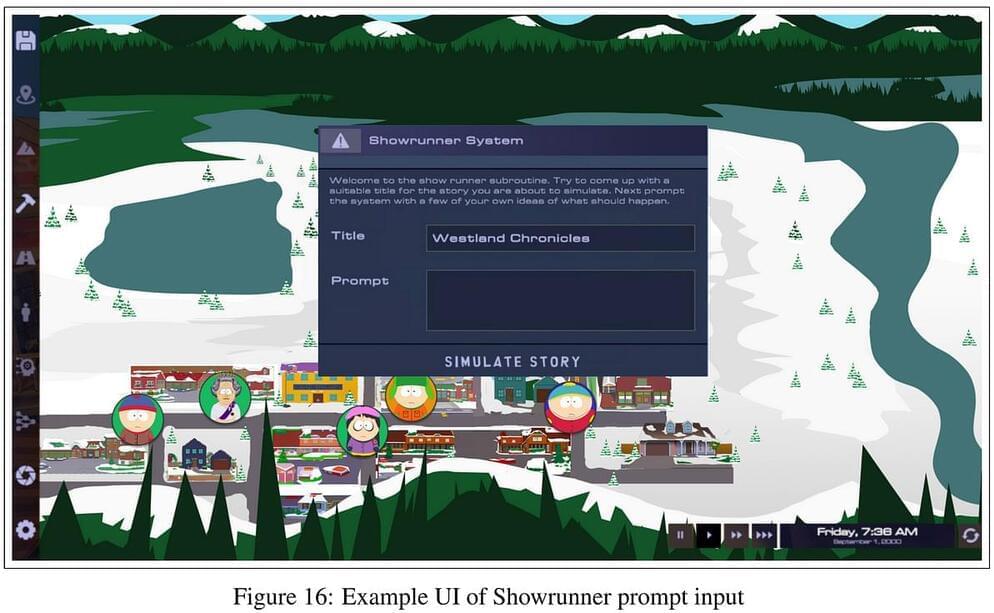
The goal is to develop an AI “showrunner” agent that can generate high-quality, customized story content aligned with the style, characters, and sensibilities of South Park. The system would allow users to essentially “program” their own new episodes by providing high-level prompts and guidance.
Key to the approach is the use of a simulated South Park world, populated by digital versions of characters like Cartman, Kyle, and Stan. This provides context and backstory to seed the creative process. Users can influence events and character behaviors within the simulation to set up storylines.