Learn more about the ways this disease travels to different parts of your body, and how treatment can help stop the spread.

The boundaries of science are constantly being pushed and expanded as newer and more advanced technology is developed, and researchers are now promising a “new era” of discovery as the world’s most powerful X-ray laser comes online.
The laser in question is the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) II, and it’s able to produce up to a million X-ray flashes every single second. That’s some 8,000 times more than the original LCLS laser, creating a virtually continuous beam of highly energetic light that is 10,000 times brighter than before.
That means it can capture processes in much more detail at the atomic scale, perhaps processes that have never been properly observed before – and from there, maybe opening up completely new fields of research.

“If you can get up to a watt per square meter, it would be very attractive from a cost perspective,” Assawaworrarit says.
The invention taps into a source of energy that’s easily overlooked
The Earth is constantly receiving a tremendous amount of energy from the Sun, to the tune of 173,000 terrawatts. Clouds, particles in the atmosphere, and reflective surfaces like snow-covered mountains immediately reflect 30 percent of that energy out into space. The rest of it ends up warming the land, oceans, clouds, atmosphere, and everything else on the planet.

In The Extended Mind: The Power of Thinking Outside the Brain (public library), Annie Murphy Paul explores the most thrilling frontiers of this growing understanding, fusing a century of scientific studies with millennia of first-hand experience from the lives and letters of great artists, scientists, inventors, and entrepreneurs. Challenging our cultural inheritance of thinking that thinking takes place only inside the brain, she illuminates the myriad ways in which we “use the world to think” — from the sensemaking language of gestures that we acquire as babies long before we can speak concepts to the singular fuel that time in nature provides for the brain’s most powerful associative network.
Paul distills this recalibration of understanding:
Thinking outside the brain means skillfully engaging entities external to our heads — the feelings and movements of our bodies, the physical spaces in which we learn and work, and the minds of the other people around us — drawing them into our own mental processes. By reaching beyond the brain to recruit these “extra-neural” resources, we are able to focus more intently, comprehend more deeply, and create more imaginatively — to entertain ideas that would be literally unthinkable by the brain alone.
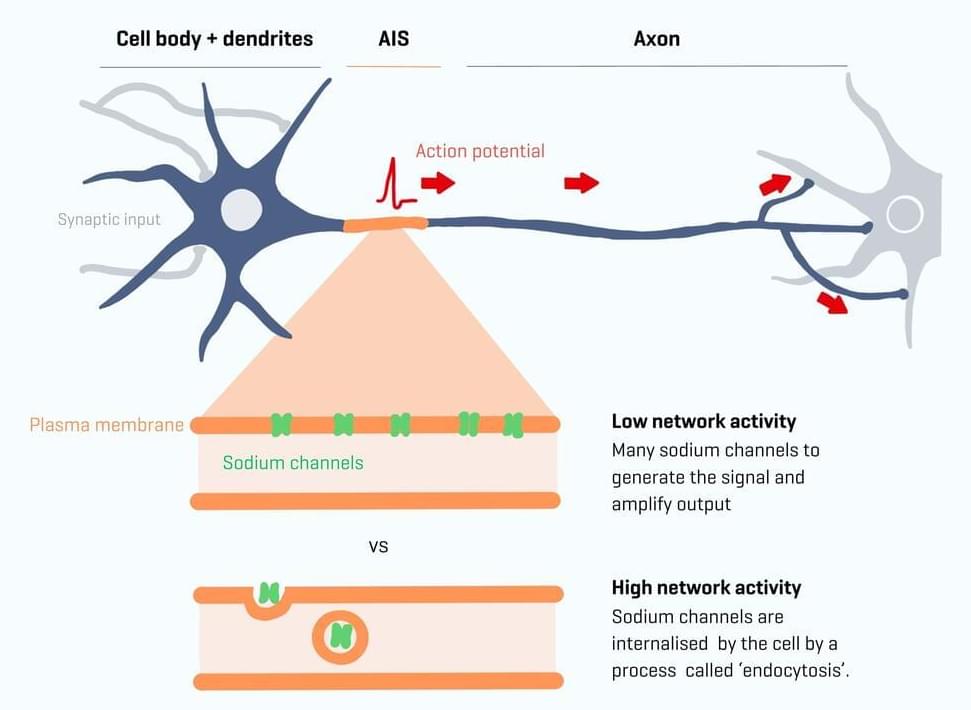
Researchers from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience have, for the first time, witnessed nerve plasticity in the axon in motion.
Our nerve cells communicate through rapid transmission of electrical signals known as action potentials. All action potentials in the brain start in one unique small area of the cell: the axon initial segment (AIS). This is the very first part of the axon, the long, thin extension of a nerve cell that transmits signals or impulses from one nerve cell to another. It acts as a control center where it is decided when an action potential is initiated before traveling further along the axon.
Previously, researchers made the surprising observation that plasticity also occurs at the AIS. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to create new connections and structures in order to scale the amount of electrical activity, which is crucial for learning and memory. AIS plasticity occurs during changes in brain network activity.
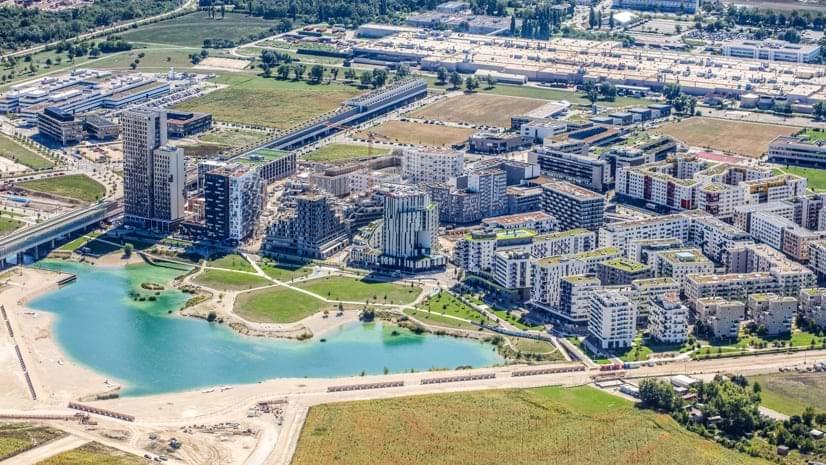

The result: aspern Seestadt, reclaims a brownfield area to create a development that embraces new urban ideals while retaining the classical urban structure of old Vienna.
As aspern Seestadt has evolved, it has emerged as one of Europe’s most dynamic planned communities and an incubator for smart city initiatives. Geographic information system (GIS) technology helps planners implement clean energy and low-emission strategies and aids the long-range planning and implementation to ensure that aspern Seestadt achieves a unique balance of sustainability and livability.
-Vienna’s sustainable city within a city can be a model used by developing and developed countries dealing with housing crisis.
Mapping tools help the City of Vienna and its partners test and apply smart city concepts to the Aspern Seestadt planned development.

PhonePe launched the Indus AppStore Developer Platform on Saturday, promising zero platform fee and no commission on in-app purchases as the Walmart-backed fintech races to win Android developers in Google’s largest market.
The Bengaluru-headquartered startup, which has amassed over 450 million registered users on its eponymous payments app, said developers can start registering and uploading their apps on the ‘made-in-India’ app store starting today. The app store, for which PhonePe has also partnered with phonemakers for distribution, features scores of locally relevant features including support for third-party payment providers, 12 Indian languages and a login system that revolves around phone numbers.
PhonePe will not charge developers any listing fee for the first year but move to a “nominal” cost thereafter, it said. The startup will additionally not levy a commission on in-app purchases, compared to Google’s 15–30% takerate. PhonePe, which leads the UPI-based payments market in India, said it has put in place an India-based team to offer support to developers, addressing the concerns of local developers who have been dissatisfied with Google’s delayed responses and U.S. timezone operating hours.
COVID-19 can affect various organs in the body, such as the brain, lungs, heart, and kidneys. But what happens to these organs after the infection is over? How long does it take for them to heal? A new study has tried to answer these questions by using MRI scans to look at multiple organs of people hospitalized with COVID-19.
The study, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, is one of the most comprehensive post–COVID–19 MRI studies to date. It involved 259 patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 in the U.K. and 50 people who had never been… More.
Credits: SvetaZi/iStock.
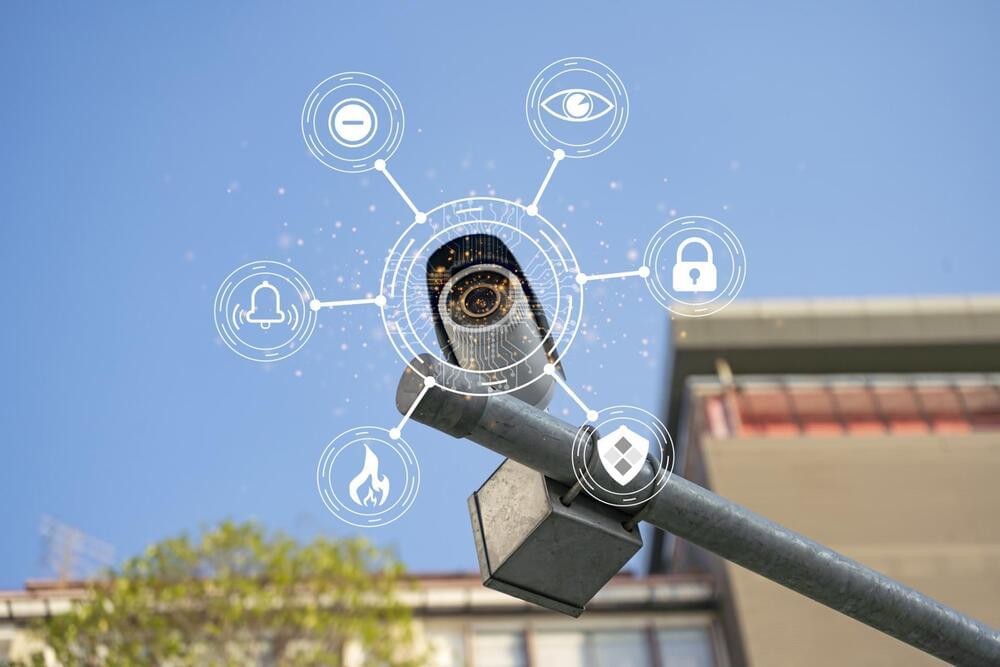

The technology is part of a project by Rogers to detect wildfires early.
A Canadian telecom is installing artificial intelligence (AI) cameras to monitor and prevent wildfires caused by climate change. This is according to a report by City News Everywhere.
“Climate change is a global issue,” said Tony Staffieri, CEO of Rogers, the company behind the new initiative.
Interesting Engineering is a cutting edge, leading community designed for all lovers of engineering, technology and science.
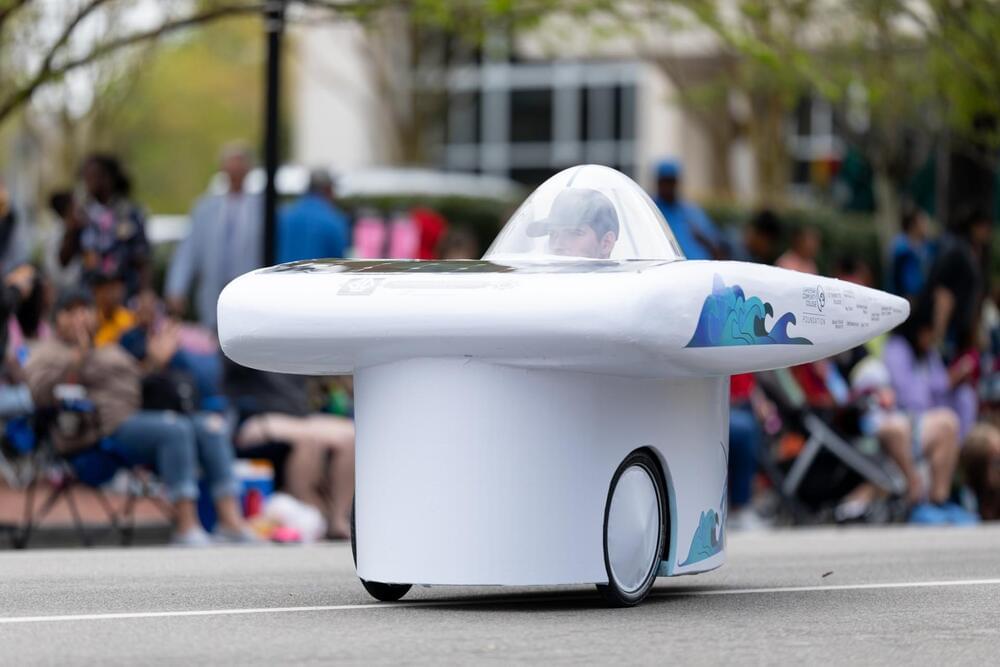

A new study modeled the behavior of solar vehicles in 100 locations around the world.
According to a new study, solar energy can provide a range of between 6 and 18 miles (11 and 29 kilometers) for electric vehicles each day, cutting down on the requirement for charging by half. The study took into account the capabilities of solar-powered vehicles in urban settings in 100 locations across the world, modeling the behavior of the cars in busy cities.
Used for limited purposes
Solar cars are automobiles that run primarily on solar energy, which is commonly captured using photovoltaic (PV) panels mounted on the surface of the car. Sunlight is converted into electricity by these panels, which can then be used to either directly power the electric engine of the vehicle or to charge batteries.