For AI hardware and quantum devices.
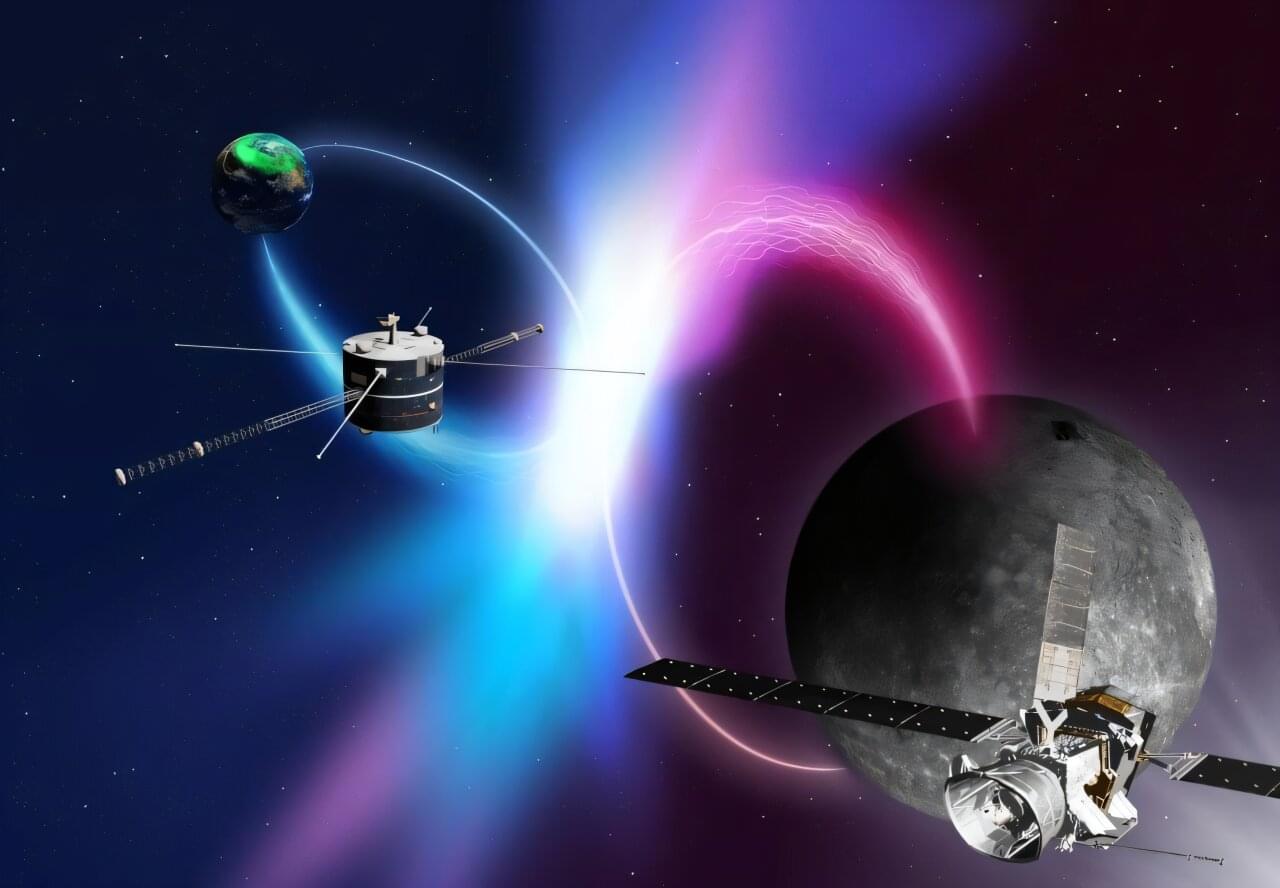


An international team from Kanazawa University (Japan), Tohoku University (Japan), LPP (France), and partners has demonstrated that chorus emissions, natural electromagnetic waves long studied in Earth’s magnetosphere, also occur in Mercury’s magnetosphere exhibiting similar chirping frequency changes.
Using the Plasma Wave Investigation instrument aboard BepiColombo’s Mercury orbiter Mio, six Mercury flybys between 2021 and 2025 detected plasma waves in the audible range. Comparison with decades of GEOTAIL data confirmed identical instantaneous frequency changes.
This provides the first reliable evidence of intense electron activity at Mercury, advancing understanding of auroral processes across the solar system.
Early diagnosis and noninvasive monitoring of neurological disorders require sensitivity to elusive cellular-level alterations that emerge much earlier than volumetric changes observable with millimeter-resolution medical imaging.
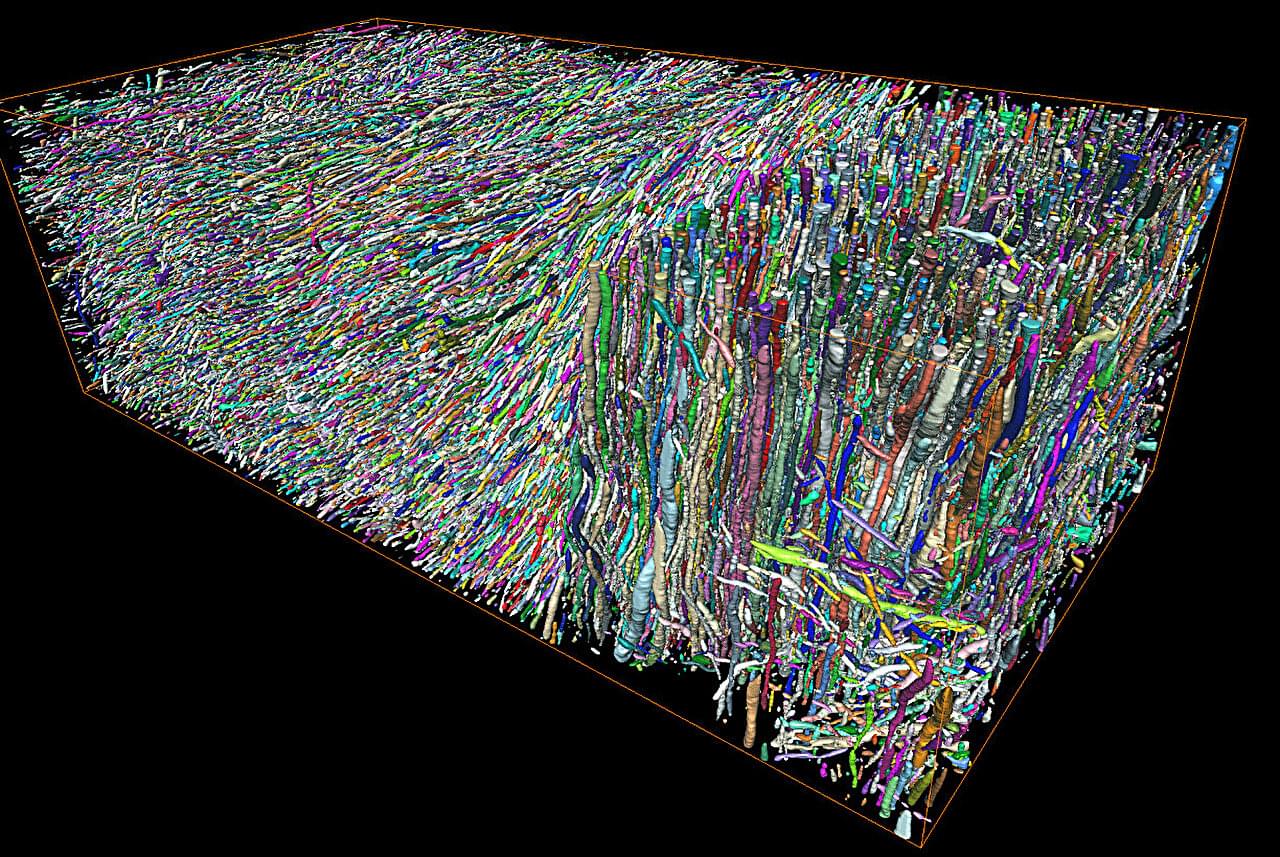
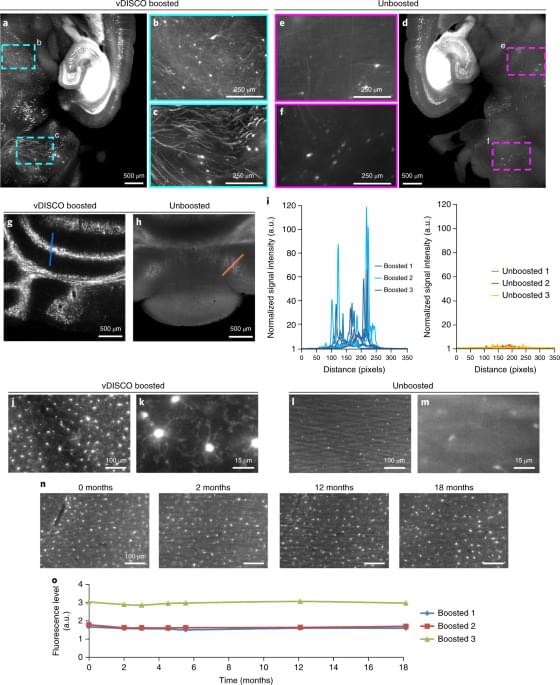
Morphological changes in axons—the tube-like projections of neurons that transmit electrical signals and constitute the bulk of the brain’s white matter—are a common hallmark of a wide range of neurological disorders, as well as normal development and aging.
A study from the University of Eastern Finland (UEF) and the New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine establishes a direct analytical link between the axonal microgeometry and noninvasive, millimeter-scale diffusion MRI (dMRI) signals—diffusion MRI measures the diffusion of water molecules within biological tissues and is sensitive to tissue microstructure.
Paediatric teams are now facing babies whose diabetes appears in the first weeks of life, then rapidly reveals deep problems in brain growth and function. A new genetic finding sheds light on how a single molecular fault can disrupt both blood sugar control and early brain development.
Neonatal diabetes is diagnosed in the first six months of life, often within days or weeks after birth. Unlike the more common type 1 diabetes, which usually shows up in children and teenagers, neonatal diabetes is almost always genetic.
Doctors typically notice poor feeding, weight loss, dehydration and extremely high blood sugar. In many cases, the root cause is a mutation that stops the pancreas from making enough insulin. That alone makes neonatal diabetes a medical emergency.

Scientists have long debated the origins of exceptional human achievements. This literature review summarizes recent evidence from multiple domains on the acquisition of world-class performance. We review published papers and synthesize developmental patterns of international top scientists, musicians, athletes, and chess players. The available evidence is highly consistent across domains: (i) Young exceptional performers and later adult world-class performers are largely two discrete populations over time. (ii) Early (e.g., youth) exceptional performance is associated with extensive discipline-specific practice, little or no multidisciplinary practice, and fast early progress. (iii) By contrast, adult world-class performance is associated with limited discipline-specific practice, increased multidisciplinary practice, and gradual early progress.


This study provides the first direct evidence of cardiomyocyte mitosis in the adult human heart following myocardial infarction, challenging the long-standing paradigm that cardiac muscle cells are incapable of regeneration. Utilizing live human heart tissue models, researchers from the University of Sydney demonstrated that while fibrotic scarring occurs post-ischemia, the heart simultaneously initiates a natural regenerative program characterized by active cell division. The investigation further identified specific regulatory proteins that drive this mitotic process, offering a molecular blueprint for endogenous tissue repair. These findings suggest that the human heart possesses a latent regenerative capacity that could be therapeutically harnessed to prevent heart failure and reverse post-infarct tissue damage, representing a significant shift in regenerative cardiovascular medicine.
A world‑first University of Sydney study reveals that the human heart can regrow muscle cells after a heart attack, paving the way for breakthrough regenerative therapies to reverse heart failure.

Collective behavior is an unusual phenomenon in condensed-matter physics. When quantum spins interact together as a system, they produce unique effects not seen in individual particles. Understanding how quantum spins interact to produce this behavior is central to modern condensed-matter physics.
Among these phenomena, the Kondo effect—the interaction between localized spins and conduction electrons—plays a central role in many quantum phenomena.
Yet in real materials, the presence of additional charges and orbital degrees of freedom make it difficult to isolate the essential quantum mechanism behind the Kondo effect. In these materials, electrons don’t just have spin, they also move around and can occupy different orbitals. When all these extra behaviors mix together, it becomes hard to focus only on the spin interactions responsible for the Kondo effect.