For decades, scientists have tried to answer a simple question: why be honest when deception is possible? Whether it is a peacock’s tail, a stag’s roar, or a human’s résumé, signals are means to influence others by transmitting information and advantages can be gained by cheating, for example by exaggeration. But if lying pays, why does communication not collapse?
The dominant theory for honest signals has long been the handicap principle, which claims that signals are honest because they are costly to produce. It argues that a peacock’s tail, for example, is an honest signal of a male’s condition or quality to potential mates because it is so costly to produce. Only high-quality birds could afford such a handicap, wasting resources growing it, demonstrating their superb quality to females, whereas poor quality males cannot afford such ornaments.
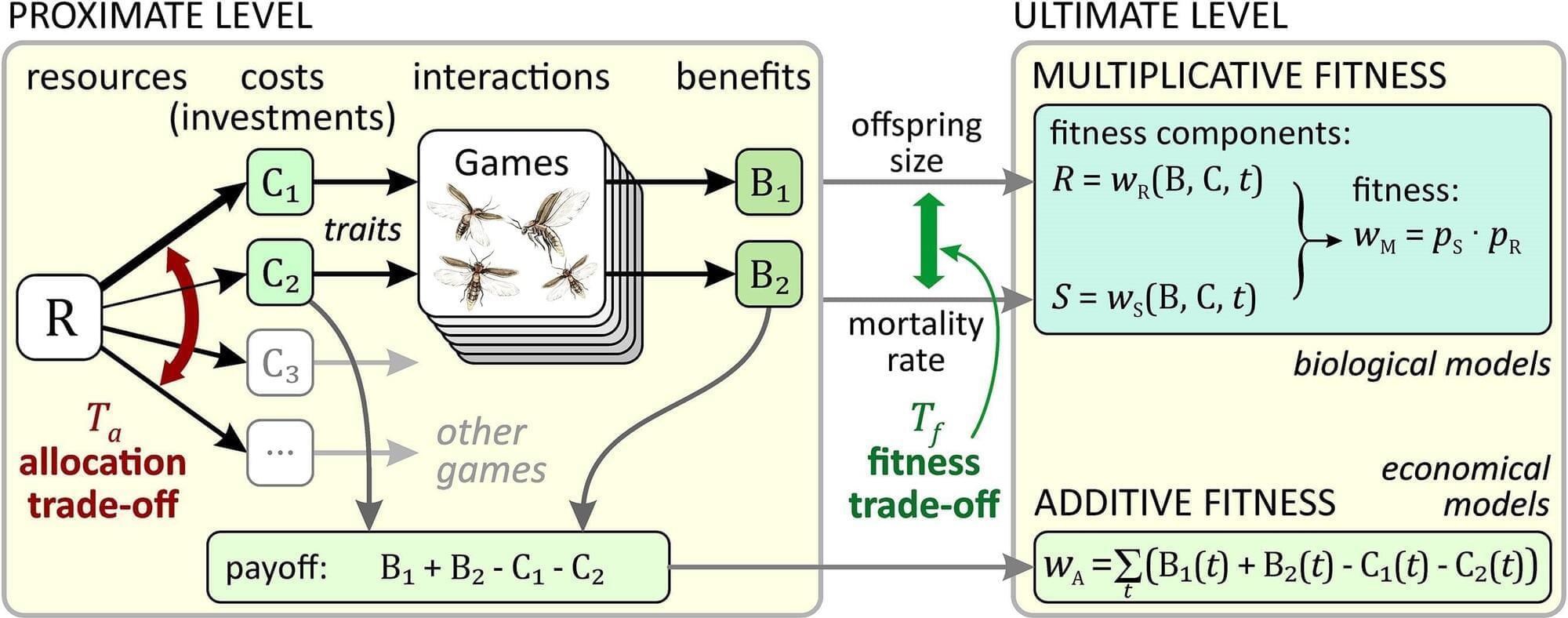
A new synthesis by Szabolcs Számadó, Dustin J. Penn and István Zachar (from the Budapest University of Technology and Economics, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna and HUN-REN Centre for Ecological Research, respectively) challenges that logic. They argue that honesty does not depend on how costly or wasteful a signal is, but rather on the trade-offs between investments and benefits, faced by signalers.