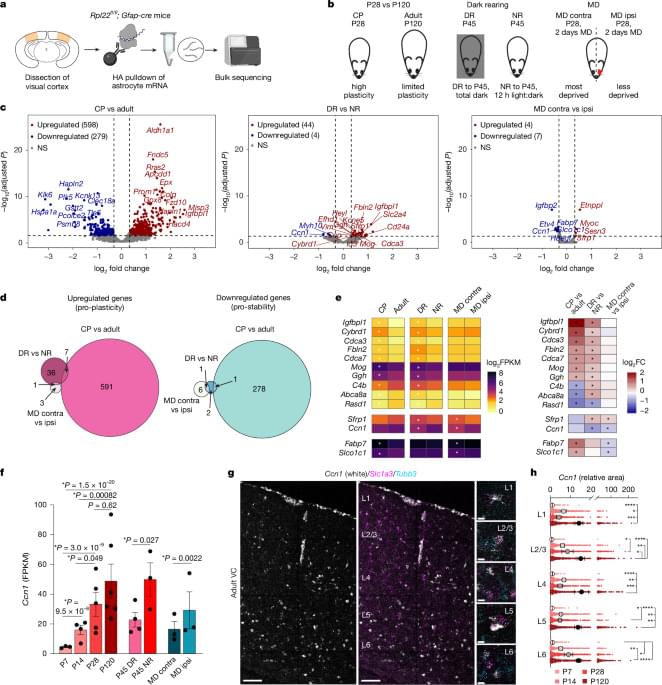
In early life, astrocytes help to mold neural pathways in response to the environment. In adulthood, however, those cells curb plasticity by secreting a protein that stabilizes circuits, according to a mouse study published last month in Nature.
“It’s a new and unique take on the field,” says Ciaran Murphy-Royal, assistant professor of neuroscience at Montreal University, who was not involved in the study. Most research focuses on how glial cells drive plasticity but “not how they apply the brakes,” he says.
Astrocytes promote synaptic remodeling during the development of sensory circuits by secreting factors and exerting physical control—in humans, a single astrocyte can clamp onto 2 million synapses, previous studies suggest. But the glial cells are also responsible for shutting down critical periods for vision and motor circuits in mice and fruit flies, respectively.
It has been unclear whether this loss of plasticity can be reversed. Some evidence hints that modifying the neuronal environment—through matrix degradation or transplantation of young neurons—can rekindle flexibility in adult brains.
The new findings confirm that in adulthood, plasticity is only dormant, rather than lost entirely, says Nicola Allen, professor of molecular neurobiology at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies and an investigator on the new paper. “Neurons don’t lose an intrinsic ability to remodel, but that process is controlled by secreted factors in the environment,” she says.
Specifically, astrocytes orchestrate that dormancy by releasing CCN1, a protein that stabilizes circuits by prompting the maturation of inhibitory neurons and glial cells, Allen’s team found. The findings suggest that astrocytes have an active role in stabilizing adult brain circuits.
The loss of plasticity in adulthood is often seen as a “sad feature of getting older,” says Laura Sancho Fernandez, project manager in Guoping Feng’s lab at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, who worked on the study as a postdoctoral researcher in Allen’s lab. “But it’s really important for maintaining stable representations and circuits in the brain.”