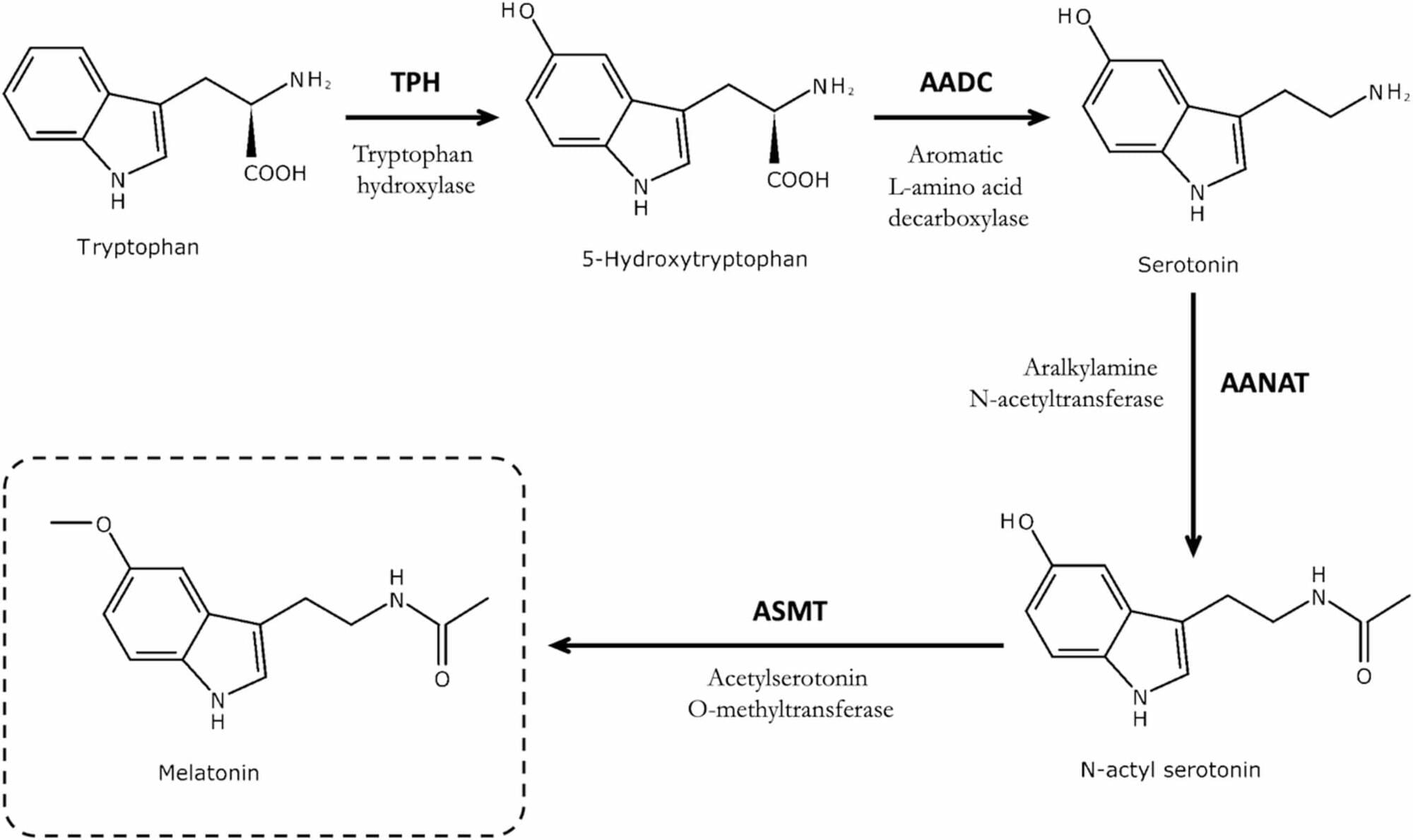
An ageing-related pathology has recently been described as one that develops and/or progresses with increasing chronological age, that is associated with, or contributes to, functional decline and that is evidenced by studies in humans. The pineal gland is a photo-neuroendocrine organ whose primary function is to produce and secrete melatonin in response to light-dark cycle environmental cues. The gland may undergo ageing-related structural and morphological changes, including calcification, gliosis, cyst formation, and reduced density of β-adrenergic receptors, which are hypothesised to reduce melatonin secretion.