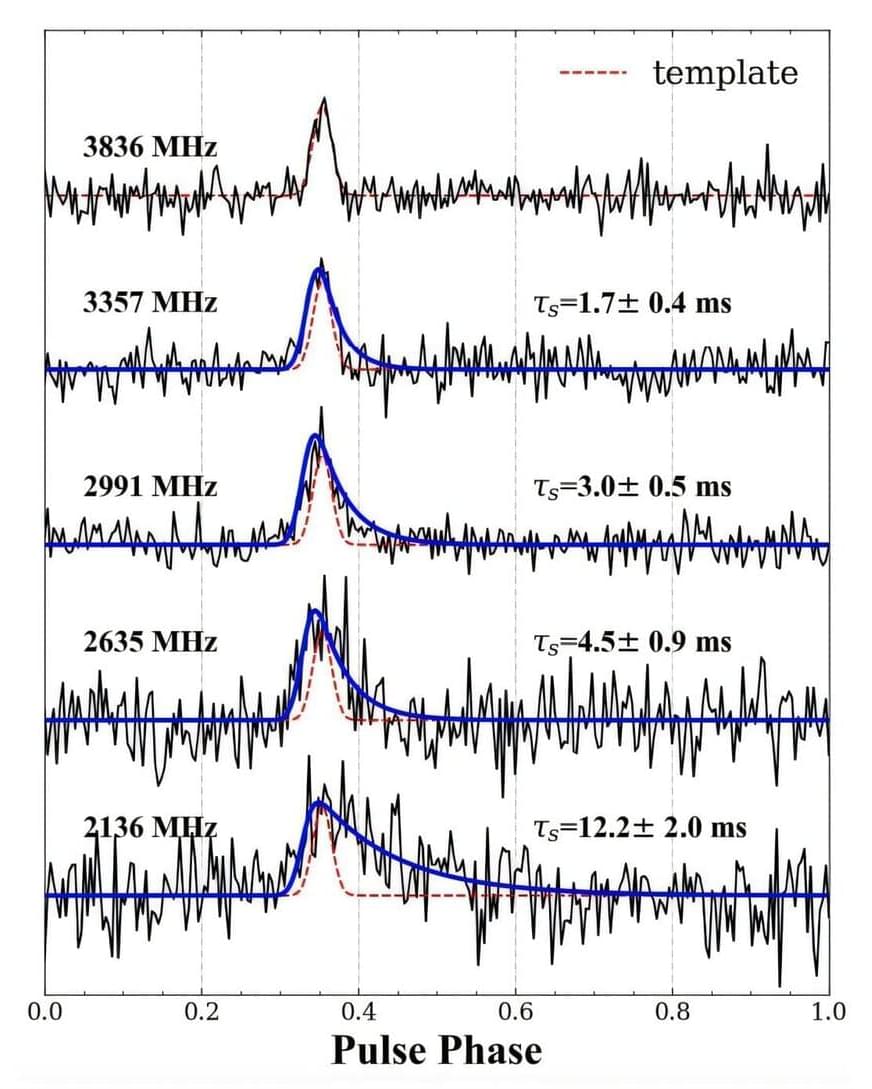
An international team of astronomers has reported the discovery of a new pulsar, which received the designation PSR J1631–4722. The newfound pulsar, which is young and energetic, turns out to be associated with a supernova remnant known as SNR G336.7+0.5. The finding was detailed in a research paper published Dec. 16 on the arXiv pre-print server.
Pulsars are highly magnetized, rotating neutron stars emitting a beam of electromagnetic radiation. They are usually detected in the form of short bursts of radio emission; however, some of them are also observed via optical, X-ray and gamma-ray telescopes.
Pulsars directly associated with known supernova remnants (SNRs) are generally rare as only dozens of such objects have been discovered to date. Finding these associations is crucial for astronomers as they could shed more light on pulsar formation history and supernova explosion mechanisms.