Simulations have shown that a high-speed kinetic weapon weighing 20kg could stop an enemy tank in its tracks.
How does the developing brain process surprising sounds and what changes as we grow up?
For children, the world is full of surprises. Adults, on the other hand, are much more difficult to surprise. And there are complex processes behind this apparently straightforward state of affairs. Researchers at the University of Basel have been using mice to decode how reactions to the unexpected develop in the growing brain.
Babies love playing peekaboo, continuing to react even on the tenth sudden appearance of their partner in the game. Recognizing the unexpected is an important cognitive ability. After all, new can also mean dangerous.
The exact way in which surprises are processed in the brain changes as we grow, however: unusual stimuli are much more quickly categorized as “important” or “uninteresting,” and are significantly less surprising the second and third time they appear. This increased efficiency makes perfect sense: new stimuli may gain our attention, but do not cause an unnecessarily strong reaction that costs us energy. While this may appear trivial at first, so far there has been very little research into this fact in the context of brain development.
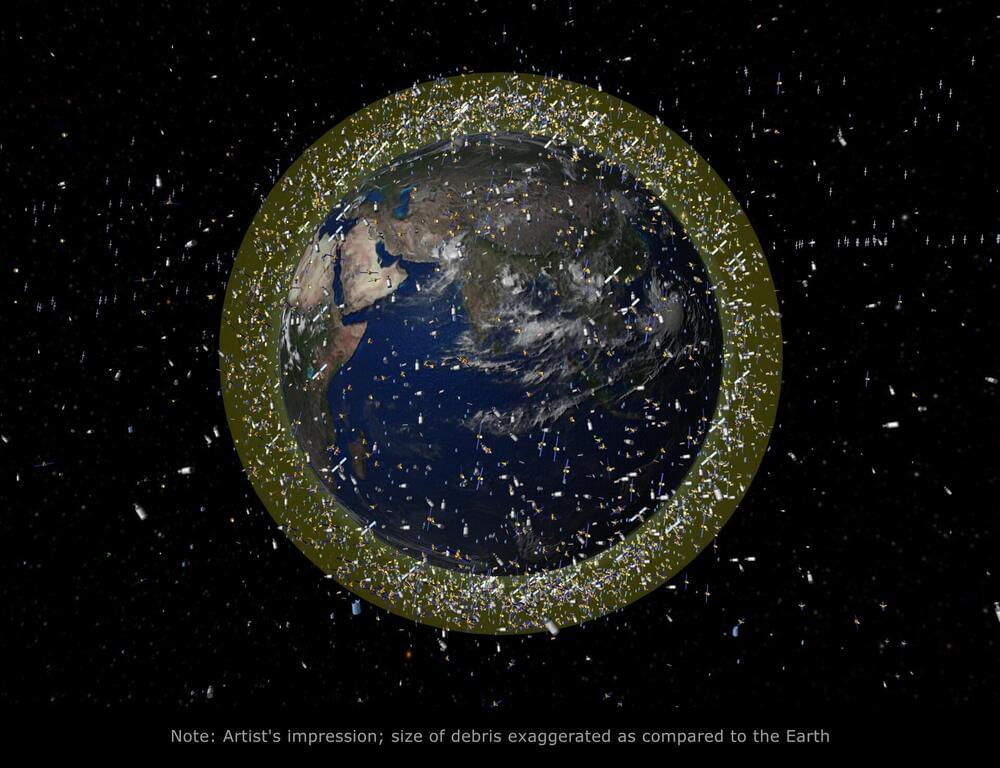
NASA space debris expert Don Kessler observed that, once past a certain critical mass, the total amount of space debris will keep on increasing: collisions give rise to more debris and lead to more collisions, in a chain reaction. So Clean Space is seeking not just to cut debris production from future ESA missions but to reduce the total mass of current debris, such as the robotic salvage of derelict satellites. The task is an urgent one: debris levels have increased 50% in the last five years in low orbit.
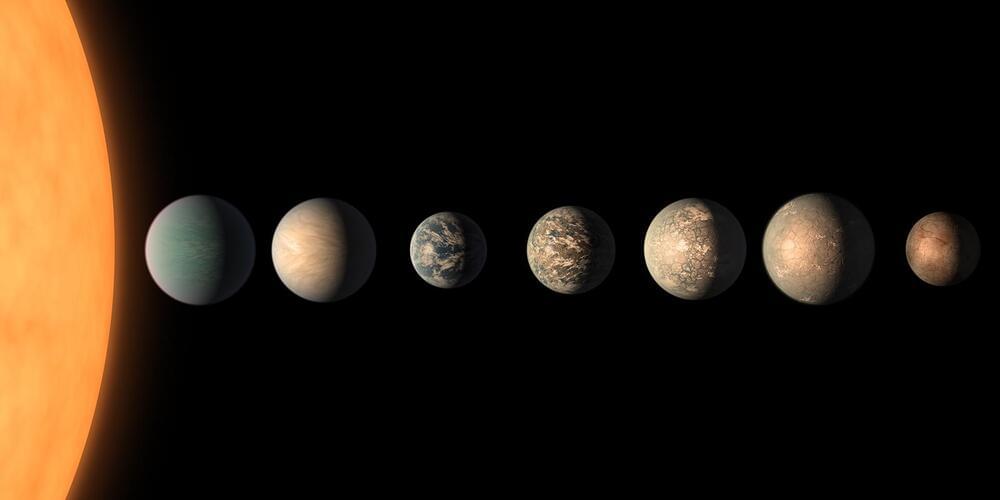
Can a lack of certain atmospheric characteristics in an exoplanet be a sign of life? This is what a team of international scientists hope to unlock as they discuss a novel strategy for detecting the lack of carbon dioxide in a rocky exoplanet’s atmosphere compared to other planets in the same system and how it could help isolate where to look for life. In a recent study published in Nature Astronomy, the researchers ascertain this investigation could be conducted using data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and holds the potential to help astronomers better understand the necessary atmospheric conditions that could be suitable for finding life as we know it throughout the cosmos.
“The Holy Grail in exoplanet science is to look for habitable worlds, and the presence of life, but all the features that have been talked about so far have been beyond the reach of the newest observatories,” said Dr. Julien de Wit, who is an assistant professor of planetary sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a co-author on the study. “Now we have a way to find out if there’s liquid water on another planet. And it’s something we can get to in the next few years.”
The researchers postulate a three-step strategy for using JWST in detecting carbon dioxide and ozone in exoplanets residing in the TRAPPIST-1 system located approximately 40 light-years from Earth. This strategy calls for detecting a planetary atmosphere around rocky exoplanets in approximately 10 transits of the parent star, assessing a lack of carbon dioxide within the exoplanet’s atmosphere in approximately 40 transits, and obtaining measurements of the atmosphere’s ozone while comparing this to the lack of carbon dioxide in approximately 100 transits.
Young gators can sprout new tails that can reach up to nine inches, helping them survive through their juvenile years.
He further mentioned that the AI tool functioned like an “extra pair of eyes,” identifying potential tumors within the video footage.
In short, the AI tool assists junior doctors during colonoscopies by analyzing video footage from the endoscope and identifying potential tumors. It aids in detecting adenomas, particularly those smaller than five millimeters (mm) in diameter.
KENNEWICK — The LIGO Hanford Observatory near Richland is expected to detect 60% more cataclysmic cosmic events — like colliding neutron stars and black holes — thanks to a quantum limit breakthrough.
Since the observatory was turned back on in May after three years of upgrades, including adding new quantum squeezing technology, it can probe a larger volume of the universe.
“Now that we have surpassed this quantum limit, we can do a lot more astronomy,” said Lee McCuller, assistant professor of physics at the California Institute of Technology and a leader in the study published in the journal “Physical Review X.”
The recently detected gravitational waves are a muddled mix of various sources, new study finds.
Rocket propulsion technology has progressed leaps and bounds since the first weaponized rockets of the Chinese and Mongolian empires. They were nothing more than rocket-powered arrows and spears but they set the foundations for our exploration of space. Liquid propellant, ion engines and solar sails have all hit the headlines as we strive for more efficient methods of travel but a team has taken the next leap with a palm-sized thruster system that could boost future tiny spacecraft across the gulf of space.
Palm-sized thrusters are quite different from the gargantuan rockets we are used to, for example the Saturn V rocket that took the Apollo astronauts to the moon that stood 110 m tall. The difference for the ATHENA thrusters is that they are designed for maneuvering and propelling cubesats and small satellites once they are in space rather than propelling rockets from the surface of the Earth.
The team led by Daniel Perez Grande, CEO and Co-Founder of IENAI Spain, have called their palm-sized thruster “Athena,” not the most catchy title but neatly represents what it does—the Adaptable, THruster based on Electrospray powered NAnotechnology. The technology has been developed for ESA and, following a successful design stage and, if all goes to plan, a prototype will be available by the end of 2024.
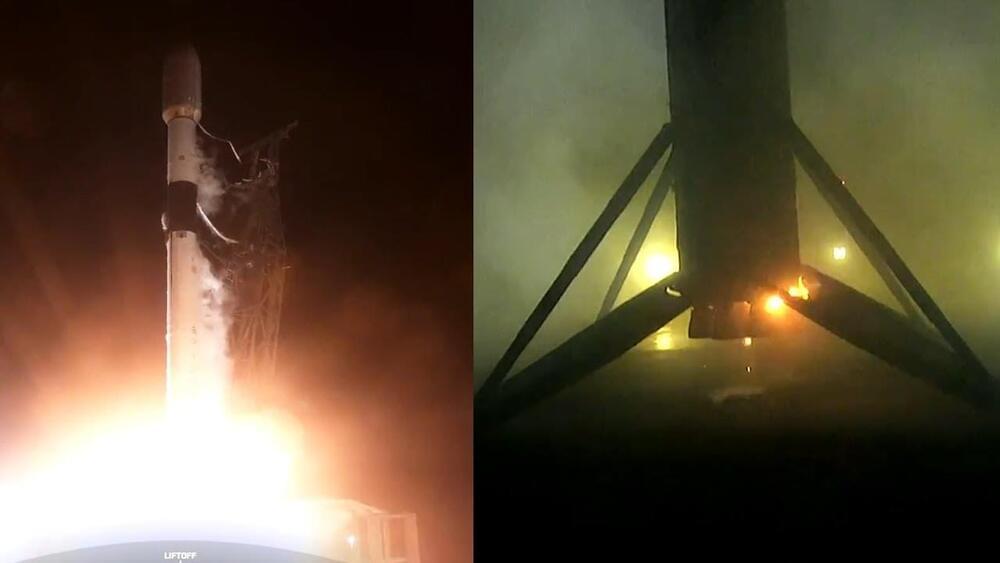
The first satellites capable of providing direct-to-cellular service via SpaceX’s Starlink network and T-Mobile’s cellular network have been sent into orbit aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
Six of the cell-capable satellites were among a batch of 21 Starlink satellites launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 7:44 p.m. PT Tuesday. The satellites were deployed successfully, and the rocket’s first-stage booster made a routine landing on a drone ship in the Pacific Ocean.
SpaceX plans to launch hundreds of the upgraded satellites in the months ahead, with the aim of beginning satellite-enabled texting later this year. 4G LTE satellite connectivity for voice and data via unmodified mobile devices would follow in 2025, pending regulatory approval.