Been waiting for this to come out since discovering the Shawn ryan show…pretty excited to be finally getting around to it!
Shawn Ryan Show · Episode.

The edible transistor is based on an existing transistor architecture, utilizing CuPc as the active material. The key component, the electrolyte-gated OFET (EGOFET), operates at low voltages (1 V) and can function stably for more than a year. The transistor showed good reproducibility, with performance characteristics that pave the way for integrating these devices into more complex edible circuits.
The circuits are constructed on a derivative of cellulose with electrical contacts being printed using inkjet technology and a solution of gold particles (which are also commonly used in the food industry for decoration). The transistor “gate” is also food-grade. This component controls the flow of electrical current between the source and drain terminals, effectively acting as a switch or amplifier. This gate is made from a gel based on chitosan another food-grade ingredient used as a gelling agent.
The research team also explored the optical and morphological properties of CuPc thin films. They found that the thickness of the CuPc layer played a crucial role in the transistor’s performance. Thinner films displayed better charge transport properties, which are essential for creating high-performing, low-voltage devices. This detailed understanding of the material’s properties allowed the team to optimize the transistor’s design for use in real-world applications.
In a new animation, scientists map the planet’s plate tectonics over the last 40 percent of its history. It’s the longest such reconstruction yet.

Scientists have used gene-editing techniques to boost the repair of nerve cells damaged in multiple sclerosis, a study shows. The innovative method, which was tested in mice, supports the development of cells that can repair the protective myelin coating around nerves, restoring their ability to conduct messages to the brain.
The findings, now published in Nature Communications, offer a potential route for future treatments to stop disability progression, experts say.
Our bodies have the ability to repair myelin, but in multiple sclerosis (MS), and as we age, this becomes less effective. There are currently no treatments to boost this process.


Anil Seth, Neuroscientist, Author, and Public Speaker who has pioneered research into the brain basis of consciousness for more than 20 years.
Moderated by Susan Schneider, Ph.D., William F Dietrich Distinguished Professor of Philosophy in the Dorothy F. Schmidt College of Arts and Letters; Member of the Brain Institute. Schneider is founding director of the Center for the Future Mind.
What does it mean to \.
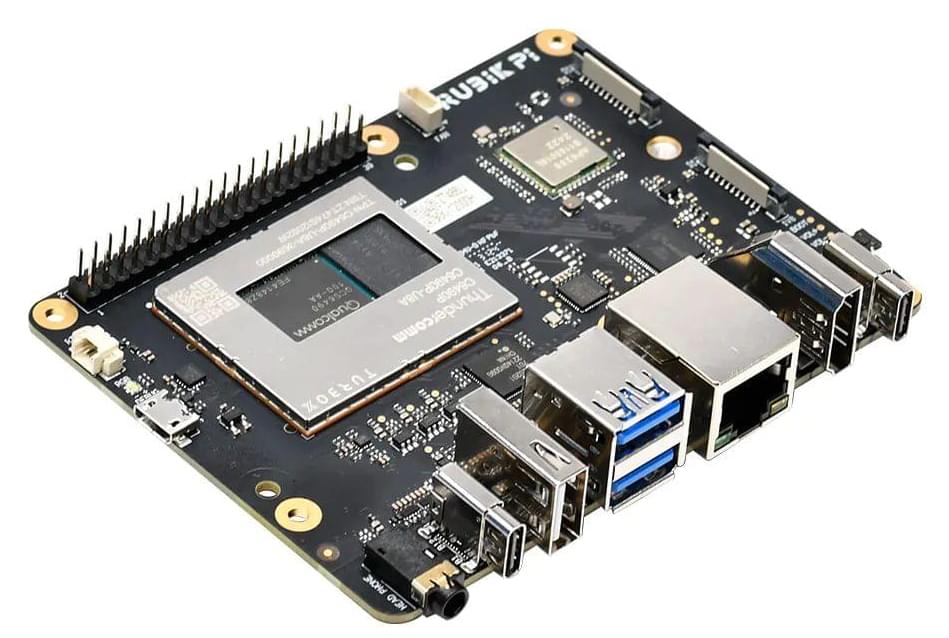

The RUBIK Pi is a dev board from Thundercomm that’s positioned as a platform for developers looking to work a Qualcomm AI processor.
At the heart of the board is a Qualcomm QCS6490 processor with eight ARMv8 CPU cores, Qualcomm Adreno 643 graphics, and a 6th-gen Qualcomm AI Engine that delivers up to 12.5 TOPS of AI performance. Thundercomm hasn’t announced how much the board will cost yet, but says it will be available for pre-order starting in early November.
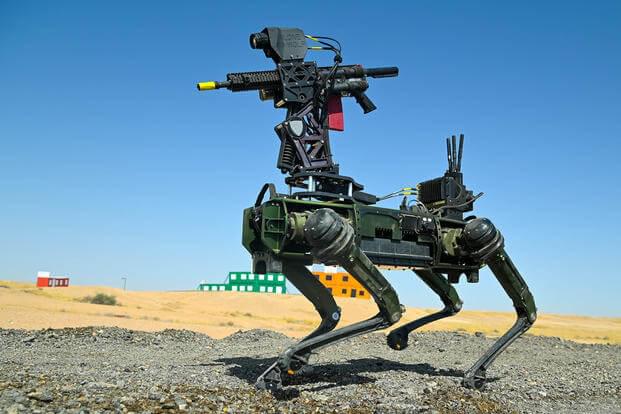

The Army has sent at least one “robot dog” armed with an artificial intelligence-enabled gun turret to the Middle East for testing as a fresh counter-drone capability for U.S. service members, service officials confirmed.
Photos published to the Defense Visual Information Distribution Service last…
The Army was testing at least one armed quadrupedal unmanned ground vehicle at an installation in Saudi Arabia.