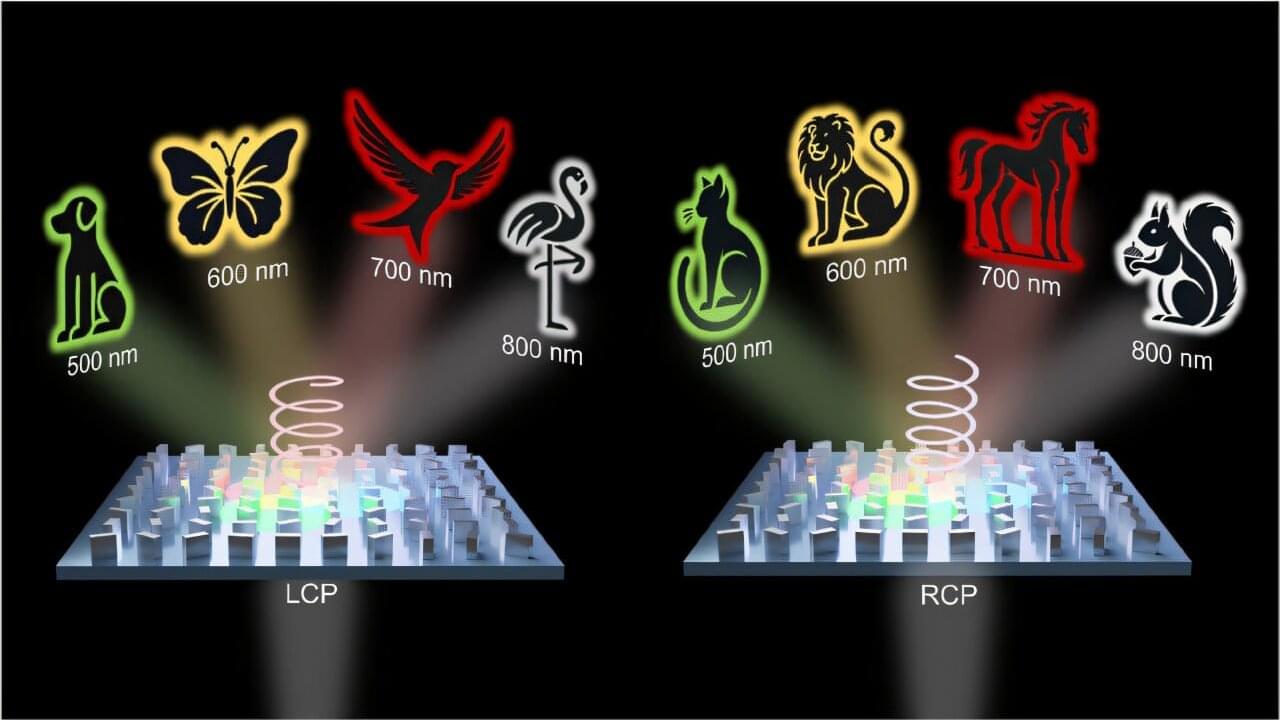
From smartphones and TVs to credit cards, technologies that manipulate light are deeply embedded in our daily lives, many of which are based on holography. However, conventional holographic technologies have faced limitations, particularly in displaying multiple images on a single screen and in maintaining high-resolution image quality.
Recently, a research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho at POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) has developed a groundbreaking metasurface technology that can display up to 36 high-resolution images on a surface thinner than a human hair. This research has been published in Advanced Science.
This achievement is driven by a special nanostructure known as a metasurface. Hundreds of times thinner than a human hair, the metasurface is capable of precisely manipulating light as it passes through. The team fabricated nanometer-scale pillars using silicon nitride, a material known for its robustness and excellent optical transparency. These pillars, referred to as meta-atoms, allow for fine control of light on the metasurface.