Senate Bill 6 tasks the state’s Public Utility Commission with creating a framework for handling the surge in data centers and bitcoin minters.



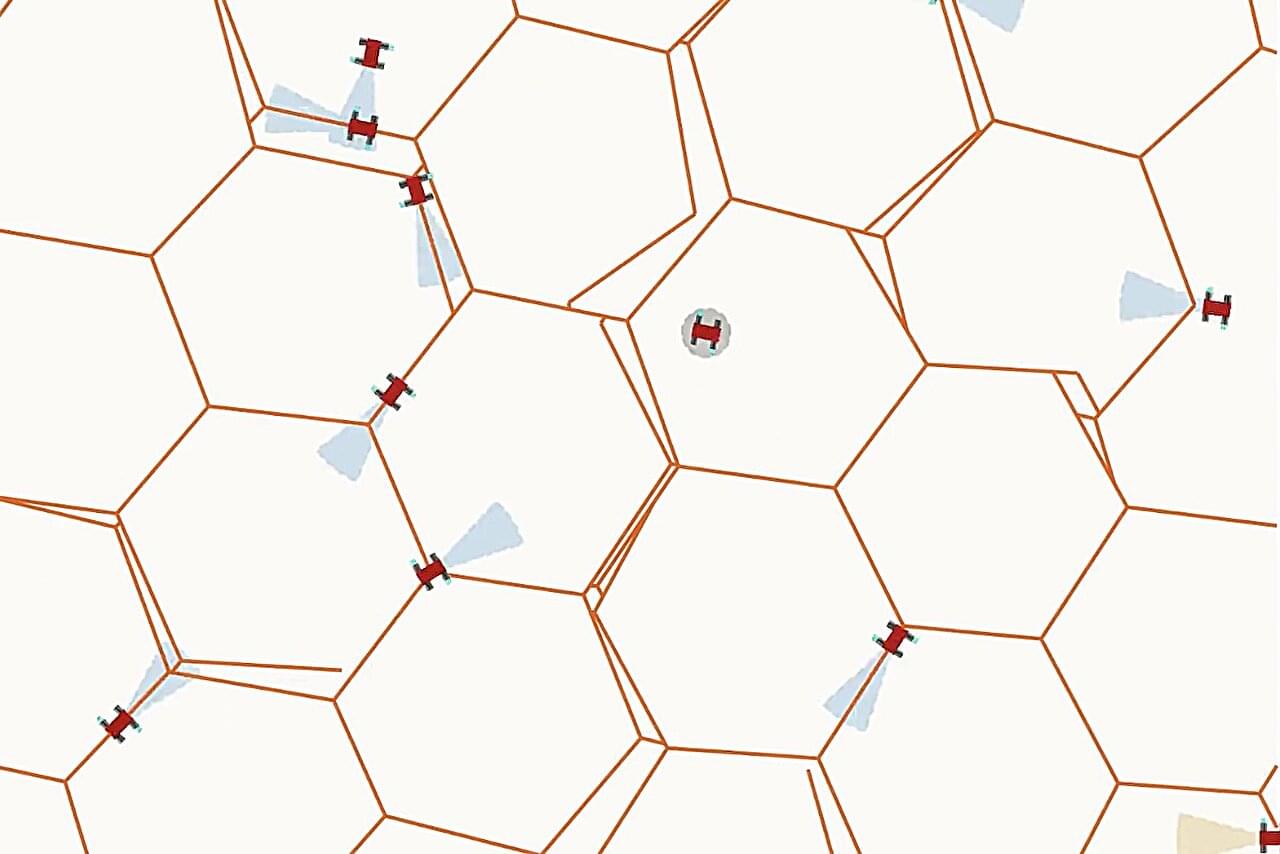
Bees, ants and termites don’t need blueprints. They may have queens, but none of these species breed architects or construction managers. Each insect worker, or drone, simply responds to cues like warmth or the presence or absence of building material. Unlike human manufacturing, the grand design emerges simply from the collective action of the drones—no central planning required.
Now, researchers at Penn Engineering have developed mathematical rules that allow virtual swarms of tiny robots to do the same. In computer simulations, the robots built honeycomb-like structures without ever following—or even being able to comprehend—a plan.
“Though what we have done is just a first step, it is a new strategy that could ultimately lead to a new paradigm in manufacturing,” says Jordan Raney, Associate Professor in Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics (MEAM), and the co-senior author of a new paper in Science Advances. “Even 3D printers work step by step, resulting in what we call a brittle process. One simple mistake, like a clogged nozzle, ruins the entire process.”

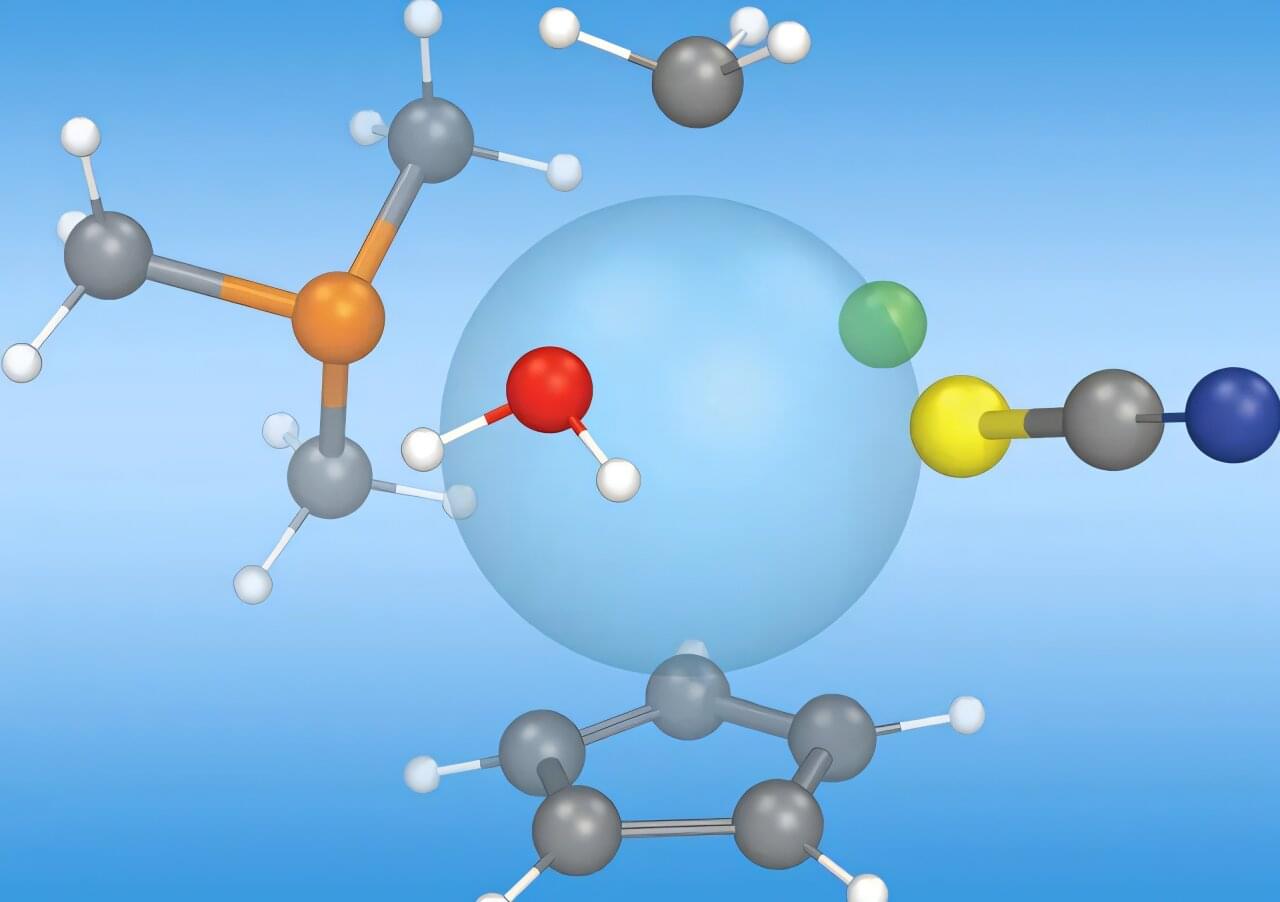
A collaborative effort between Meta, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Los Alamos National Laboratory leverages Los Alamos’ expertise in building tools for molecular screening capabilities. The release of “Open Molecules 2025”, an unprecedented dataset of molecular simulations, can accelerate opportunities for machine learning to transform research in fields such as biology, materials science and energy technologies.
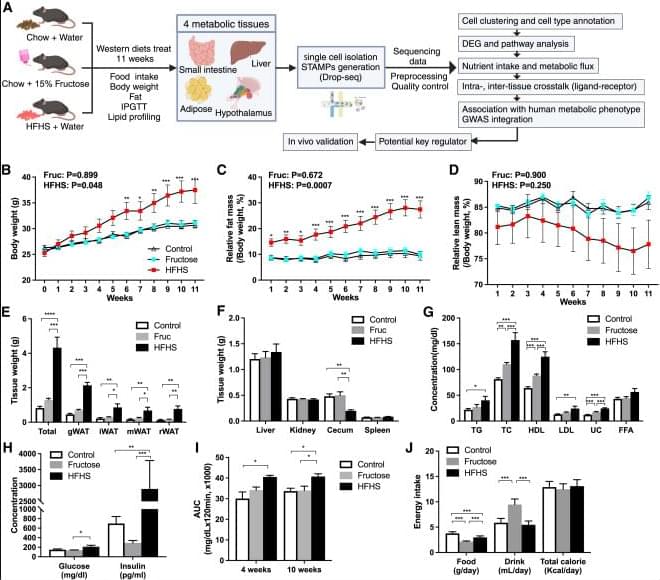
Chen et al. compared scRNA-seq profiles of four tissues in metabolic syndrome (MetS) models induced by fructose or high-fat high-sucrose diets, revealing differential tissue, cellular, and molecular vulnerability between diets. Regulatory genes and pathways were identified, and networks were rewired in MetS. mt-Rnr2 was validated as a key regulator.
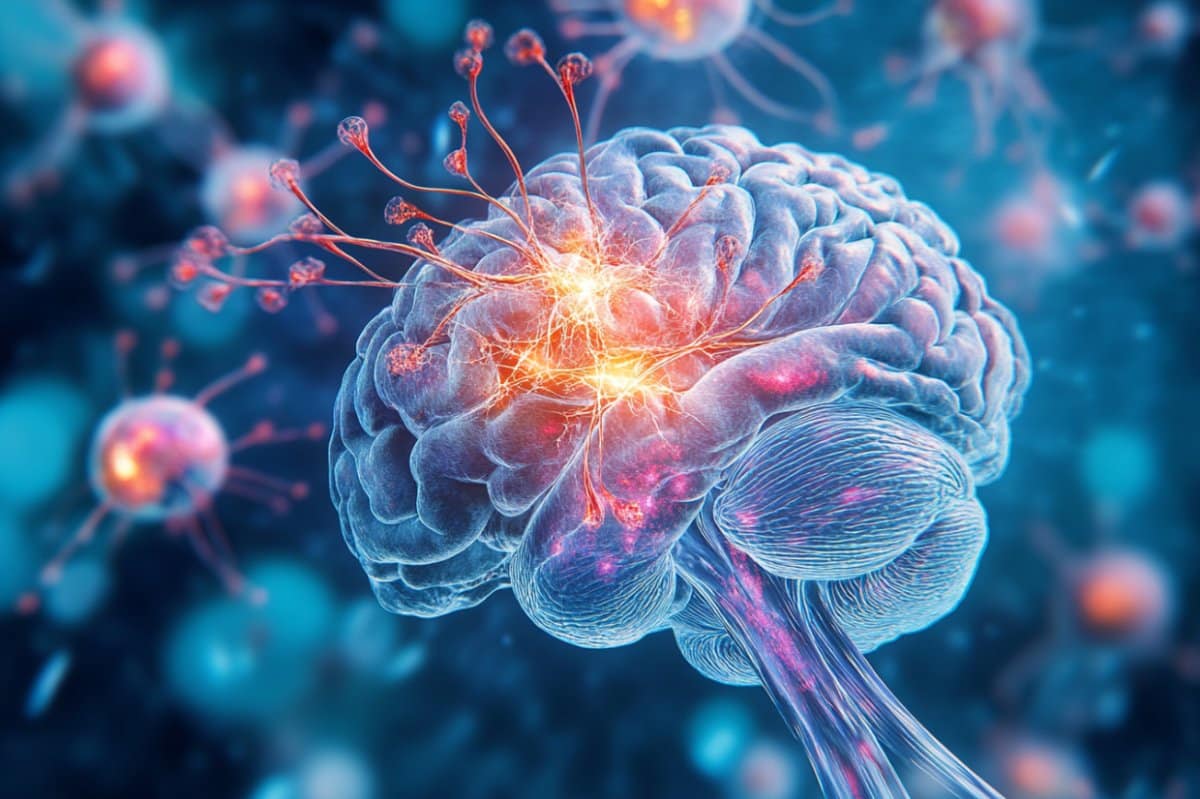
There are new hints that the fabric of space-time may be made of “memory cells” that record the whole history of the universe. If true, it could explain the nature of dark matter and much more