Results of a study show convergent genetic adaptation under hypoxia (lack of oxygen) between populations living at high-altitude in the Himalayan region such as Tibetans and Sherpas, and the development of oxygen-starved cancer cells. The study was directed by Rodrigo Toledo, Head of the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology’s (VHIO) Biomarkers and Clonal Dynamics Group and published in the journal Cancer Discovery.
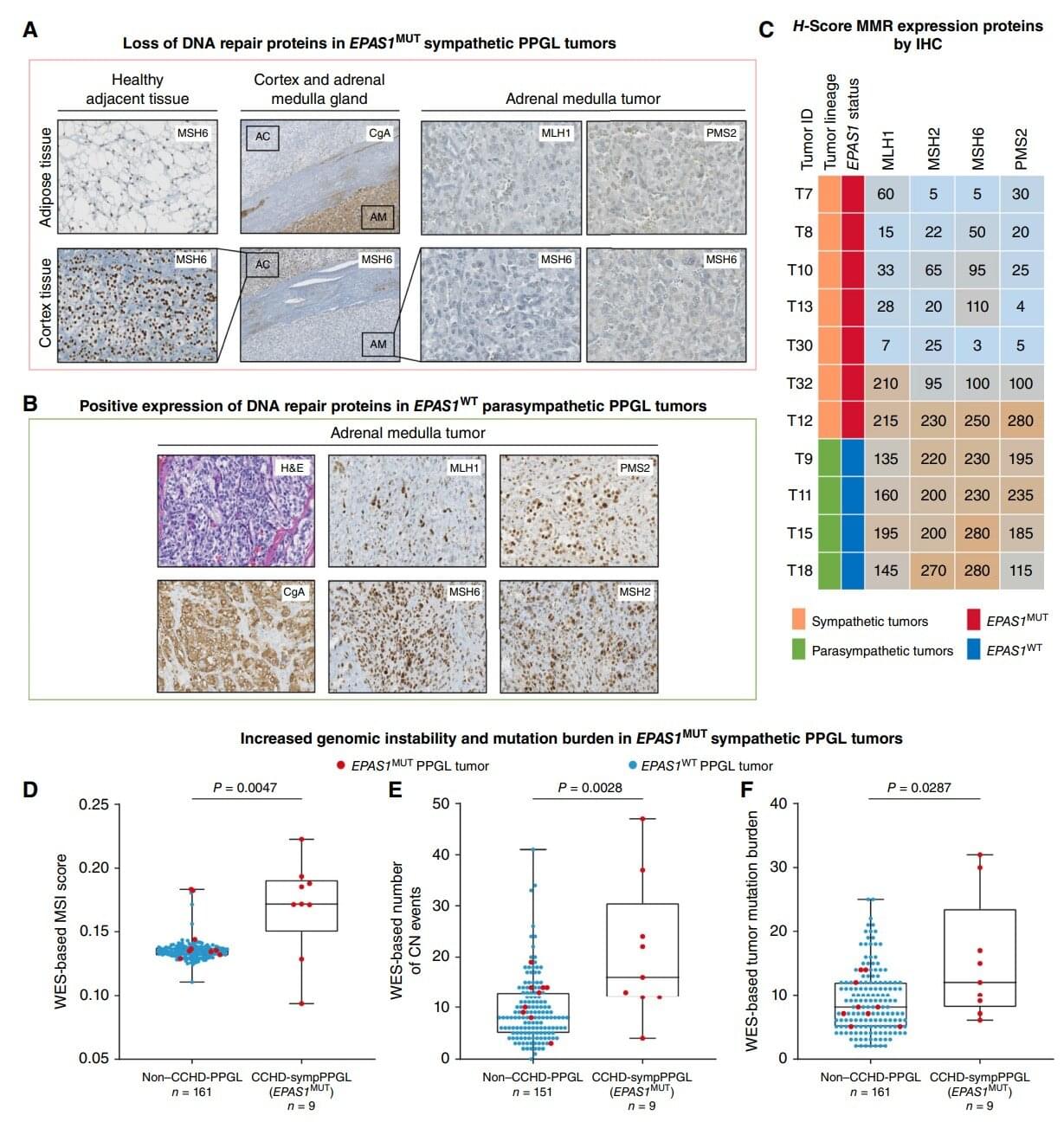
Patients with cyanotic congenital heart disease (CCHD) are chronically hypoxic and have an estimated six-fold higher risk of developing pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL), which are associated with neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) of the adrenal glands and/or paraganglia, respectively. These cancers can continue to grow and proliferate under chronic hypoxia.
“With this study, we aimed to achieve deeper insights into how tumors can survive, grow, and even metastasize under low oxygen conditions, known as hypoxia. Our findings reveal a broad convergence in genetic adaptation in tumors that continue to develop and grow under hypoxia, and in high-altitude populations who thrive in such a challenging environment,” said Toledo, corresponding author of this present article.