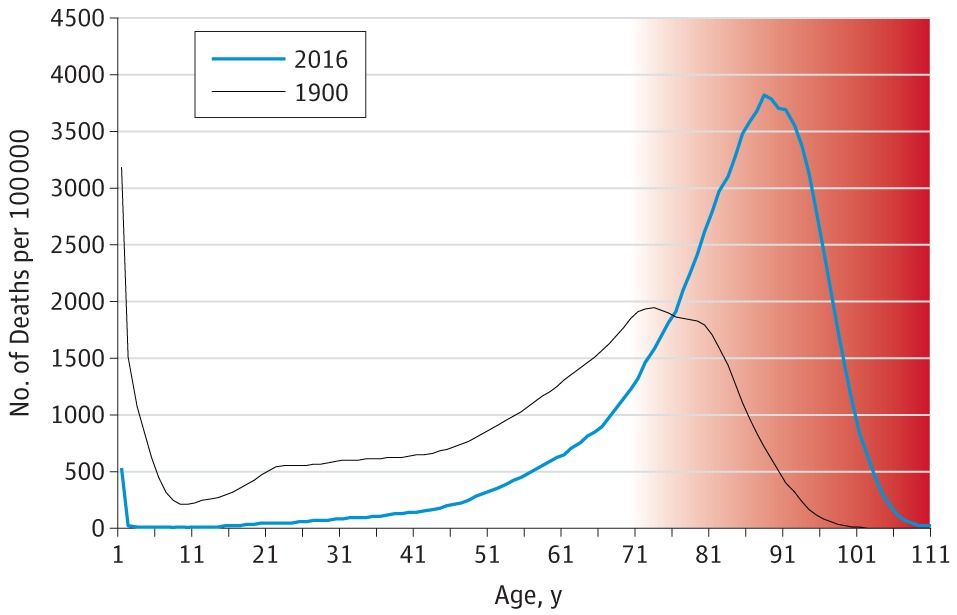
New paper calls for the use of advances human-relevant methods to enable understanding of the initiation and progression of Parkinson’s disease.


WASHINGTON (Reuters) — The White House will hold a meeting on Monday on U.S. government efforts to boost quantum information science, with administration officials, leading companies including Alphabet Inc ( GOOGL.O ), IBM Corp ( IBM.N ), JPMorgan Chase & Co ( JPM.N ) and academic experts taking part.
Some patterns of electrical activity generated by the brain during sleep are inherited, according to a study of teenage twins published in JNeurosci. Pinpointing the relative contributions of biology and experience to sleep neurophysiology could inform therapies for numerous psychiatric disorders in which alterations in brain activity during sleep can be detected.


Researchers have used gene editing to completely eliminate populations of mosquitoes in the lab.
The team tested their technique on the mosquito Anopheles gambiae, which transmits malaria.
They altered part of a gene called doublesex, which determines whether an individual mosquito develops as a male or as a female.
Researchers at Syracuse University, working with collaborators at the University of Wisconsin (UW)-Madison, have developed a new technique for measuring the state of quantum bits, or qubits, in a quantum computer.
Their findings are the subject of an article in Science magazine, which elaborates on the experimental efforts involved with creating such a technique.
The Plourde Group—led by Britton Plourde, professor of physics in Syracuse’s College of Arts and Sciences (A&S)—specializes in the fabrication of superconducting devices and their measurement at low temperatures.
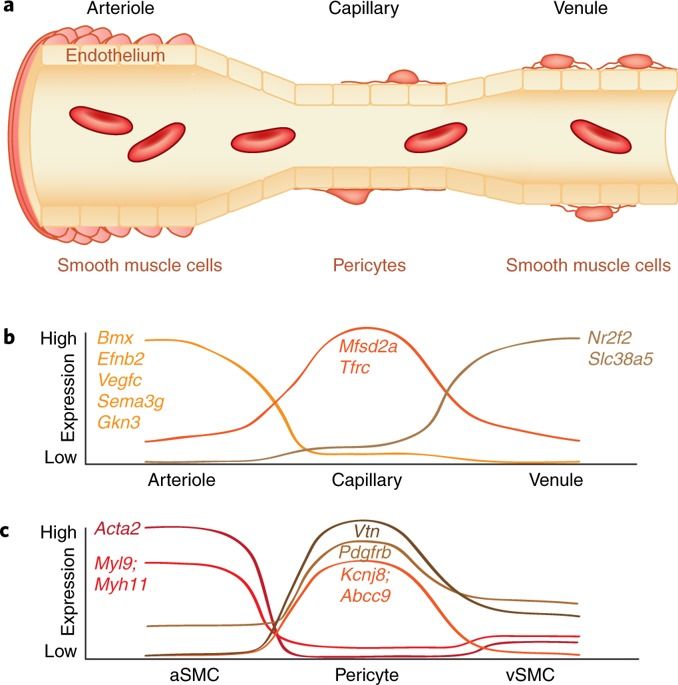
Adequate supply of blood and structural and functional integrity of blood vessels are key to normal brain functioning. On the other hand, cerebral blood flow shortfalls and blood–brain barrier dysfunction are early findings in neurodegenerative disorders in humans and animal models. Here we first examine molecular definition of cerebral blood vessels, as well as pathways regulating cerebral blood flow and blood–brain barrier integrity. Then we examine the role of cerebral blood flow and blood–brain barrier in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple sclerosis. We focus on Alzheimer’s disease as a platform of our analysis because more is known about neurovascular dysfunction in this disease than in other neurodegenerative disorders. Finally, we propose a hypothetical model of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers to include brain vasculature as a factor contributing to the disease onset and progression, and we suggest a common pathway linking brain vascular contributions to neurodegeneration in multiple neurodegenerative disorders.