What if we tried to prevent future problems, instead of just solving the ones in front of us?
In the blackland prairie of Texas, an ocean is thousands of miles away. But Benjamin Blumenthal, co-founder and chief executive officer of SunToWater Technologies, says we’re all standing under the sixth ocean — the one that’s above our heads.
The Carrollton startup makes an appliance that unlocks that water supply. The company’s water generators — each about the size of a central air conditioning unit — use air, salt and solar power to produce gallons of drinkable water. They could bring water to rural communities without a municipal water supply, regions stricken by drought or developing countries with water contamination.
But the company will target a higher-end market first: Homeowners with large lawns to water and swimming pools to fill. Blumenthal said SunToWater is focusing on customers in California and Texas, two states that have coped with an unpredictable, and often limited, water supply and the water restrictions and high utility bills that come with it.
Making the cloud safe for intel
Posted in futurism
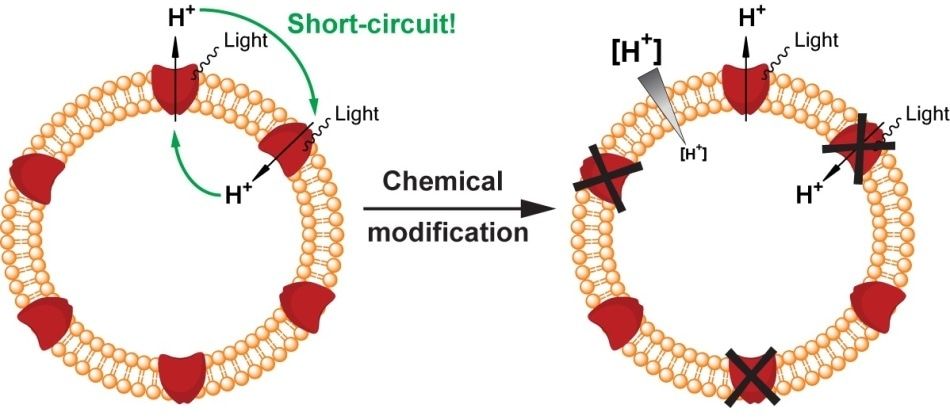
Synthetic biology is an emerging and rapidly evolving engineering discipline. Within the NCCR Molecular Systems Engineering, Scientists from Bernese have developed a version of the light-driven proton pump proteorhodopsin, which is chemically switchable and it is also an essential tool to efficiently power synthetic cells and molecular factories.
Synthetic biology is a highly complex field with numerous knowledge branches that incorporate physics, biology, and chemistry into engineering. It aims to design synthetic cells and molecular factories with innovative functions or properties that can be applied in medical and biological research or healthcare, industry research.
These artificial systems are available in the nanometer scale and are developed by assembling and combining current, synthetic or engineered building blocks (e.g., proteins). Molecular systems are applicable for a wide range of applications, for instance these systems can be used for waste disposal, medical treatment or diagnosis, energy supply and chemical compound synthesis.
Interview conducted by April Cashin-Garbutt, MA (Cantab)
Prior to your study, how much was known about the way brain circuits develop? How has your recent study advanced our understanding?
There’s a tremendous amount known about brain circuit development. Our work was inspired by experiments that were done over 50 years ago by scientists at Harvard University, Hubel and Wiesel. They received a Nobel Prize for their work and have inspired many additional experiments over the last 50 or 60 years.
Hmmm.
With the advent of CRISPR genetic engineering technology, humanity is on the cusp of an evolutionary revolution. We now possess the technology to modify our own genetic code (DNA). In a few more years, it will become more reliable, less expensive, and more available.
That is, of course, assuming that governments don’t outright ban the technology. We all know how successful government prohibition of technology or medical procedures (not very) has been, but that isn’t to say they can’t cause untold suffering in the meantime. How?
While existing methods like cold, flash and cloud storage are trying to remake themselves in the age of Big Data, there are also a number of alternative methods being developed that suggest looking outside of traditional methods could be our best bet for storing and managing such unprecedented amounts of data.
Here are three methods to look out for:
We are about to witness a data storage breakthrough in which digital information could be embedded into the primary fabric of our being: the double helix of DNA. As a storage system, DNA is both compact and durable, with a single gram of DNA able to store almost a zettabyte of digital data. Now that scientists can successfully create synthetic DNA, it follows that we will be able to control what information gets stored on those strands.
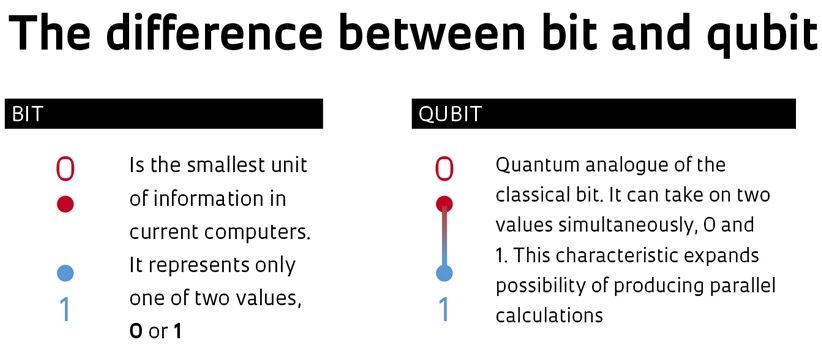
Article repeats a lot of the knowns on QC such as bit v. Qubit; and finally provides some good info on pros and cons of Bitcoin and Lamport signatures technique with QC. However, the author didn’t seem to mention any of the work that D-Wave for example is doing with Block chaining. Also, I saw no mention of the work by Oxford on the logic gate which improve both the information processing performance and the security of information transmissions.
In a classical computer bits are used that can either be 0 or 1. In a quantum computer these bits are replaced with Qubits (quantum bits). These Qubits can be 0 or 1, or both at the same time. This is caused by a phenomenon in the quantum realm called superposition. At scales the size of an atom and small molecules, the spin of particles is not determined until it is observed. A pair of Qubits can be in any quantum superposition of 4 states, and three Qubits in any superposition of 8 states. In general, a quantum computer with n Qubits can be in a superposition of up to 2^n different states simultaneously (this compares to a normal computer that can only be in one of these 2^n states at any one time). Because of this, a quantum computer is able to perform computations at the same time, while classical computers perform computations one at a time.
This effectively means that the computing power grows exponentially for each Qubit you add to the system. A quantum computer will be able to make really difficult calculations all the classical computers in the world together would not be able to do before the end of times, in a relatively short amount of time. This opens to world of computing to be able to perform amazingly complex calculations, such as weather or large scale quantum mechanics, with extremely high precision. Unfortunatly, it will also be great at cracking certain types of cryptography.