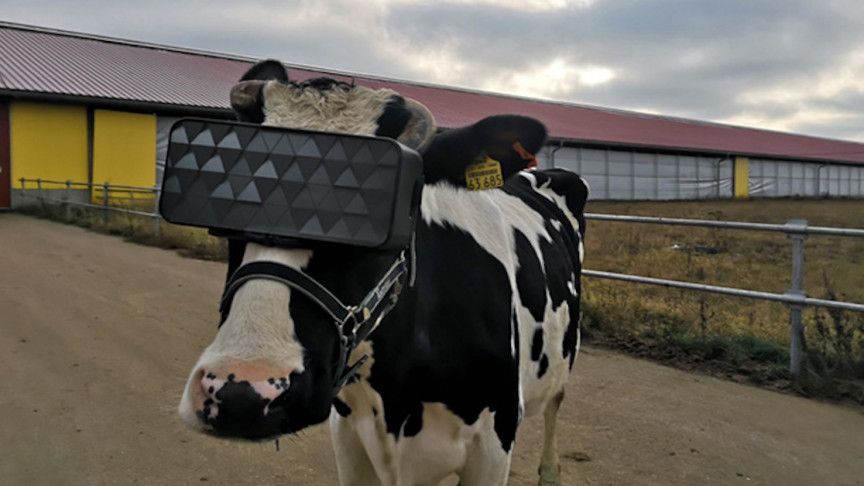
On a farm near Moscow, the cows are walking around with VR goggles strapped to their heads in an effort to improve their living conditions, relax them, with the ultimate goal for them to produce more milk.
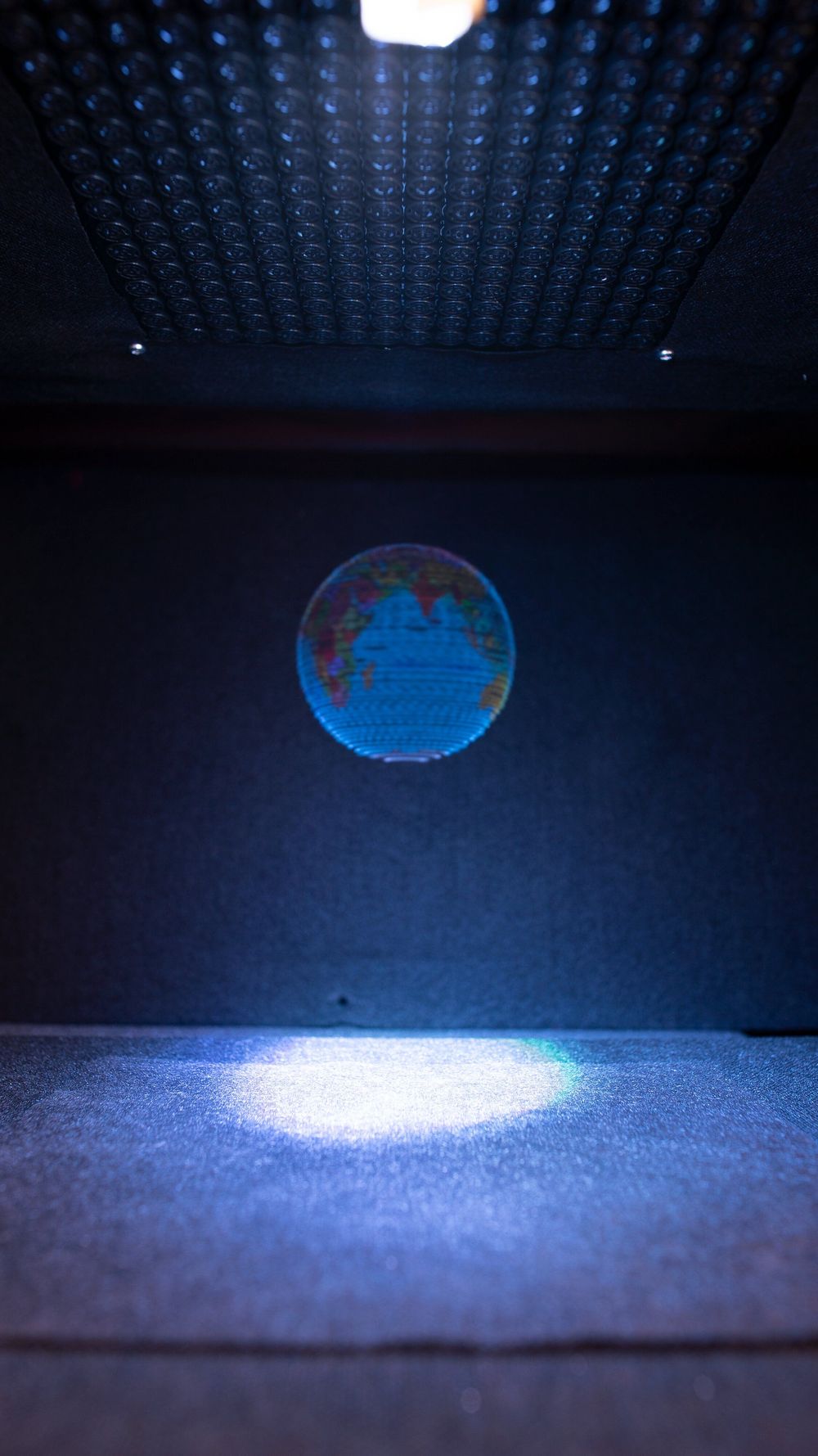



Walking, talking holograms have been a staple of sci-fi films since Princess Leia was magically brought to life in “Star Wars”.
Now scientists in Britain say they can make even more realistic 3D versions—a butterfly, a globe, an emoji—which can be seen with the naked eye, heard and even felt without the need for any virtual reality systems.
Writing in the journal Nature, a team at the University of Sussex in southern England, said technology currently in use can create 3D images but they are slow, short-lived and “most importantly, rely on operating principles that cannot produce tactile and auditive content as well”.

An important aspect of human memory is our ability to conjure specific moments from the vast array of experiences that have occurred in any given setting. For example, if asked to recommend a tourist itinerary for a city you have visited many times, your brain somehow enables you to selectively recall and distinguish specific memories from your different trips to provide an answer.
Studies have shown that declarative memory—the kind of memory you can consciously recall like your home address or your mother’s name—relies on healthy medial temporal lobe structures in the brain, including the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex (EC). These regions are also important for spatial cognition, demonstrated by the Nobel-Prize-winning discovery of “place cells” and “grid cells” in these regions—neurons that activate to represent specific locations in the environment during navigation (akin to a GPS). However, it has not been clear if or how this “spatial map” in the brain relates to a person’s memory of events at those locations, and how neuronal activity in these regions enables us to target a particular memory for retrieval among related experiences.
A team led by neuroengineers at Columbia Engineering has found the first evidence that individual neurons in the human brain target specific memories during recall. They studied recordings in neurosurgical patients who had electrodes implanted in their brains and examined how the patients’ brain signals corresponded to their behavior while performing a virtual-reality (VR) object-location memory task. The researchers identified “memory-trace cells” whose activity was spatially tuned to the location where subjects remembered encountering specific objects. The study is published today in Nature Neuroscience.
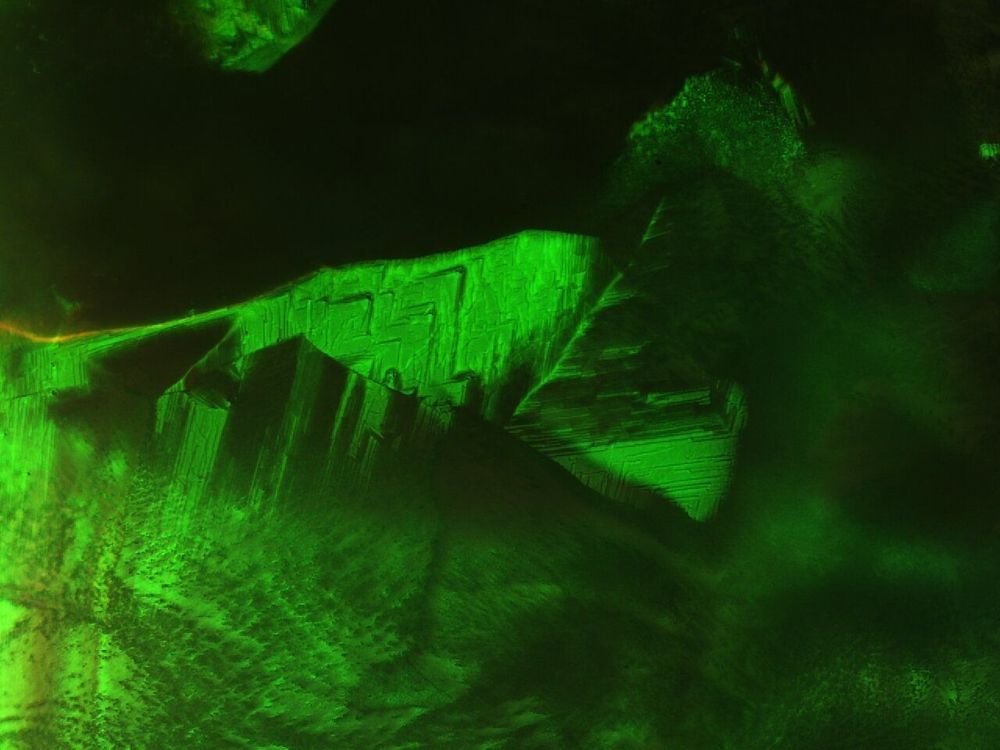
A new technique to change the structure of liquid crystals could lead to the development of fast-responding liquid crystals suitable for next generation displays—3D, augmented and virtual reality—and advanced photonic applications such as mirrorless lasers, bio-sensors and fast/slow light generation, according to an international team of researchers from Penn State, the Air Force Research Laboratory and the National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan.
“The liquid crystals we are working with are called blue-phase liquid crystals,” said Iam Choon Khoo, the William E. Leonhard Professor of Electrical Engineering, who is the corresponding author for this article. “The most important thing about this research is the fundamental understanding of what happens when you apply a field, which has led to the development of Repetitively-Applied Field technique. We believe that this method is almost a universal template that can be used for reconfiguring many similar types of liquid crystals and soft matter.”
Blue-phase liquid crystals typically self-assemble into a cubic photonic-crystal structure. The researchers believed that by creating other structures they could develop properties not present in the current form. After nearly two years of experimentation, they realized that by applying an intermittent electrical field and allowing the system to relax between applications and to dissipate accumulated heat, they could slowly coax the crystals into stable and field-free orthorhombic and tetragonal structures.

“…consider Robert Nozick’s thought-experiment in conjunction with Felipe De Brigard’s inverse experience machine argument: “If you like it, does it matter if it’s real?”
Does Nozick’s experience machine prove anything?
Perhaps consider Robert Nozick’s thought-experiment in conjunction with Felipe De Brigard’s inverse experience machine argument: “If you like it, does it matter if it’s real?”
For sure, many subjects say they wouldn’t plug into Nozick’s Experience Machine; but conversely, many of these same respondents claim they wouldn’t want to unplug from an Experience Machine if told their existing lives were based on a lie. In short, maybe what is really being measured is not simply our (lack of) commitment to hedonism or realism, but rather status quo bias.
Even self-avowed classical utilitarians may balk on realising what their own ethics entails.

By contemplating the full spectrum of scenarios of the coming technological singularity many can place their bets in favor of the Cybernetic Singularity which is a sure path to digital immortality and godhood as opposed to the AI Singularity when Homo sapiens is retired as a senescent parent. This meta-system transition from the networked Global Brain to the Gaian Mind is all about evolution of our own individual minds, it’s all about our own Self-Transcendence. https://www.ecstadelic.net/top-stories/the-ouroboros-code-br…etaphysics #OuroborosCode
All AI & Cybernetics Cognitive Science Complexity Consciousness Cosmology Digital Philosophy Digital Physics Economics Emergence Environment Epigenetics Ethics Evolution Evolutionary Biology Experiential Realism Experimental Science Fermi Paradox Free Will Vs. Determinism Futurism Gaia 2.0 Global Brain Immortality Machine Learning Mathematics Memetics Mind Uploading Nanotechnology Neo Transcendentalism Neural Networks Neurophilosophy Neuroscience Phenomenology Philosophy Of Mind Physics Of Time Psychedelics Psychology Quantum Computing Quantum Gravity Quantum Physics Sci Fi Simulation Hypothesis Sociology Spirituality Technological Singularity Theology Transhumanism Virtual Reality


Something called the fast Fourier transform is running on your cell phone right now. The FFT, as it is known, is a signal-processing algorithm that you use more than you realize. It is, according to the title of one research paper, “an algorithm the whole family can use.”
Alexander Stoytchev – an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at Iowa State University who’s also affiliated with the university’s Virtual Reality Applications Center, its Human Computer Interaction graduate program and the department of computer science – says the FFT algorithm and its inverse (known as the IFFT) are at the heart of signal processing.
And, as such, “These are algorithms that made the digital revolution possible,” he said.
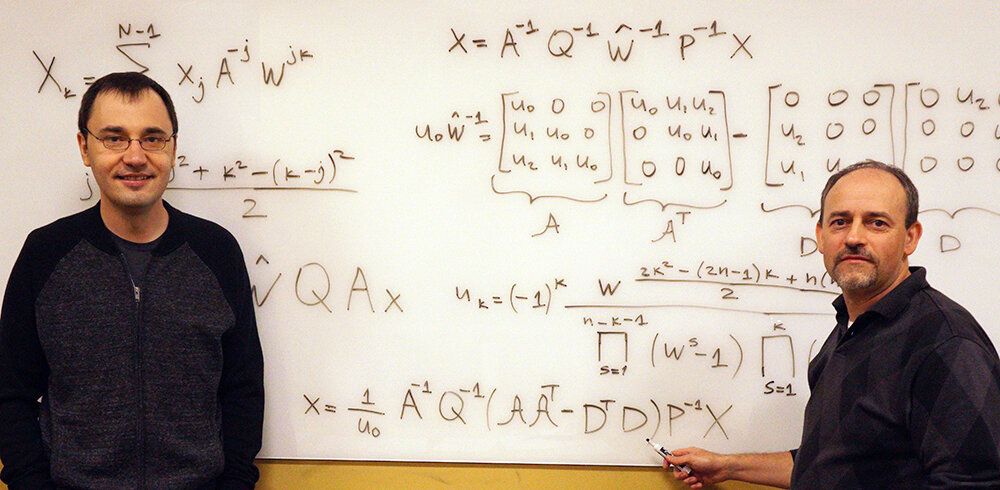
Something called the fast Fourier transform is running on your cell phone right now. The FFT, as it is known, is a signal-processing algorithm that you use more than you realize. It is, according to the title of one research paper, “an algorithm the whole family can use.”
Alexander Stoytchev—an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at Iowa State University who’s also affiliated with the university’s Virtual Reality Applications Center, its Human Computer Interaction graduate program and the department of computer science—says the FFT algorithm and its inverse (known as the IFFT) are at the heart of signal processing.
And, as such, “These are algorithms that made the digital revolution possible,” he said.