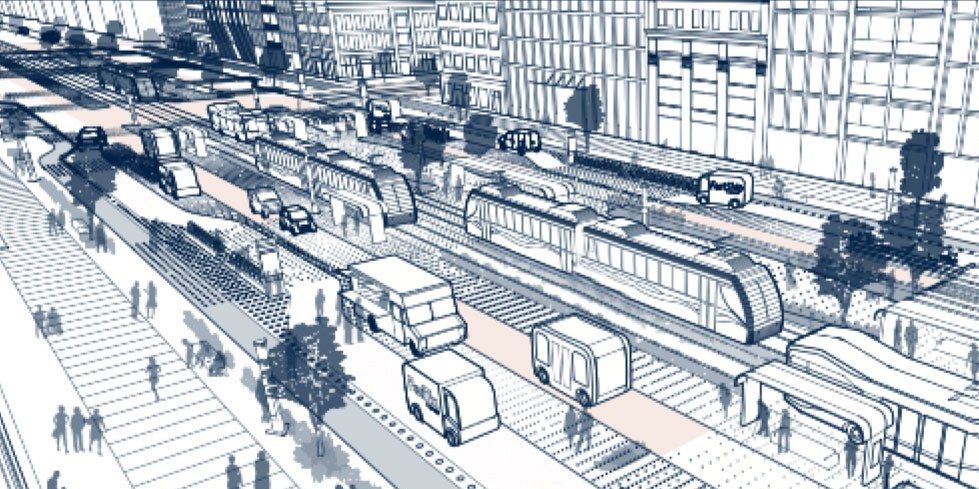
A new blueprint from city transportation planners and engineers, who say it’s never too early to start thinking about the future.


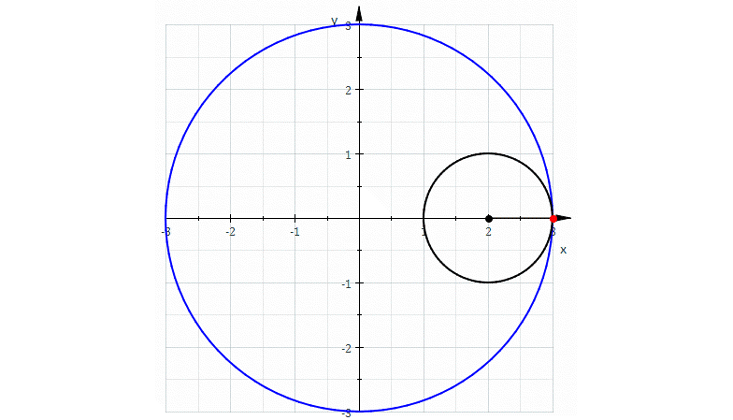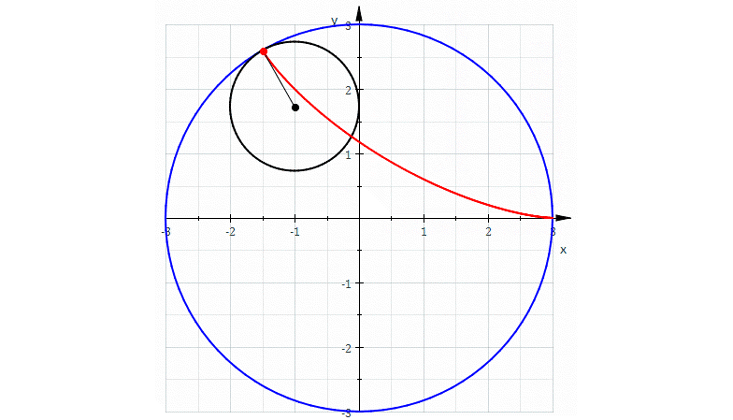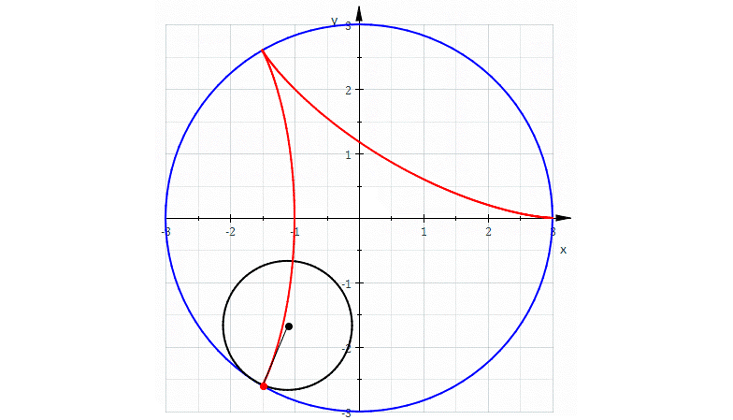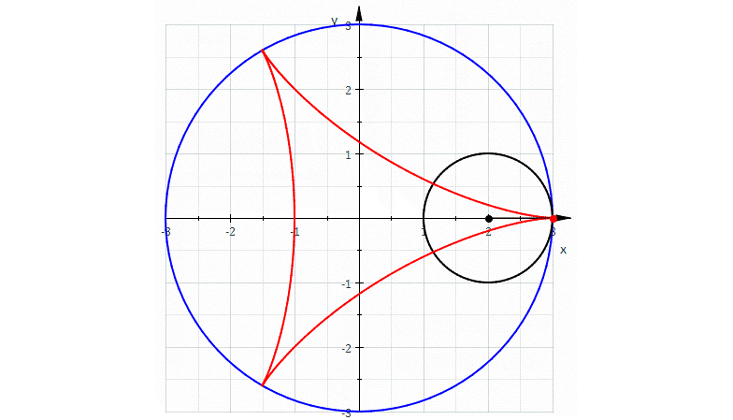
In my 50s, too old to become a real expert, I have finally fallen in love with algebraic geometry. As the name suggests, this is the study of geometry using algebra. Around 1637, René Descartes laid the groundwork for this subject by taking a plane, mentally drawing a grid on it, as we now do with graph paper, and calling the coordinates x and y. We can write down an equation like x + y = 1, and there will be a curve consisting of points whose coordinates obey this equation. In this example, we get a circle!
It was a revolutionary idea at the time, because it let us systematically convert questions about geometry into questions about equations, which we can solve if we’re good enough at algebra. Some mathematicians spend their whole lives on this majestic subject. But I never really liked it much until recently—now that I’ve connected it to my interest in quantum physics.
If we can figure out how to reduce topology to algebra, it might help us formulate a theory of quantum gravity.

Jetpack Aviation has leap-frogged its own flying car project with the announcement that it’s taking pre-orders now on a self-stabilizing, jet turbine-powered flying motorcycle capable of 150 mph speeds, 20 minute endurance and 15,000 ft altitudes.

Porsche made headlines for a battery it says can be charged with 400 kilometers (250 miles) of range in 15 minutes. If Piëch’s claims about a 4:40 charge hold up, Engadget pointed out, they’ll blow Porsche’s technology out of the water.
“We have developed a sports car that we ourselves would like to buy, and we talked for a long time to many enthusiasts about what was missing on the market,” co-founder Toni Piëch said in the press release. “We want to offer a modern classic that isn’t subject to consumer cycles. The driver of this sports car should enjoy any minute they can spend in the car.”
READ MORE: Piëch’s electric coupe charges to 80 percent in five minutes [Engadget] .

Quartz’s Lyft story isn’t the most groundbreaking work of journalism in the world, but it’s an interesting proof of concept about how reporters can leverage new tools to pull interesting takeaways from otherwise dry public records — and, perhaps, a preview of things to come.
“This is taking [data journalism] to the next level where we’re trying to get journalists comfortable using computers to do some of this pattern matching, sorting, grouping, anomaly detection — really working with especially large data sets,” John Keefe, Quartz’s technical architect for bots and machine learning, told Digiday back when the Quartz AI Studio first launched.
READ MORE: Here’s what Lyft talks about as risk factors that other companies don’t [Quartz].
Take a look at Goodyear’s vision for the future of transport.



Another flying car company is preparing to join the race to the skies, as Australia’s Macchina Volantis gears up to build a prototype of its road-drivable 5-seat electric aircraft. With VTOL capability, winged flight mode and a diesel range extender, this thing promises to fly at three times highway speed and offer some serious range.
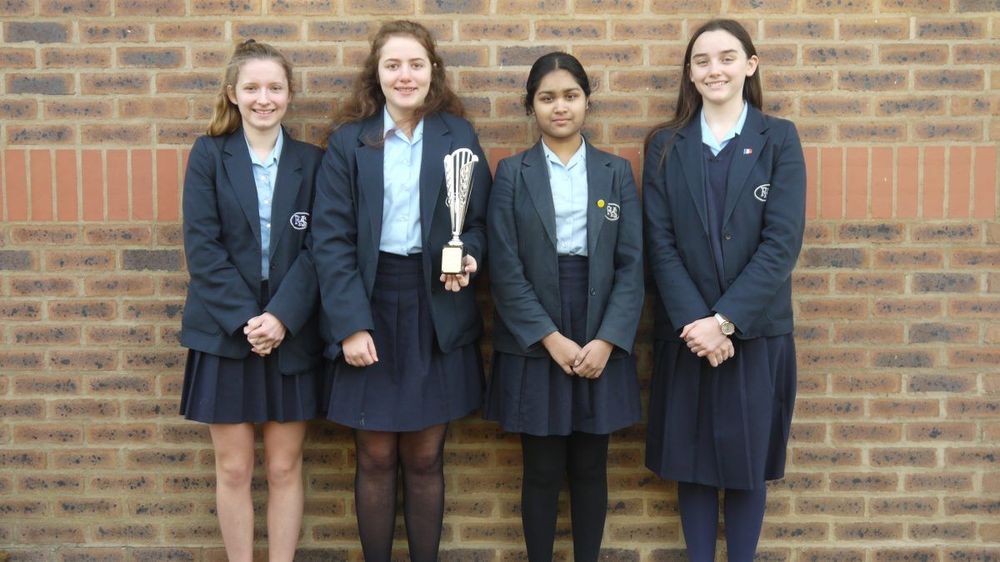

A DAY of science challenges and investigations run by the Institute of Physics was hosted by Rugby High School.
Teams from 12 schools from across the West Midlands came to take part in Super Physics Day.
The teams of four used their knowledge of science to conduct three timed investigations including ‘Air Drop’, an RAF challenge to drop relief packages from a plane to the desired location.