Category: transportation – Page 246
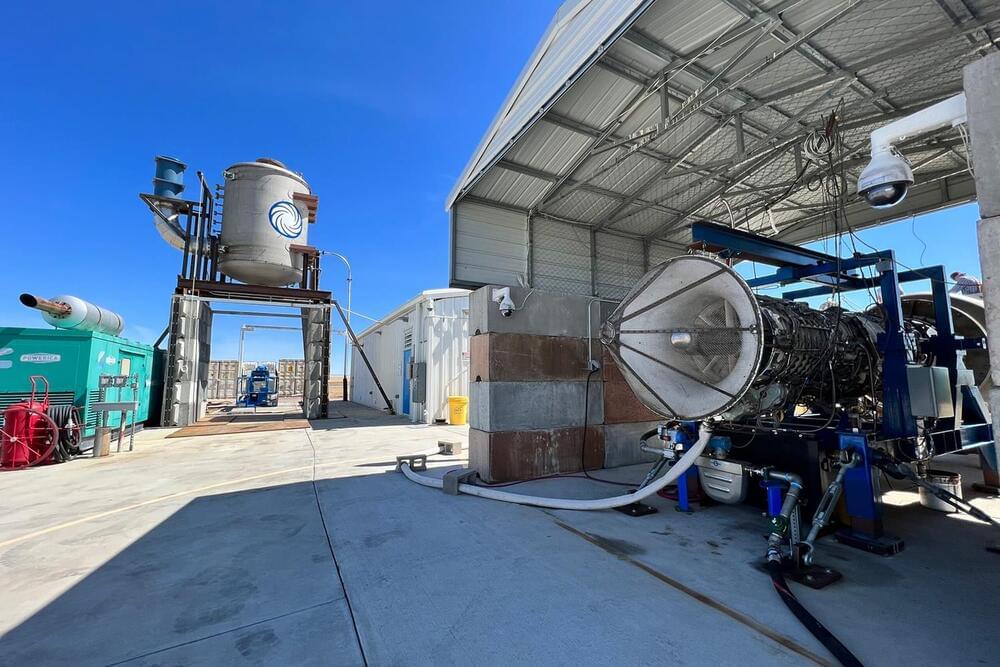

Reaction Engines begins testing its high-Mach propulsion technology
U.K.’s Reaction Engines has revealed the start of a new testing campaign to expand the performance envelope of their high-Mach propulsion technology. Over the coming weeks, the company hopes to prove that its technology could enable current jet engines to operate from takeoff up through Mach 4 and beyond.
The new tests are being conducted in conjunction with the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) as a part of the Foreign Comparative Testing (FCT) Program at the Department of Defense. The FCT program is administered by the Directorate of Defense Research and Engineering for Advanced Capabilities and is focused on the discovery, assessment, and testing of leading foreign technology with the potential to satisfy U.S. Defense technical demands. The program seeks high Technology Readiness Level (TRL) technologies that could rapidly and economically satisfy current and emerging requirements.
“FCT demonstrates U.S. commitment to a ‘two-way street’ for defense procurements with both allied and friendly nations. Reaction Engines technology is world-class and is a great fit for the FCT program,” describes William Reed, the Air Force FCT manager.
$26K solar car now has a factory — and will roll out this year
A California startup has developed a light-weight, three-wheeled solar car. They were built with affordability in mind.
Japan JUST REVEALED New Fully performing Female Robots
🔔 Subscribe for more Artificial Intelligence news, Robot news, Tech news and more.
🦾 Support us NOW so we can create more videos: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCItylrp-EOkBwsUT7c_Xkxg.
Every week we will update you about the Robotic news in Japan.
Living Human Skin for Robots.
From action heroes to villainous assassins, biohybrid robots made of both living and artificial materials have been at the center of many sci-fi fantasies, inspiring today’s robotic innovations. It’s still a long way until human-like robots walk among us in our daily lives, but scientists from Japan are bringing us one step closer by crafting living human skin on robots. The method developed not only gave a robotic finger skin-like texture, but also water-repellent and self-healing functions. “The finger looks slightly ‘sweaty’ straight out of the culture medium,” says first author Shoji Takeuchi, a professor at the University of Tokyo, Japan. “Since the finger is driven by an electric motor, it is also interesting to hear the clicking sounds of the motor in harmony with a finger that looks just like a real one.“
Looking “real” like a human is one of the top priorities for humanoid robots that are often tasked to interact with humans in healthcare and service industries. A human-like appearance can improve communication efficiency and evoke likability. While current silicone skin made for robots can mimic human appearance, it falls short when it comes to delicate textures like wrinkles and lacks skin-specific functions.
Artificial Intelligence that Acts More Human.
A research group from the Graduate School of Informatics, Nagoya University, has taken a big step towards creating a neural network with metamemory through a computer-based evolution experiment. In recent years, there has been rapid progress in designing artificial intelligence technology using neural networks that imitate brain circuits. One goal of this field of research is understanding the evolution of metamemory to use it to create artificial intelligence with a human-like mind.
Metamemory is the process by which we ask ourselves whether we remember what we had for dinner yesterday and then use that memory to decide whether to eat something different tonight. While this may seem like a simple question, answering it involves a complex process. Metamemory is important because it involves a person having knowledge of their own memory capabilities and adjusting their behavior accordingly.
Smart Robot Helps at Narita Airport.
A robot equipped with artificial intelligence has been put to work to help sort out congestion problems at Narita International Airport near Tokyo. The robot is shaped like a small vehicle and stands about 1.2 meters high. The AI instantly analyzes images taken by its cameras. The robot can quickly grasp how and where congestion occurs. It gives instructions to keep order when it detects long queues blocking the way. The robot also keeps an eye out for suspicious items. It informs the command center when baggage is left unattended for too long.
Soof Azani and Lir Braverman propose collapsible solar-powered bike for last-mile deliveries
Soof Azani and Lir Braverman’s proposal for a solar-powered cargo bike that aims to facilitate local deliveries is the latest of 10 visionary transportation projects selected for Dezeen’s Future Mobility Competition powered by Arrival.
Called D50, Azani and Braverman’s concept aims to combine solar power with micro-mobility in a bid to improve the distribution of goods while reducing carbon emissions.
The vehicle, which is intended for developing countries, is designed for heavy loads to expedite last-mile deliveries for traders and businesses.
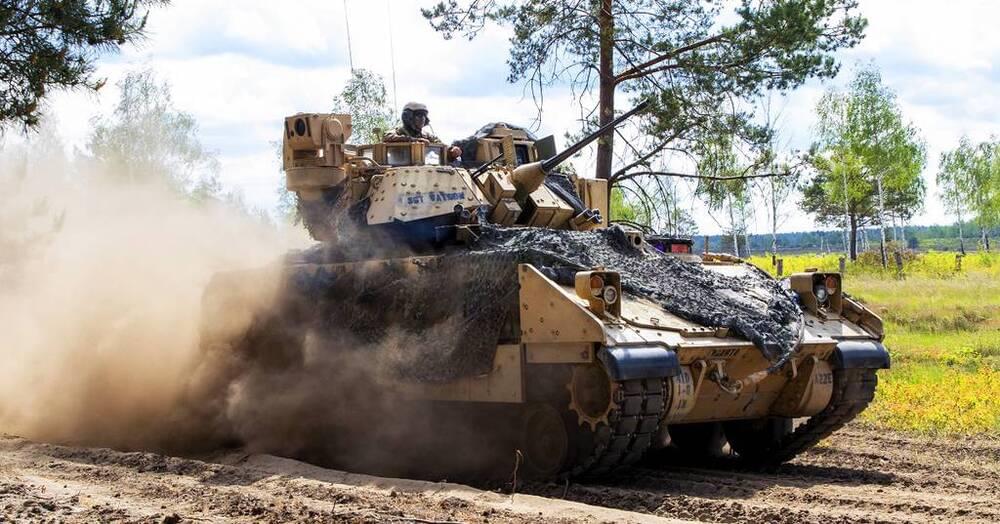


Competition to replace Bradley vehicles enters design, prototype phase
UPDATE — This story has been updated to include additional information from an Army press release.
WASHINGTON — The U.S. Army has opened up the competition to design and build prototypes for its Bradley Infantry Fighting Vehicle replacement, releasing a request for proposals to industry July 1 on the government contracting website Sam.gov.
The details of the RFP covering both a detailed design (phase 3) and prototyping (phase 4) are not yet publicly available.
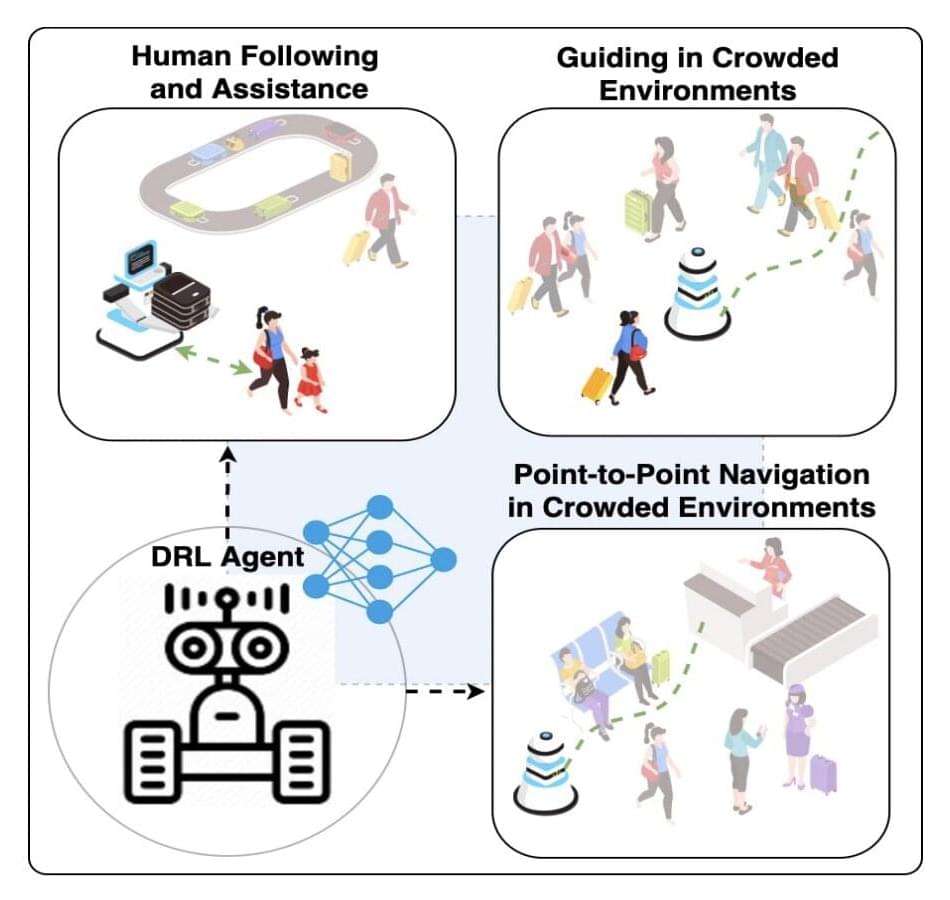
A model that allows robots to follow and guide humans in crowded environments
Assistance robots are typically mobile robots designed to assist humans in malls, airports, health care facilities, home environments and various other settings. Among other things, these robots could help users to find their way around unknown environments, for instance guiding them to a specific location or sharing important information with them.
While the capabilities of assistance robots have improved significantly over the past decade, the systems that have so far been implemented in real-world environments are not yet capable of following or guiding humans efficiently within crowded spaces. In fact, training robots to track a specific user while navigating a dynamic environment characterized by many randomly moving “obstacles” is far from a simple task.
Researchers at the Berlin Institute of Technology have recently introduced a new model based on deep reinforcement learning that could allow mobile robots to guide a specific user to a desired location or follow him/her around while carrying their belongings, all within a crowded environment. This model, introduced in a paper pre-published on arXiv, could help to significantly enhance the capabilities of robots in malls, airports and other public places.