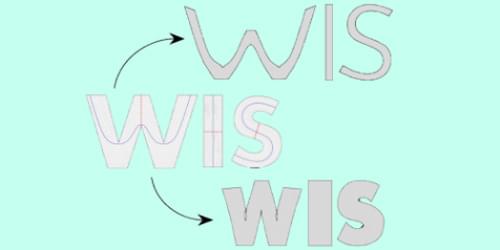
Liquid-crystal elastomers (LCEs) are shape-shifting materials that stretch or squeeze when stimulated by an external input such as heat, light, or a voltage. Designing these materials to produce desired shapes is a challenging math problem, but Daniel Castro and Hillel Aharoni from the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, have now provided an analytical solution for flat materials that shape-shift within a single plane—like font-changing letters on a page [1]. Such “planar” designs could help in producing rods that change their cross section (from, say, round to square) without buckling.
LCEs consist of networks of polymer fibers containing liquid-crystal molecules. When exposed to a stimulus, the molecules align in a way that causes the material to shrink or extend in a predefined direction—called the director. Researchers can design an LCE by choosing the director orientation at each point in the material. However, calculating the “director field” for an arbitrary shape change is difficult, so approximate methods are typically used.
Castro and Aharoni focused on a specific design problem: how to create an LCE that stretches only in two dimensions. These planar LCEs often suffer from residual stress that causes the material to wrinkle or buckle out of the plane. The researchers showed that finding a buckle-free design is similar to a well-known mathematical problem that has been studied in other contexts, such as minimizing the mass of load-carrying structures. Taking inspiration from these previous studies, Castro and Aharoni provided a method for exactly deriving the director field for any desired planar LCE. “Our results could be readily implemented by a wide range of experimentalists, as well as by engineers and designers,” Aharoni says.