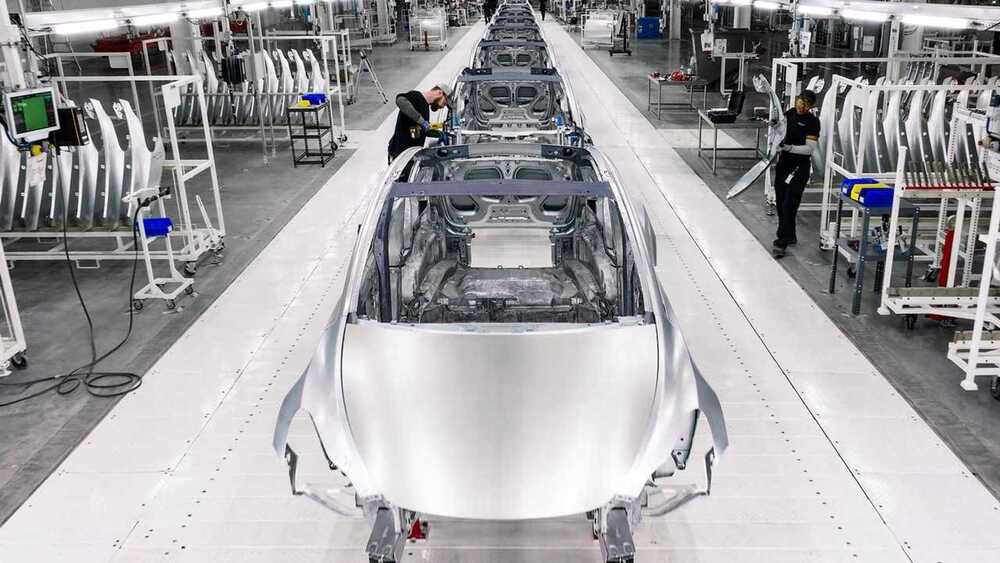
Needless to say, this could transform the way Tesla builds EVs and contribute decisively to halving production costs, which is a long-time goal of CEO Elon Musk.
The sources said the know-how to achieve that is core to Tesla’s “unboxed” manufacturing strategy unveiled by Elon Musk in March, which is key to his plan to build tens of millions of cheaper EVs over the next ten years, and still turn a profit.
Two of the insiders said Tesla’s new design and manufacturing techniques could allow the company to develop a car from the ground up in 18–24 months, compared to 3–4 years for most rivals.