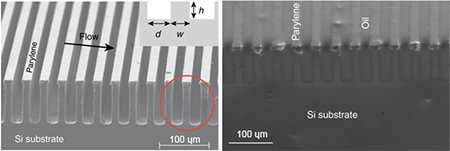
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a super-hydrophobic surface that can be used to generate electrical voltage. When salt water flows over this specially patterned surface, it can produce at least 50 millivolts. The proof-of-concept work could lead to the development of new power sources for lab-on-a-chip platforms and other microfluidics devices. It could someday be extended to energy harvesting methods in water desalination plants, researchers said.
A team of researchers led by Prab Bandaru, a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, and first author Bei Fan, a graduate student in Bandaru’s research group, published their work in the Oct. 3 issue of Nature Communications.
The main idea behind this work is to create electrical voltage by moving ions over a charged surface. And the faster you can move these ions, the more voltage you can generate, explained Bandaru.