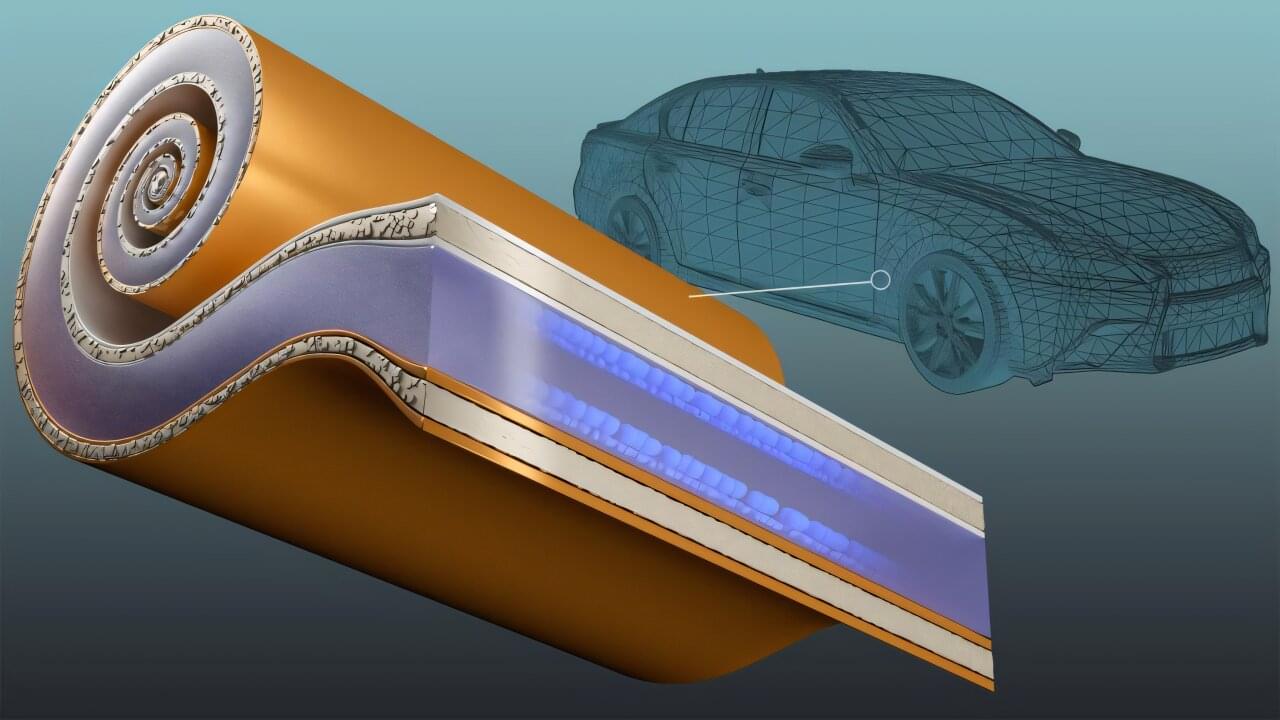
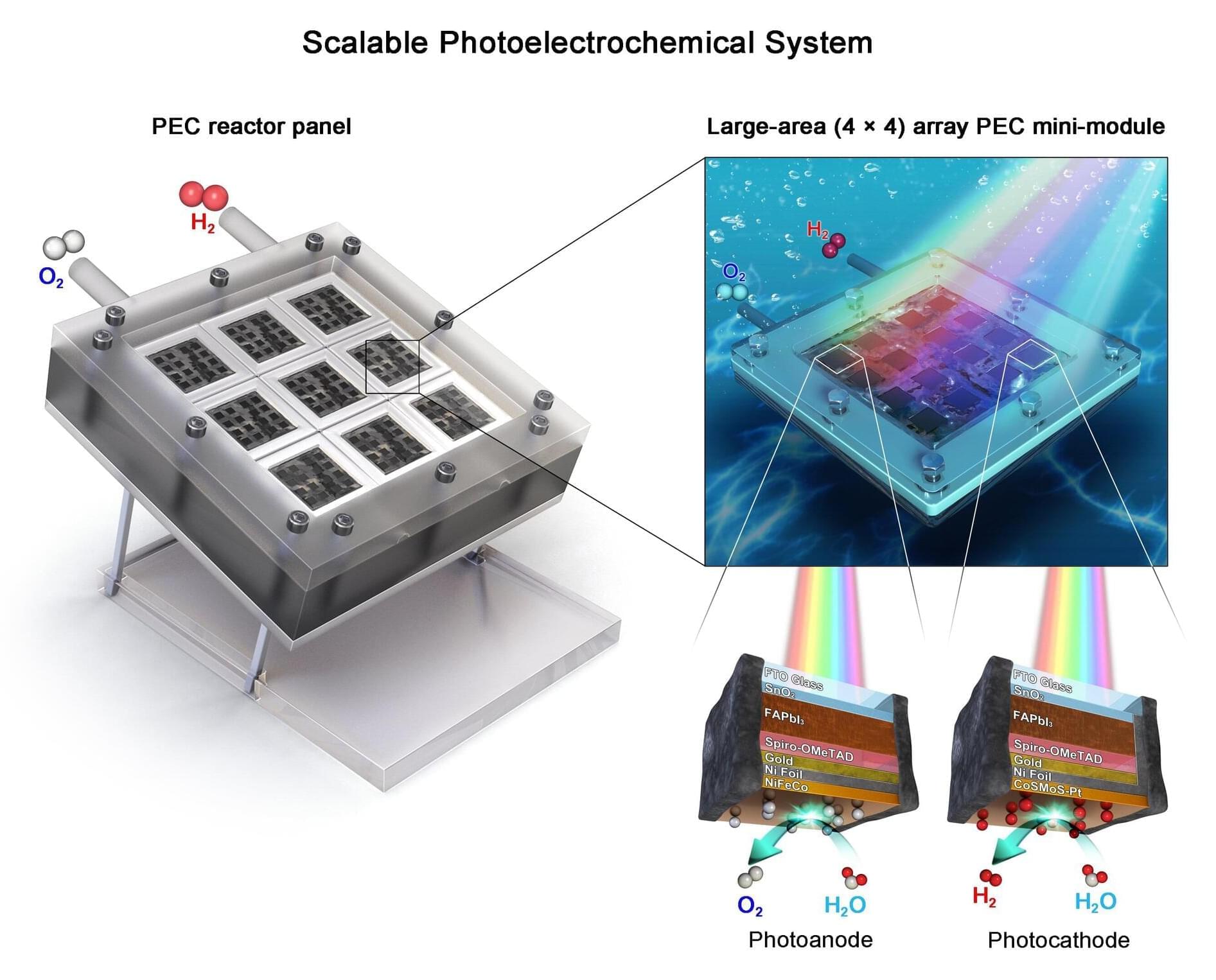
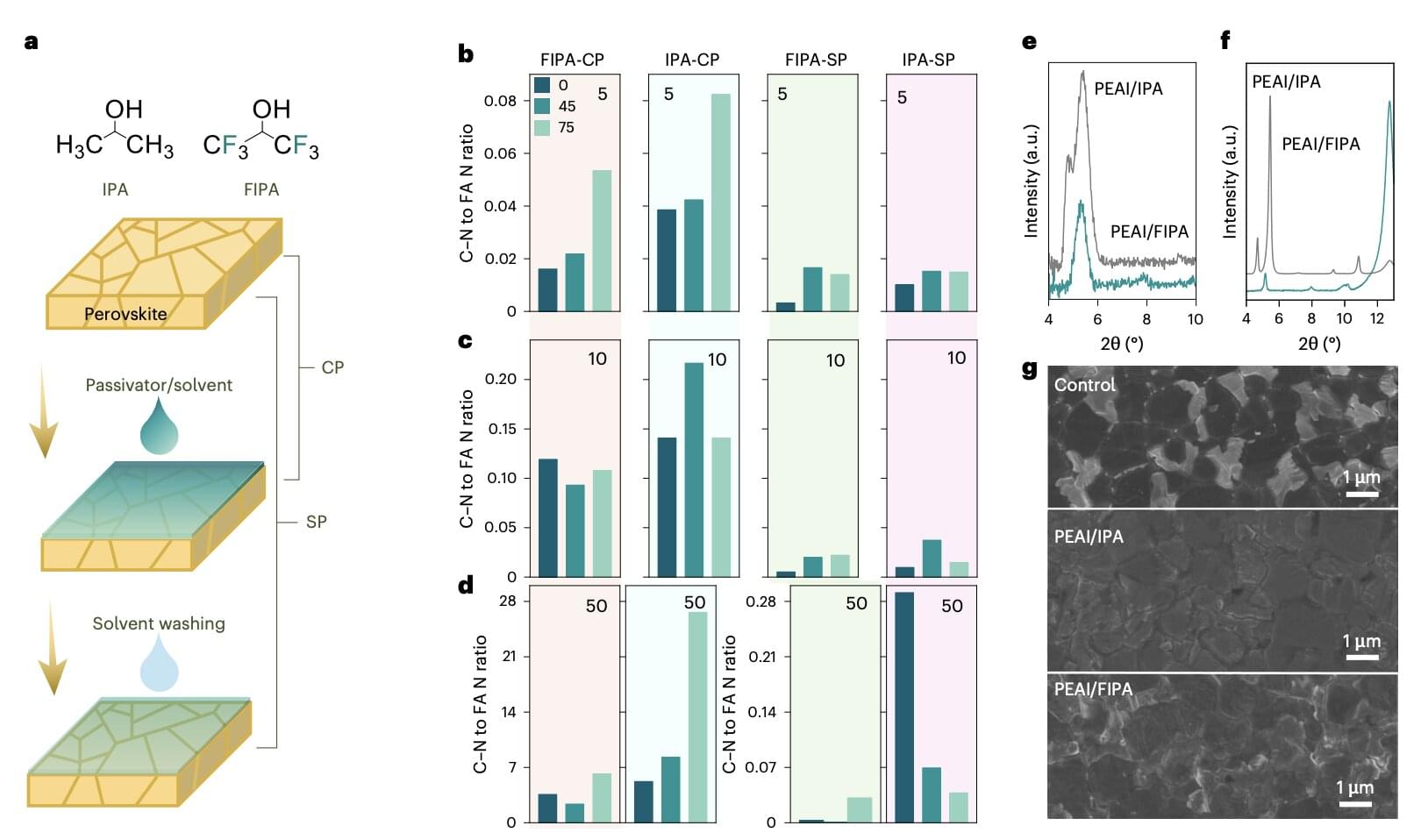
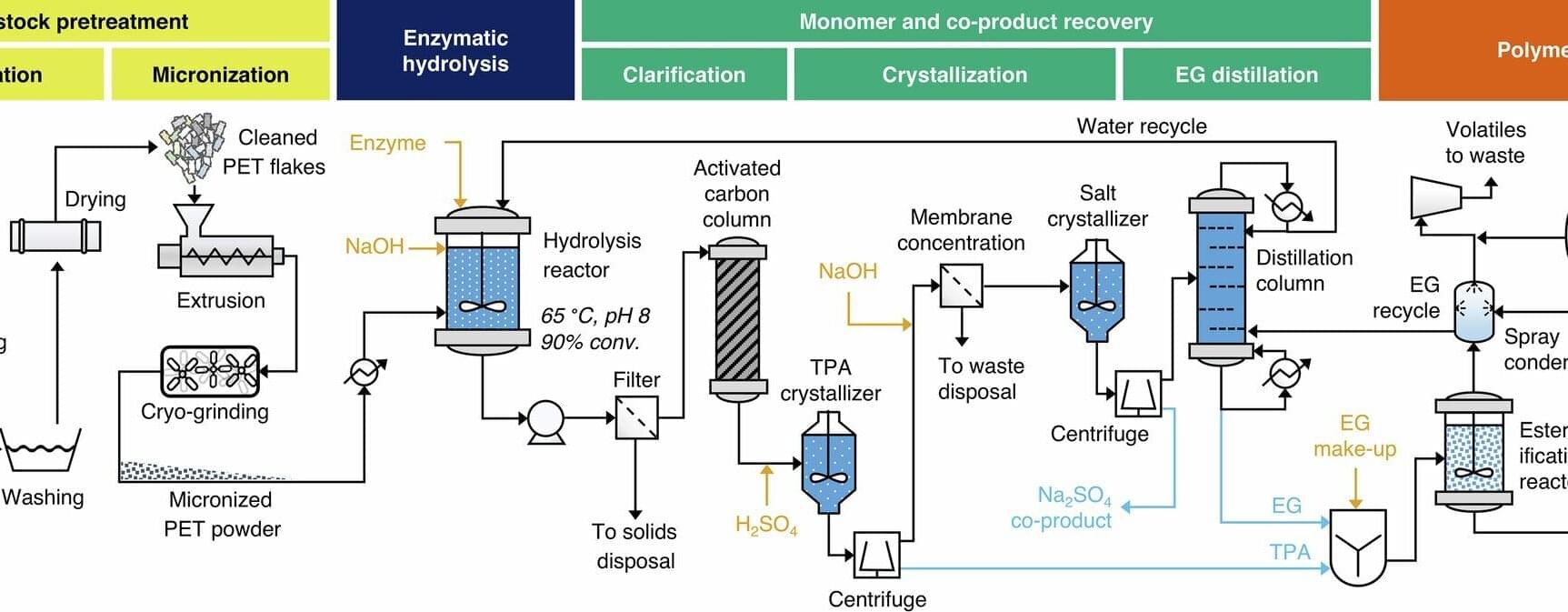
Mark Hersam is a nanotechnologist who believes that understanding materials at the shortest of length scales can provide solutions to the world’s largest problems. Using an interdisciplinary approach at the intersection of neuroscience and nanoelectronics, Hersam presents a solution to the greatest societal threat posed by AI.
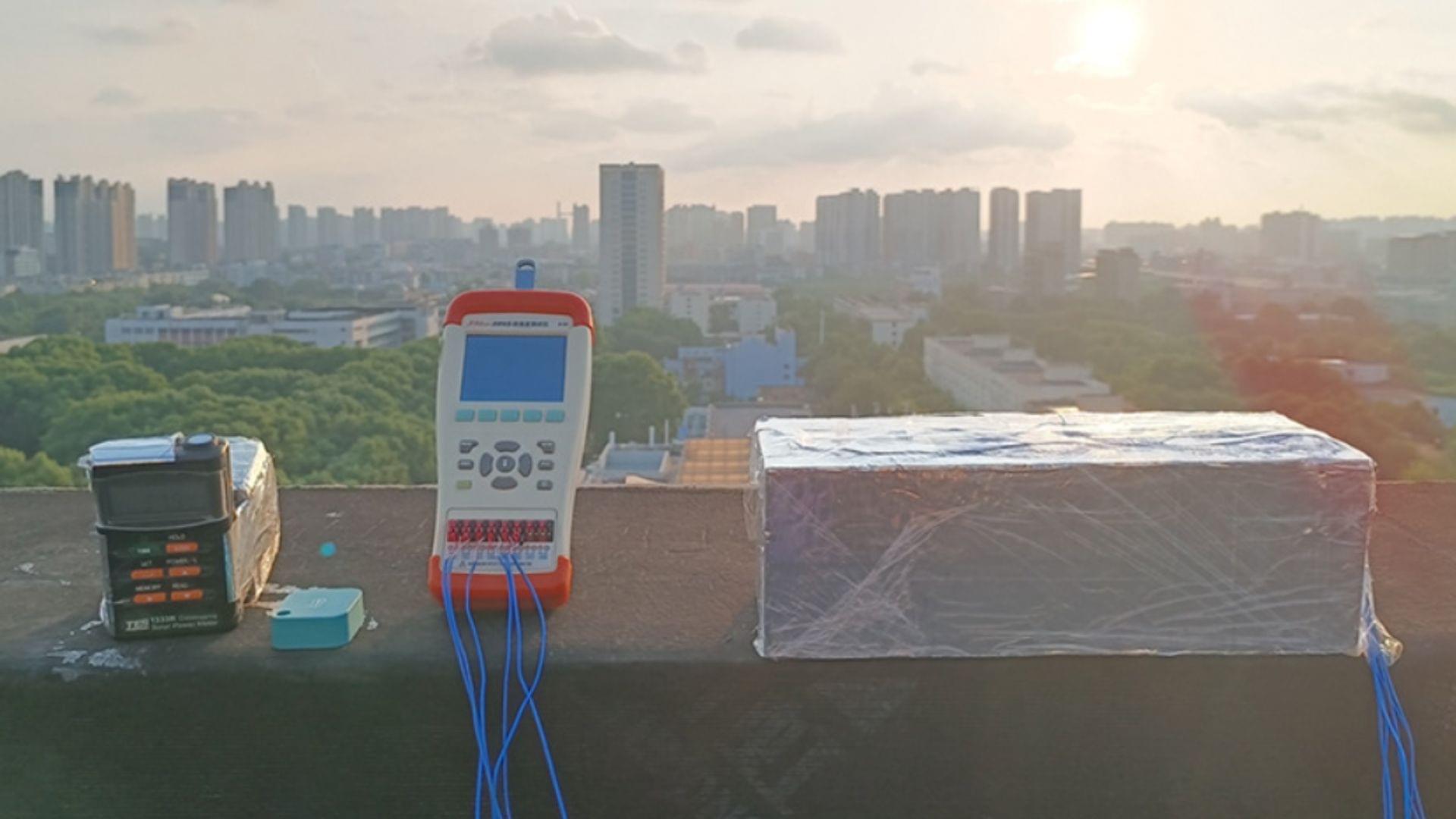
Dr. Mark C. Hersam, the Walter P. Murphy Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, Director of the Materials Research Center, and Chair of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at Northwestern University, has made major breakthroughs in the field of nanotechnology. His research interests include nanomaterials, additive manufacturing, nanoelectronics, scanning probe microscopy, renewable energy, and quantum information science. Dr. Hersam has received several honors including the Marshall Scholarship, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, American Vacuum Society Medard Welch Award, U.S. Science Envoy, and MacArthur Fellowship. In addition, he is an elected member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, National Academy of Engineering, and National Academy of Inventors and has founded two companies, NanoIntegris and Volexion, which are suppliers of nanoelectronic and battery materials, respectively.
This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.