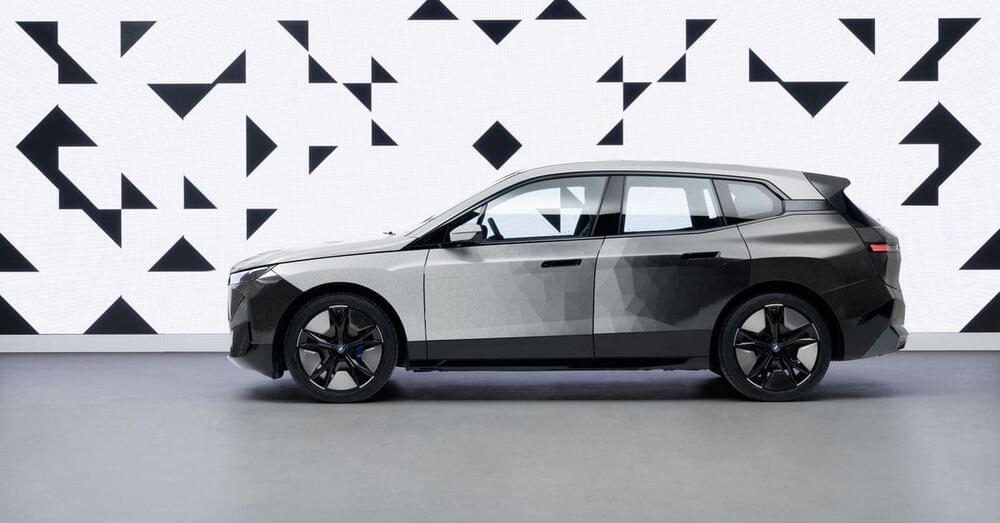
At the touch of a button, the car changes colors.
The surface coating of the BMW iX Flow featuring E Ink contains many millions of microcapsules, with a diameter equivalent to the thickness of a human hair. Each of these microcapsules contains negatively charged white pigments and positively charged black pigments. Depending on the chosen setting, stimulation by means of an electrical field causes either the white or the black pigments to collect at the surface of the microcapsule, giving the car body the desired shade.
Just don’t expect to see this at your local BMW dealership anytime soon: the automaker says this is just an “advanced research and design project.”
The innovative paint scheme can be triggered at the touch of a button. Right now, the colors are limited to white, black, and grey. But despite the constrained palette, BMW says it could have implications for the efficiency of its electric vehicles.