Ancient crystals reveal that Earth began recycling its crust and forming continents billions of years earlier than scientists once believed.


Questions to inspire discussion.
📈 Q: What is the potential annual production capacity for Cybercabs at full speed? A: At full speed with multiple production lines, Tesla’s Cybercab production could reach 2 million vehicles per year.
Tesla’s FSD and Autonomous Driving.
🧠 Q: When is FSD14 expected to be released? A: FSD14 is anticipated to be released in September 2025.
🚗 Q: What capability will FSD14 enable for Tesla vehicles? A: FSD14 will enable unsupervised robo taxi operation for Tesla vehicles.
💼 Q: How might Tesla’s FSD subscription model change? A: Tesla’s FSD subscription could become mandatory for new vehicle purchases.
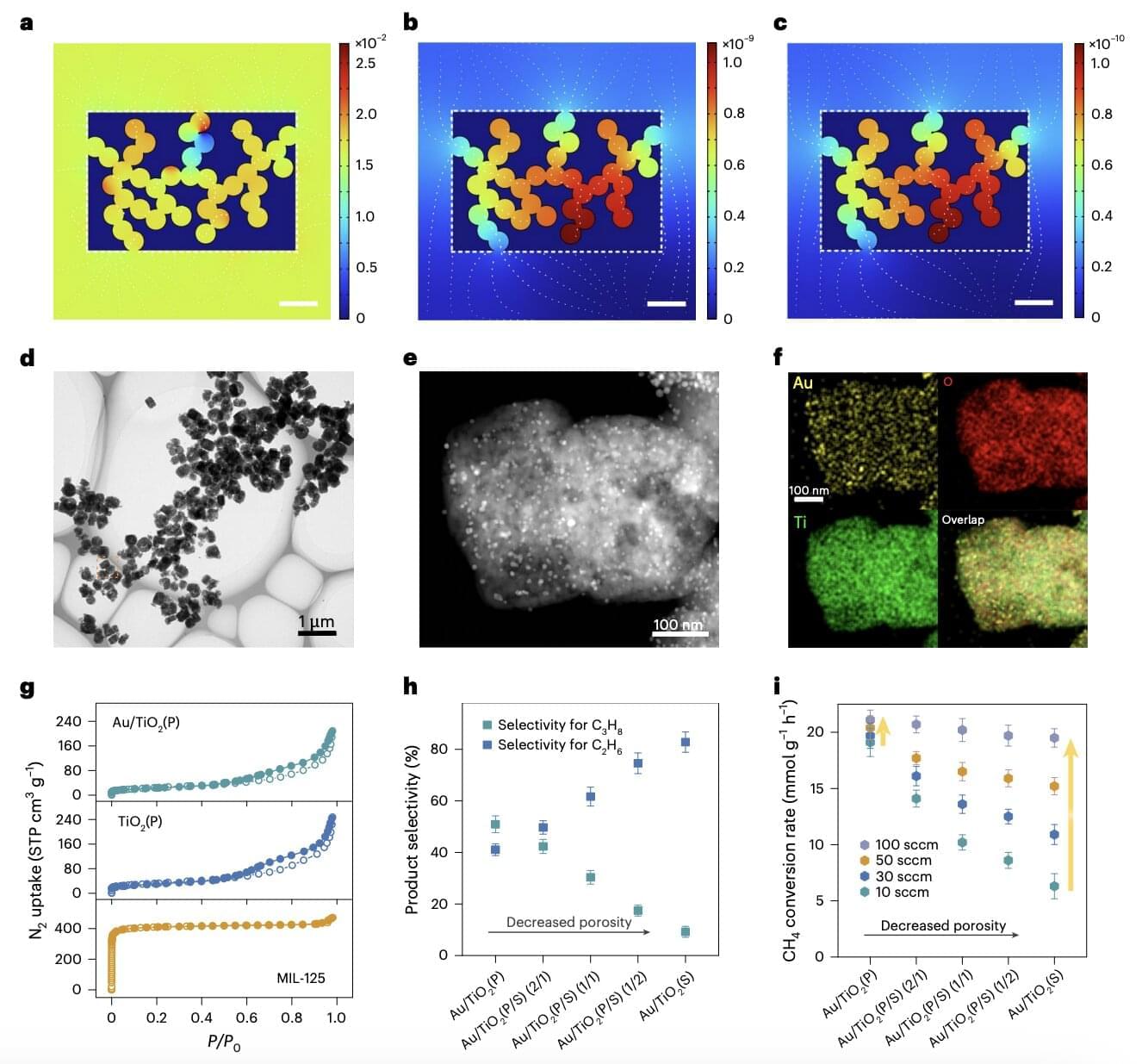
Methane (CH₄), the colorless and odorless gas that makes up most natural gas on Earth, has so far been converted into useful fuels and chemicals via energy-intensive processes that need to be carried out at high temperatures. Some energy researchers, however, have been exploring the possibility of transforming this gas into useful hydrocarbons and chemicals via photocatalysis.
Photocatalysis is a process through which the energy contained in light, typically solar energy, activates a material known as a “catalyst,” driving desired chemical reactions. Converting CH₄ into specific fuels or chemicals via photocatalysis instead of conventional methods that rely on the burning of fossil fuels could be highly advantageous, as it could contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Researchers at Hebei University and other institutes in China recently introduced a new photocatalysis-driven approach to convert CH₄ into propane (C₃H₈), a hydrocarbon that is easier to use in real-world settings, as it becomes liquid at specific pressures, which facilitates its storage and transport.
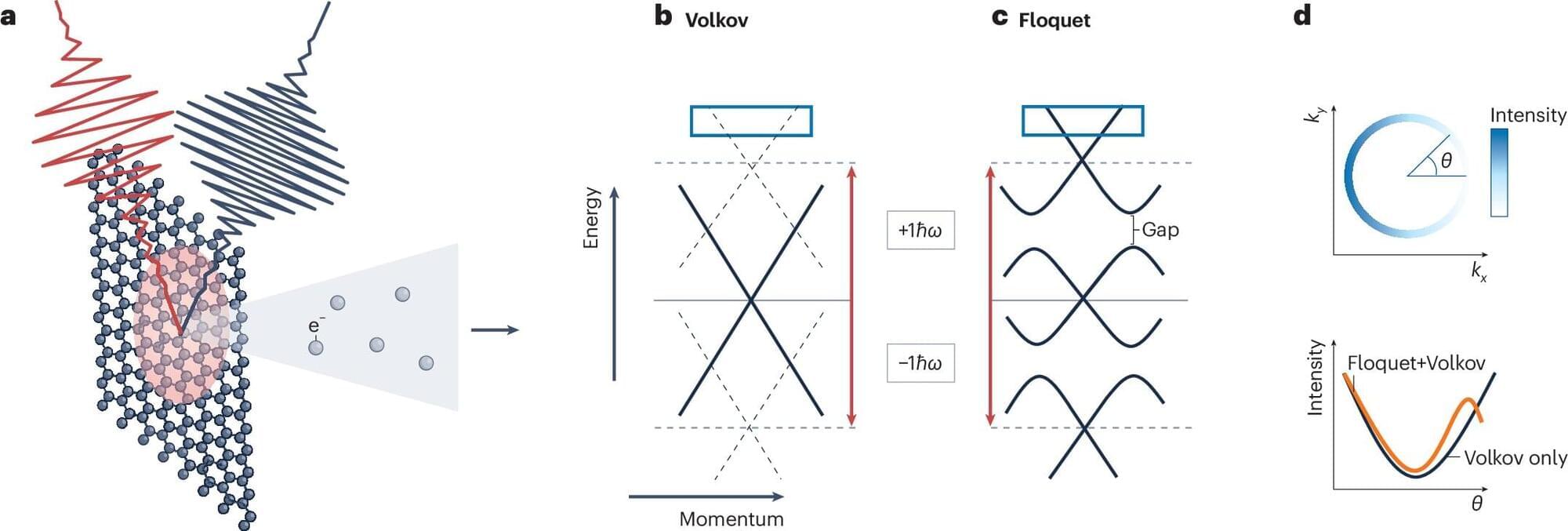
Graphene is an extraordinary material—a sheet of interlocking carbon atoms just one atom thick that is stable and extremely conductive. This makes it useful in a range of areas, such as flexible electronic displays, highly precise sensors, powerful batteries, and efficient solar cells.
A new study—led by researchers from the University of Göttingen, working together with colleagues from Braunschweig and Bremen in Germany, and Fribourg in Switzerland—now takes graphene’s potential to a whole new level. The team has directly observed “Floquet effects” in graphene for the first time.
This resolves a long-standing debate: Floquet engineering—a method in which the properties of a material are very precisely altered using pulses of light—also works in metallic and semi-metallic quantum materials such as graphene. The study is published in Nature Physics.
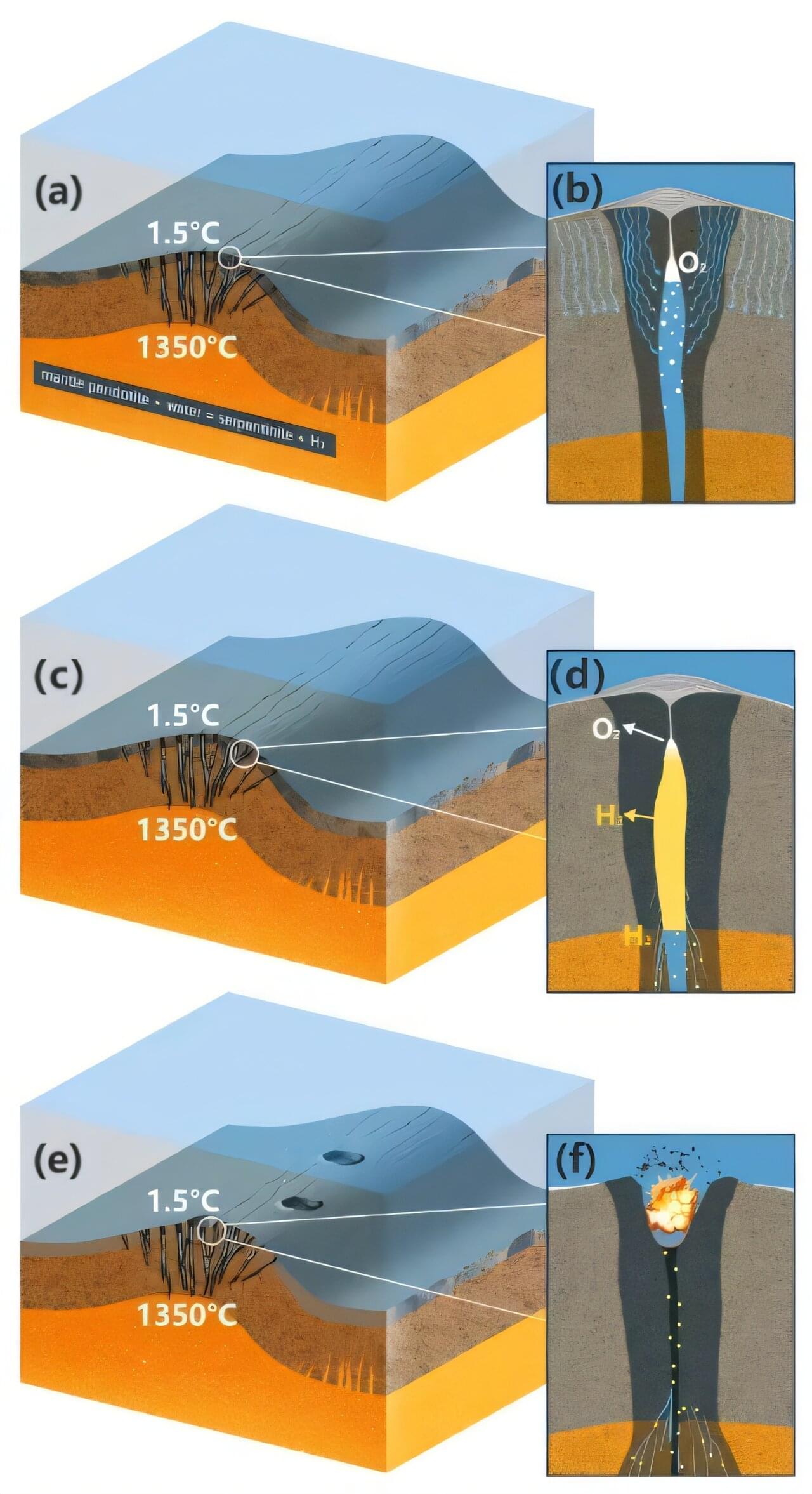
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the solar system. As a source of clean energy, hydrogen is well-suited for sustainable development, and Earth is a natural hydrogen factory. However, most hydrogen vents reported to date are small, and the geological processes responsible for hydrogen formation—as well as the quantities that can be preserved in geological settings—remain unclear.

Questions to inspire discussion.
🌐 Q: How quickly will Tesla expand its robo taxi service? A: Tesla plans to rapidly expand access to its ride-hailing service in the Bay Area and robo taxi service in Austin, Texas, by scaling its fleet and improving autonomous driving technology.
🚕 Q: What impact will Tesla’s robo taxi service have on the ride-hailing industry? A: Tesla’s service is expected to disrupt traditional ride-hailing, potentially becoming the most cost-effective option for customers while advancing sustainable energy transition.
Revenue and Profitability.
📈 Q: How will the robo taxi service affect Tesla’s revenue? A: The service is anticipated to generate significant revenue for Tesla, leveraging its cost advantage and autonomous technology to become potentially the most profitable ride-hailing option.
🔋 Q: How does the robo taxi service align with Tesla’s broader mission? A: The service supports Tesla’s ambition statement of accelerating the world’s transition to sustainable energy while offering a competitive and cost-effective transportation solution.

In a major leap for artificial intelligence (AI) and photonics, researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have created optical generative models capable of producing novel images using the physics of light instead of conventional electronic computation.
Published in Nature, the work presents a new paradigm for generative AI that could dramatically reduce energy use while enabling scalable, high-performance content creation.
Generative models, including diffusion models and large language models, form the backbone of today’s AI revolution. These systems can create realistic images, videos, and human-like text, but their rapid growth comes at a steep cost: escalating power demands, large carbon footprints, and increasingly complex hardware requirements. Running such models requires massive computational infrastructure, raising concerns about their long-term sustainability.

Huawei has shocked the electric vehicle (EV) world by filing a patent for a solid-state battery that claims a potential range of 3,000 kilometres and the ability to recharge to full in just five minutes. Normally, we have to assume this particular patent will go nowhere, and we will forget about it; however, it could be the start of something new.

Researchers at the University of Missouri are working to make hydrogen energy as safe as possible. As more countries and industries invest heavily in cleaner, renewable energy, hydrogen-powered factories and vehicles are gaining in popularity. But hydrogen fuel comes with risks—leaks can lead to explosions, accidents and environmental harm. Most hydrogen-detecting sensors on the market are expensive, can’t operate continuously and aren’t sensitive enough to detect tiny leaks quickly.