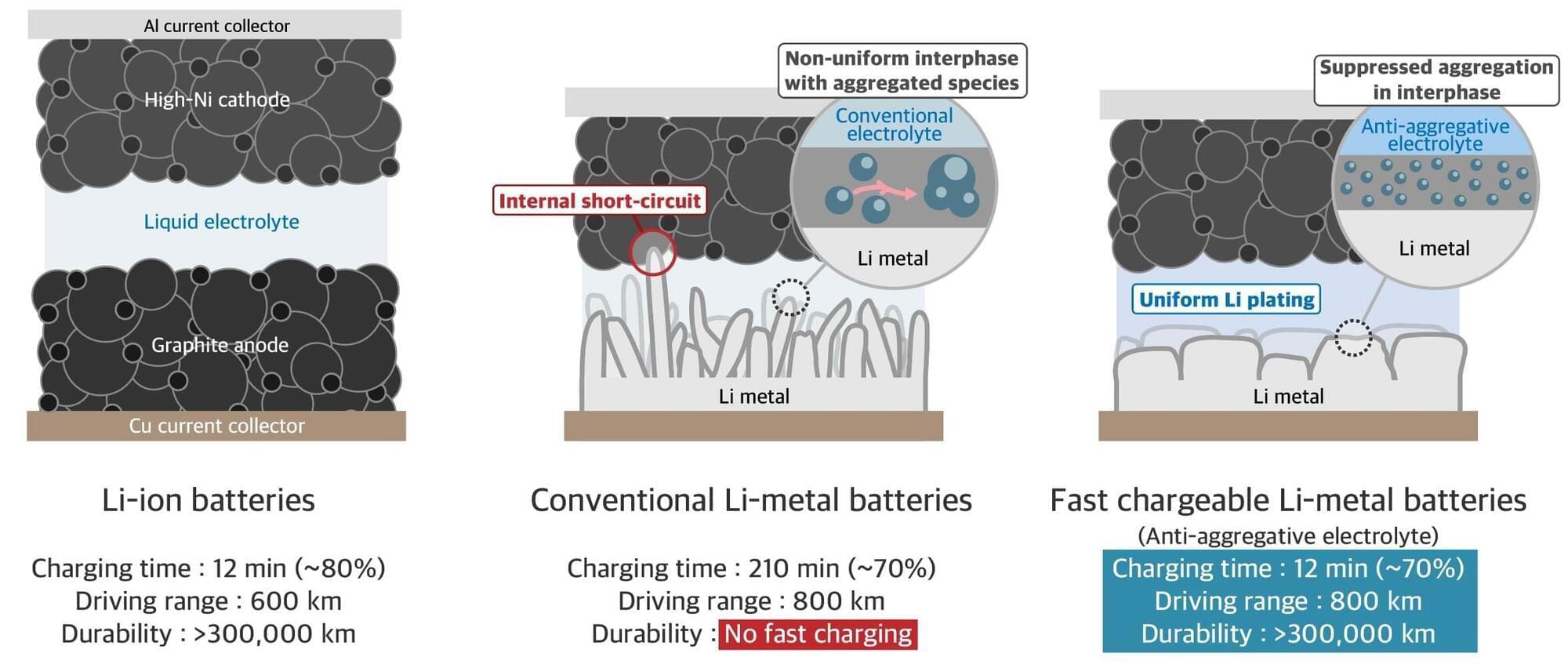
Korean researchers have ushered in a new era for electric vehicle (EV) battery technology by solving the long-standing dendrite problem in lithium-metal batteries. While conventional lithium-ion batteries are limited to a maximum range of 600 km, the new battery can achieve a range of 800 km on a single charge, a lifespan of over 300,000 km, and a super-fast charging time of just 12 minutes.
A research team from the Frontier Research Laboratory (FRL), a joint project between Professor Hee Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and LG Energy Solution, has developed a “cohesion-inhibiting new liquid electrolyte” original technology that can dramatically increase the performance of lithium-metal batteries. Their paper is published in Nature Energy.
Lithium-metal batteries replace the graphite anode, a key component of lithium-ion batteries, with lithium metal. However, lithium metal has a technical challenge known as dendrite, which makes it difficult to secure the battery’s lifespan and stability. Dendrites are tree-like lithium crystals that form on the anode surface during battery charging, negatively affecting battery performance and stability.