Stand back.
SpaceX is currently developing the Starship, a stainless steel rocket designed to send humans to Mars and beyond. Elon Musk aims to establish a city on Mars by 2050.

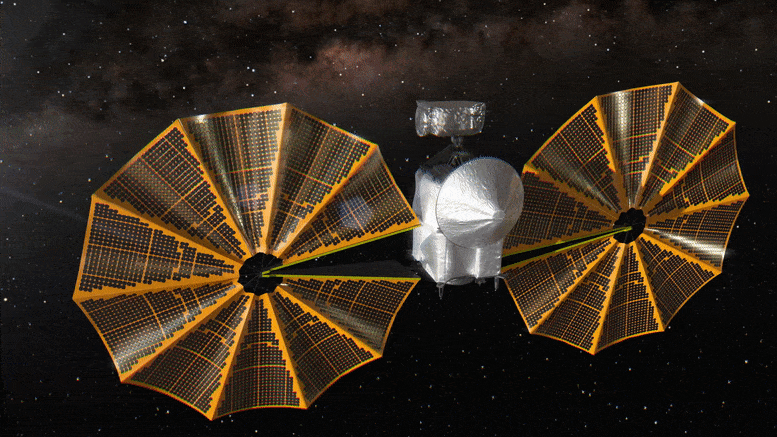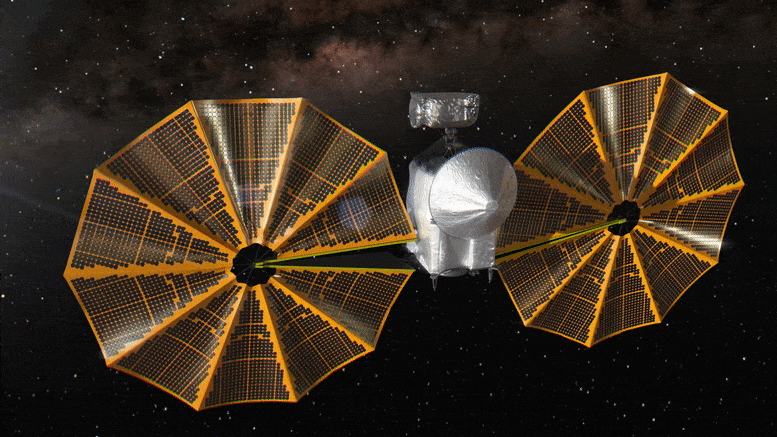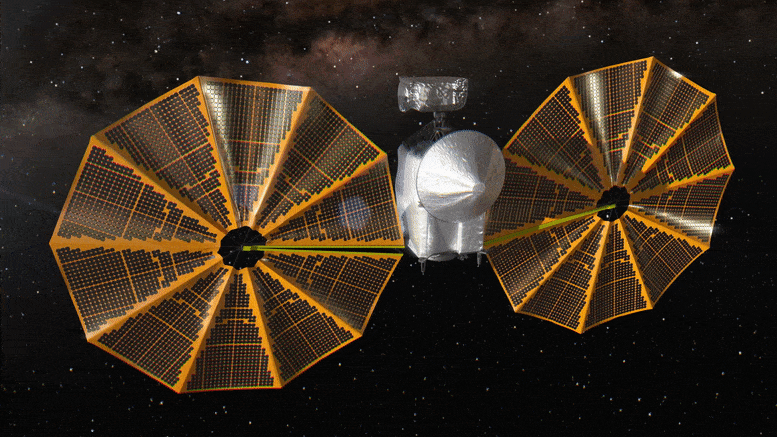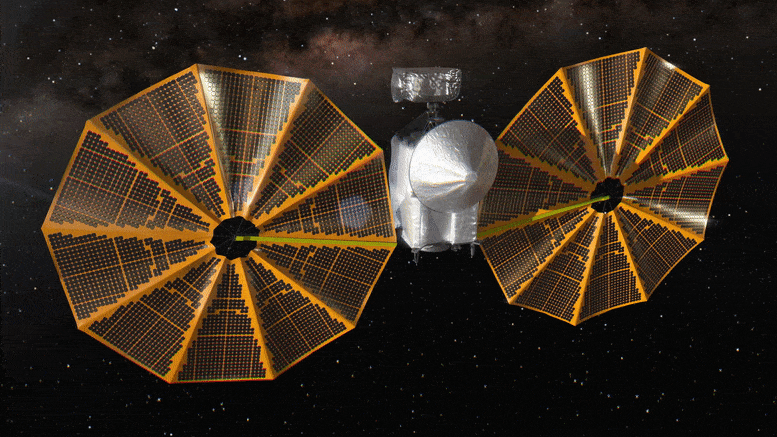
Lucy Spacecraft Healthy as NASA
Established in 1,958 the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government that succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. It’s vision is “To discover and expand knowledge for the benefit of humanity.”



The spacecraft could launch with just 8.5 days’ notice.
China just launched what is planned to be its longest crewed mission to date, but the next spacecraft in the series is ready to blast off should the Shenzhou 13 astronauts need rescuing.
Shenzhou 13 lifted off on Oct. 15 with commander Zhai Zhigang and colleagues Wang Yaping and Ye Guangfu arriving at the orbiting Tianhe module of the Tiangong space station 6.5 hours later. Back on the ground at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert, Shenzhou 14 and its Long March 2F launch vehicle are already on standby.

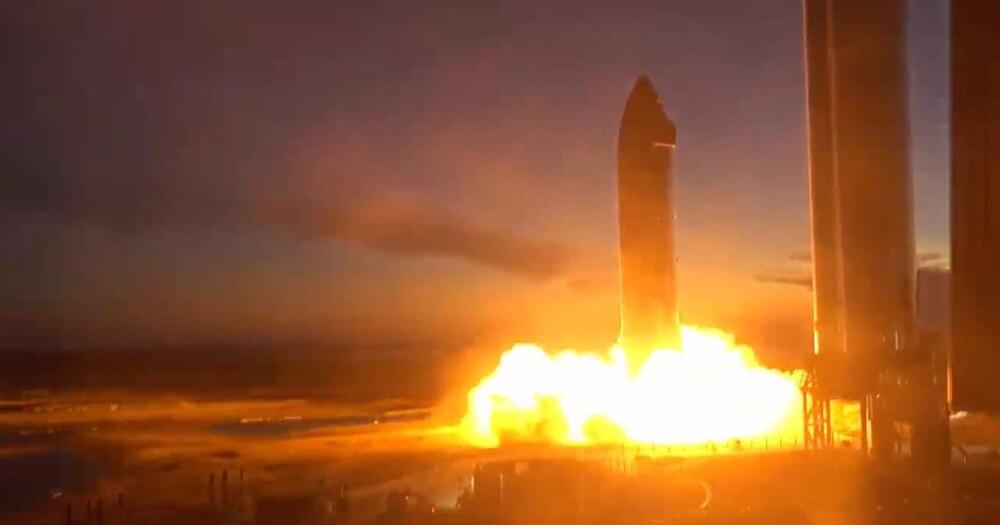
Starship will be ready for its orbital launch next month, pending regulatory approval — Elon Musk.
SpaceX’s Starship rocket is still being built in southeast Texas, with significant work being made on crucial parts like the launch tower construction and the installation of the vacuum-rated Raptor engines that will power the spacecraft once it reaches space.
Elon Musk claims that it might be ready for its maiden orbital flight attempt next month if it receives the necessary regulatory approvals.
To make the effort, SpaceX will need clearance from the United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), as it has for all of its previous test flights of Starship from its development facility outside of Brownsville, Texas.

Last week, China launched what was seen as its most ambitious manned space mission. Shortly after this, the communist country has announced another breakthrough in its rocket engine technology.
On October 16 China launched a spacecraft with three astronauts (taikonauts) on board, including a woman, into the core module of what is believed to be China’s own future space station in the Earth’s orbit. The astronauts are expected to stay in space for six months, which is the longest duration for a Chinese manned space mission so far.

Elon Musk has built two industrial behemoths— Tesla and SpaceX—revolutionizing two industries along the way. But that’s not all he has done to change global industry.
Musk has also given manufacturing companies a new word: gigafactory.
The practical definition of a gigafactory is a larger, modern manufacturing facility for products that are designed to lower global carbon emissions.
October 22 2021 2:30pm – 4pm ET (6:30 – 8pm UTC) 📅 Save to Google Calendar REGISTER FOR THE EVENT THE OVERVIEW EFFECT & HUMANITY’S FUTURE Join us for engaging discussions between astronauts, philosophers, and artists on the new era of space exploration, Frank White’s theory of The Overview Effect phenomenon, and what it could […].
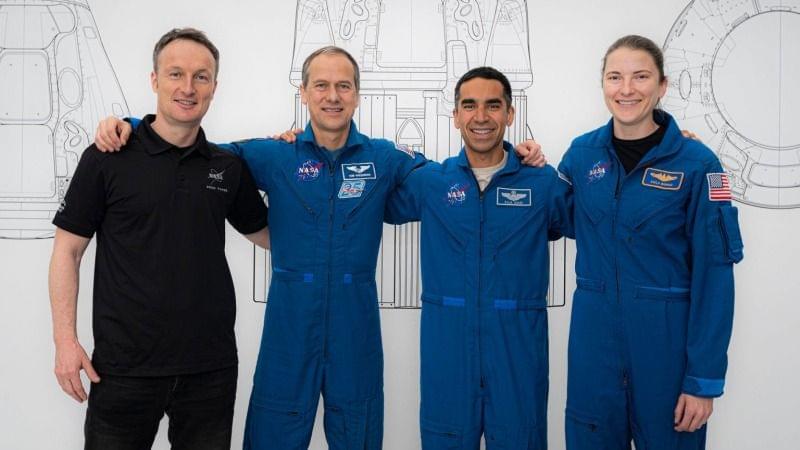

Four astronauts are getting ready to launch from Florida.
NASA’s next space station launch is set for Halloween and will put four more astronauts into space on a SpaceX rocket.
The Crew-3 launch is scheduled for Sunday, Oct. 31 at 2:21 a.m. EDT (0721 GMT), using a Falcon 9 rocket. The launch will take place at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA Television and SpaceX broadcast details will be released at a later date.