Starbase, the city that never sleeps.
As the Federal Aviation Administration conducts research into SpaceX’s Texas project, a new video shows the company hard at work on its big rocket.
Starbase, the city that never sleeps.
As the Federal Aviation Administration conducts research into SpaceX’s Texas project, a new video shows the company hard at work on its big rocket.
It takes seven months to get to Mars in an efficiently engineered spaceship, covering the distance of 480 million kilometers. On this journey, a crew would have to survive in a confined space with no opportunity to experience nature or interact with new people. It is easy to imagine how this much isolation could have a severe impact on the crew’s well-being and productivity.
The challenges long-duration space travelers experience are not foreign to regular folk, although to … See more.

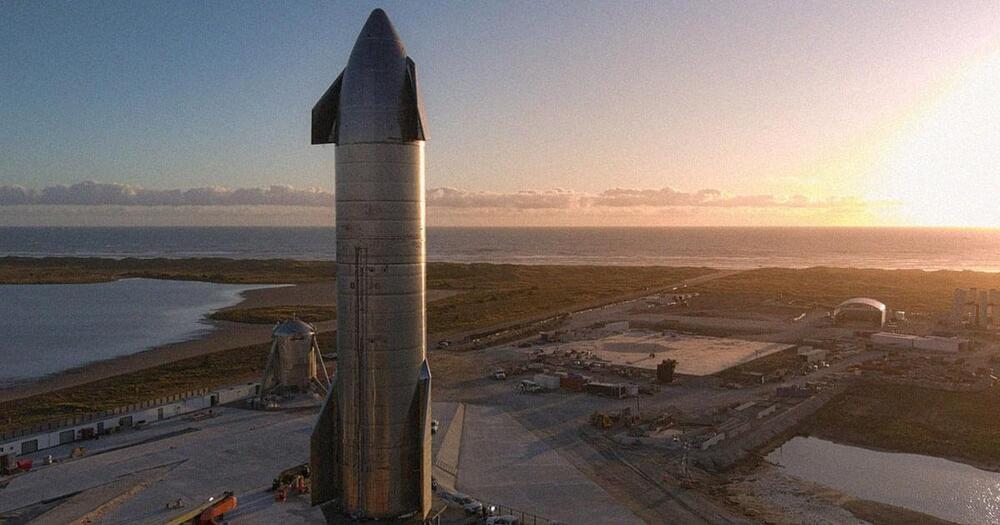
With the maiden orbital flight of Starship approaching, Orbital Launch Pad A in Starbase, Texas, is being built up to launch readiness. Over a year of construction has brought the complex’s various elements to the verge of launching the most powerful rocket in history.
Assembly Timeline
SpaceX started construction of the orbital launch pad on June 22 2020, when teams began to install the concrete rebar for the six pillars of the orbital launch mount. After building up steel rebar for reinforcement, a steel cylinder was sleeved over the rebar and each pillar was filled with concrete, covered, then left to cure.
A Liebherr LR 11,000 painted in a black and white SpaceX livery, was delivered to the launch site and assembled. Meanwhile, crews continue to work on the Chopsticks and more beams for the Wide Bay were lifted.
Video and Pictures from Mary (@BocaChicaGal) and the NSF Robots. Edited by Patrick Colquhoun (@Patrick_Colqu).
All content copyright to NSF. Not to be used elsewhere without explicit permission from NSF.
Click “Join” for access to early fast turnaround clips, exclusive discord access with the NSF team, etc — to support the channel.
Rolling Updates and Discussion: https://forum.nasaspaceflight.com/index.php?board=72.
Here’s what you need to know.
The third Crew Dragon mission to the ISS will launch on Halloween. Here’s your guide to the launch schedule and how to see it live.
SpaceX had to fix the toilet on its capsule before this mission could fly.
Early in the morning on October 31st, SpaceX will launch its next astronauts to the International Space Station for NASA, part of the company’s Crew-3 mission. Liftoff is scheduled for 2:21AM ET out of Cape Canaveral, Florida.
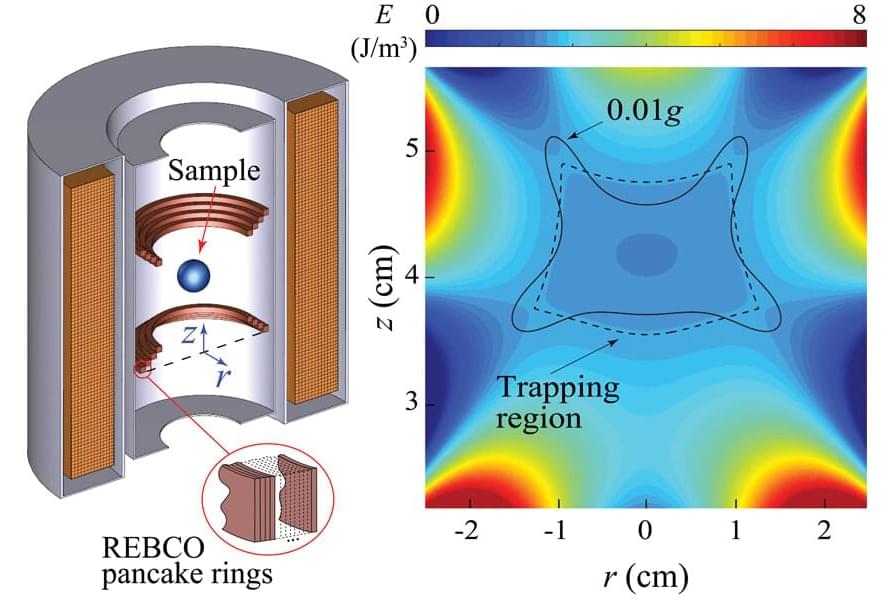
As humanity continues its exploration of the universe, the low-gravity environment of space presents unusual challenges for scientists and engineers.
Researchers at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the Florida State University-headquartered National High Magnetic Field Laboratory have developed a new tool to help meet that challenge—a novel design for a low-gravity simulator that promises to break new ground for future space research and habitation.
Their new design for a magnetic levitation-based low-gravity simulator can create an area of low gravity with a volume about 1,000 times larger than existing simulators of the same type. The work was published in the journal npj Microgravity.

Weird flex, but OK.