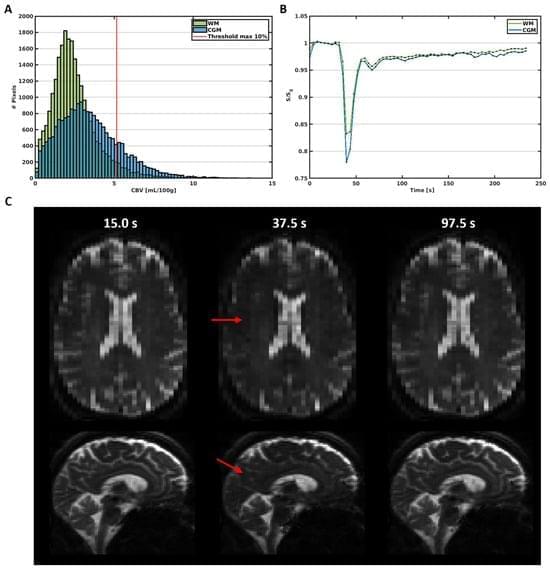
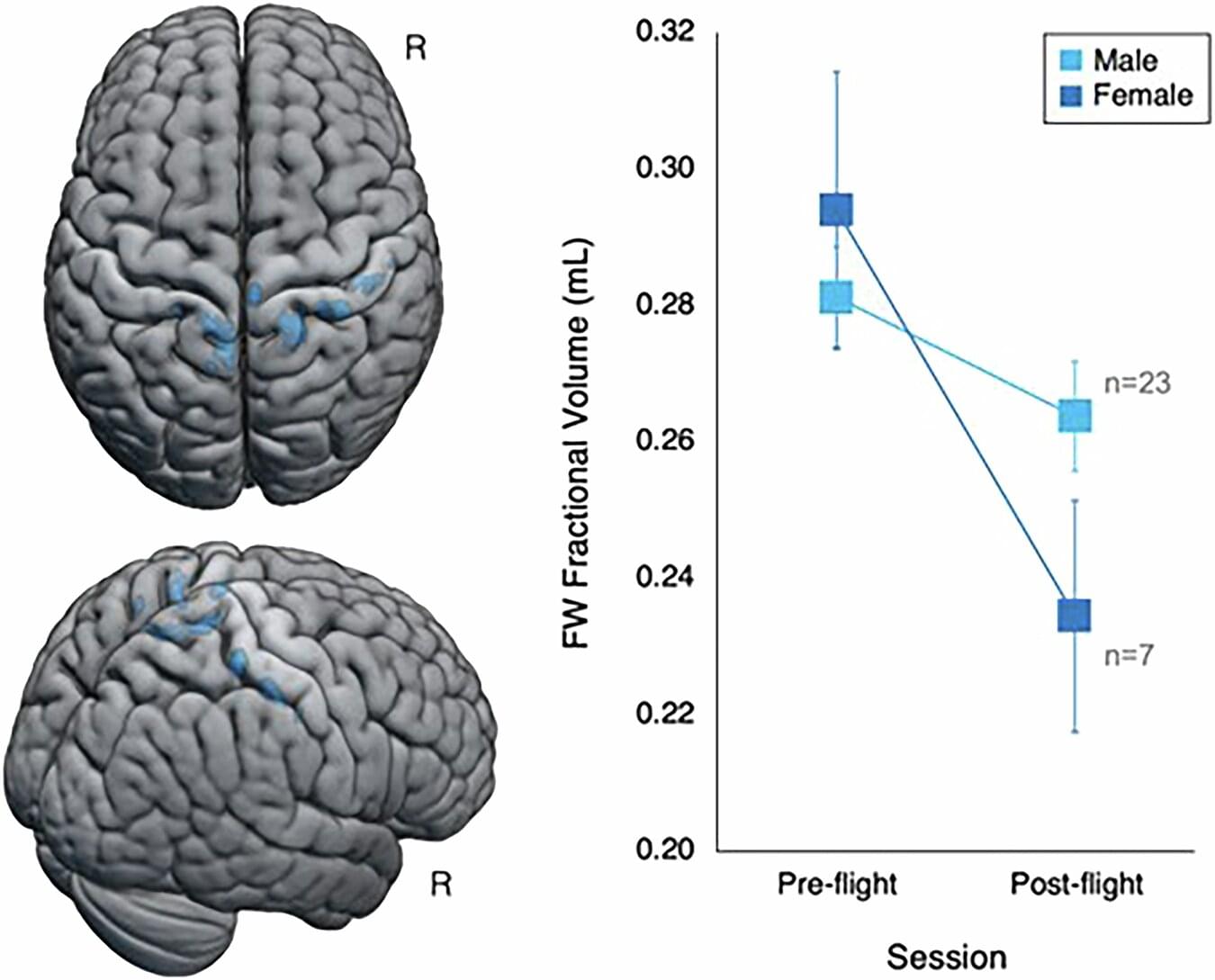
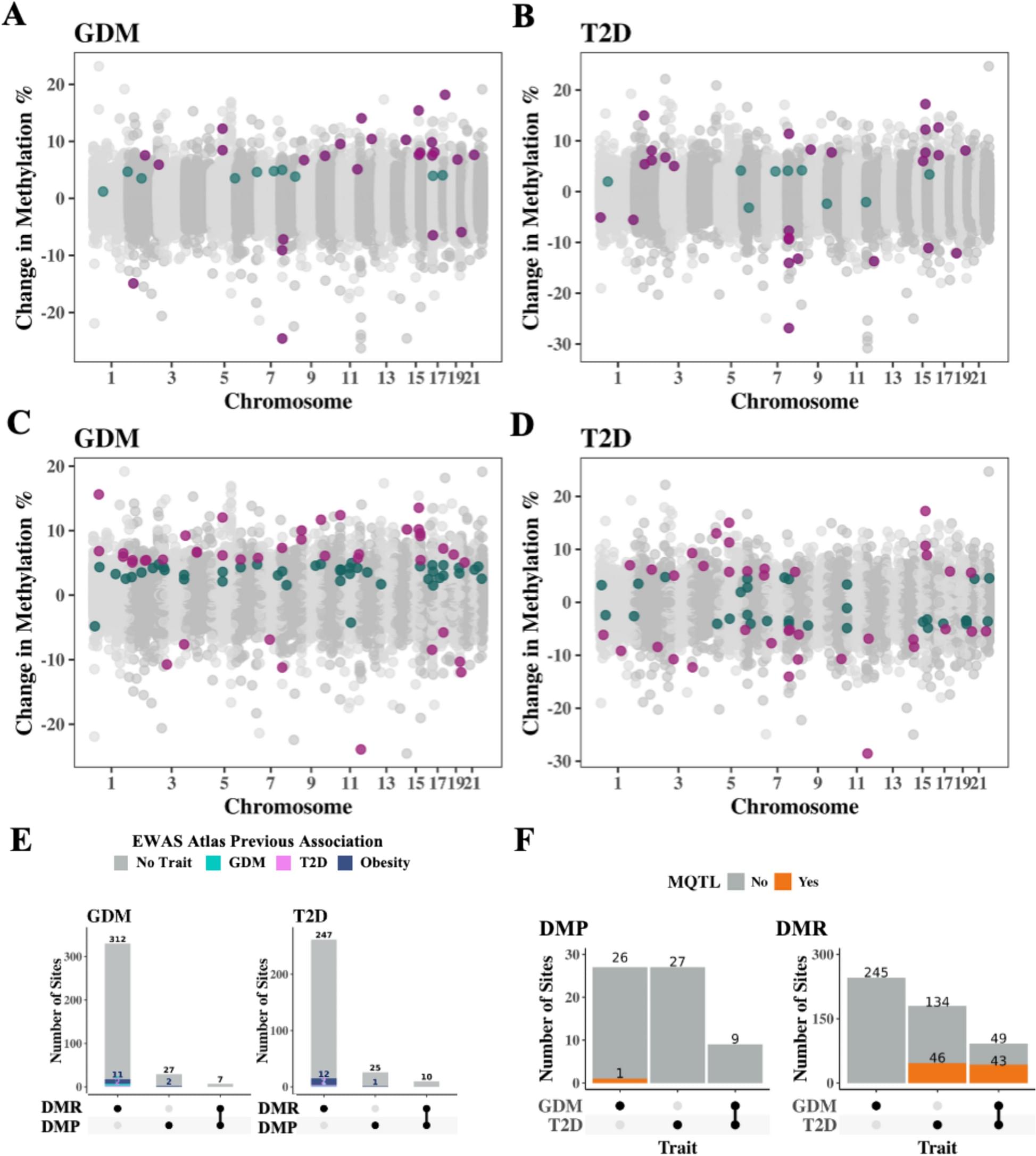
Perfusion measures of the total vasculature are commonly derived with gradient-echo (GE) dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR images, which are acquired during the early passes of a contrast agent. Alternatively, spin-echo (SE) DSC can be used to achieve specific sensitivity to the capillary signal. For an improved contrast-to-noise ratio, ultra-high-field MRI makes this technique more appealing to study cerebral microvascular physiology. Therefore, this study assessed the applicability of SE-DSC MRI at 7 T. Forty-one elderly adults underwent 7 T MRI using a multi-slice SE-EPI DSC sequence. The cerebral blood volume (CBV) and cerebral blood flow (CBF) were determined in the cortical grey matter (CGM) and white matter (WM) and compared to values from the literature. The relation of CBV and CBF with age and sex was investigated.