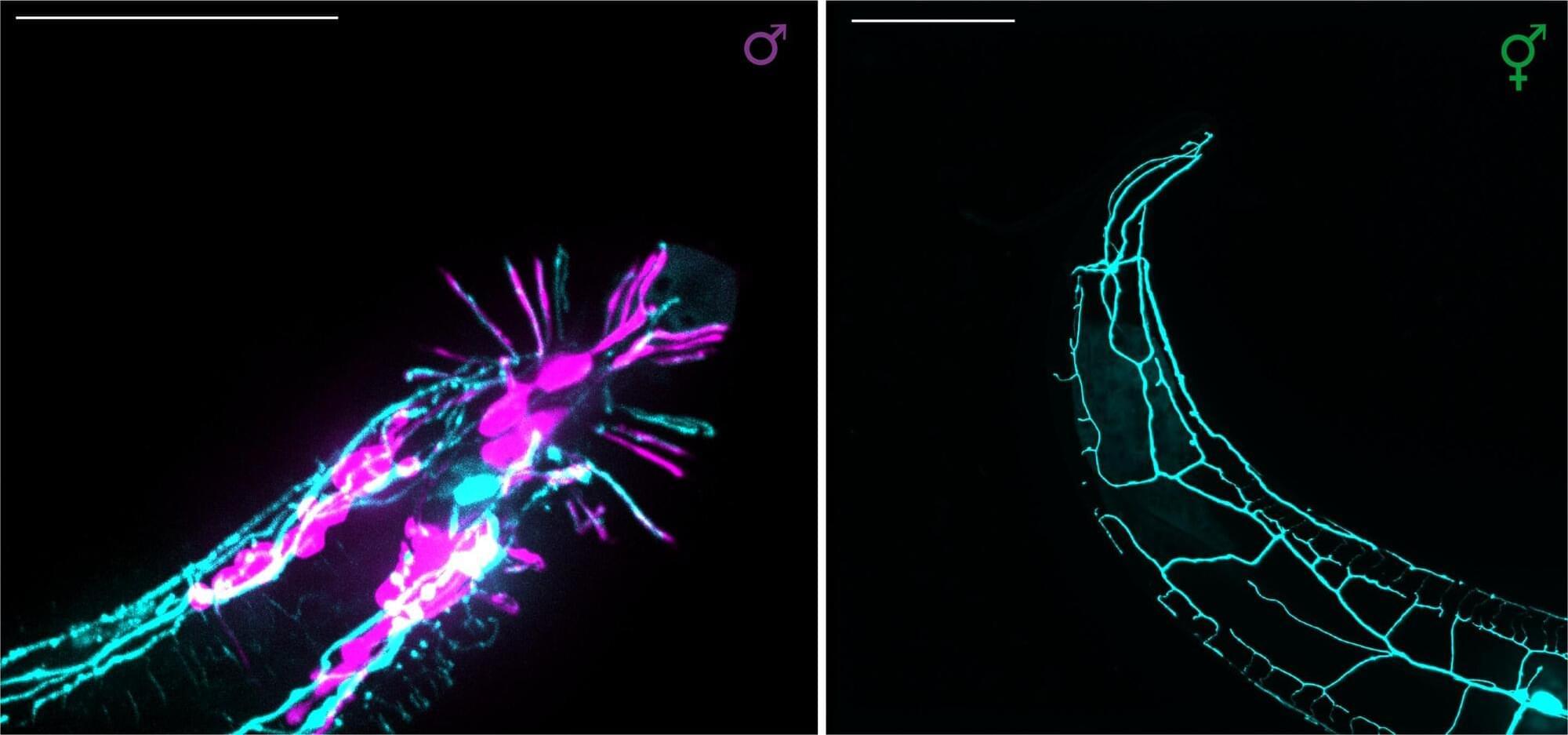
Is there a difference in brain structure between men and women? If we were to find such a difference in a single neuron, would it matter?
One of the most useful models for studying these questions is the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). This tiny worm has several characteristics that make it an excellent research model, one of which is that every cell in its body has a predetermined identity and lineage.
Like humans, C. elegans has two sexes. However, instead of male and female, the two sexes of this worm are male and hermaphrodite—a self-fertilizing individual capable of producing both male and female gametes (sperm and eggs), allowing it to reproduce without a partner.