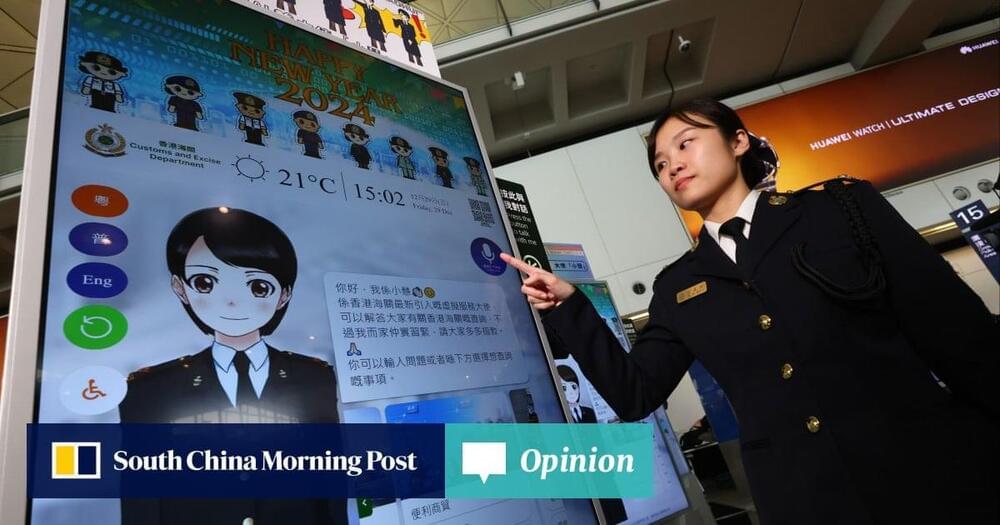
Generative AI is also expected to play a significant role in 6G mobile technology. This year, work to set and agree on 6G standards will continue with the anticipation that the first standards could be introduced between 2027 and 2028, and the technology could reach commercialisation by 2030. Generative AI can be applied to various aspects of 6G, such as network resource management, spectrum allocation and network topology optimisation.
It is also capable of meeting the demands of “connective intelligence” for new technologies. Connective intelligence is a key force driving the development of the 6G network, enabling real-time, reliable and ubiquitous interaction and communication between humans, the physical world and the digital world. This results in the creation of a decentralised and continually evolving intelligence, making it easier for users to share their discoveries and experiences with each other.
In summary, by the end of 2024, generative AI will become an invaluable assistant, providing support and help across different industries. Its powerful analysis and predictive capabilities will enable people to handle complex tasks and problems more efficiently, offering real-time solutions and recommendations.