Weather and climate experts are divided on whether AI or more traditional methods are most effective. In this new model, Google’s researchers bet on both.




It seems that Silicon Valley giants, AAA game developers, and other companies desperately clinging to the AI trend and trying to integrate the technology into any product they own will soon have to rethink their marketing strategies, as a new study conducted by researchers from Washington State University indicates that using terms like “AI” or “artificial intelligence” in product descriptions can negatively impact sales.
To explore the impact of including “AI” in goods and service descriptions on consumers’ purchase intentions, the team conducted six experiments and surveyed over a thousand people, discovering that the use of these terms decreases purchase intention and lowers emotional trust, leading to what any company fears the most – diminishing sales numbers.
Furthermore, the researchers found that putting artificial intelligence in the spotlight can be even more detrimental when it comes to high-risk products – those consumers typically think twice about buying, such as expensive gadgets and medical services – compared to low-risk items, primarily because of the greater likelihood of incurring monetary losses or facing health risks.

In Light: Science & Applications journal UCLA researchers introduce an innovative design for diffractive deep neural networks (D2NNs). This new architecture, termed Pyramid-D2NN (P-D2NN), achieves unidirectional image magnification and demagnification, significantly reducing the number of diffractive features required.

Everyone thinks they know but no one can agree. And that’s a problem.
Focus on good things: creative activities:
Neura’s 4NE-1 is a humanoid robot capable of carrying out multiple daily and industrial chores, according to the company.

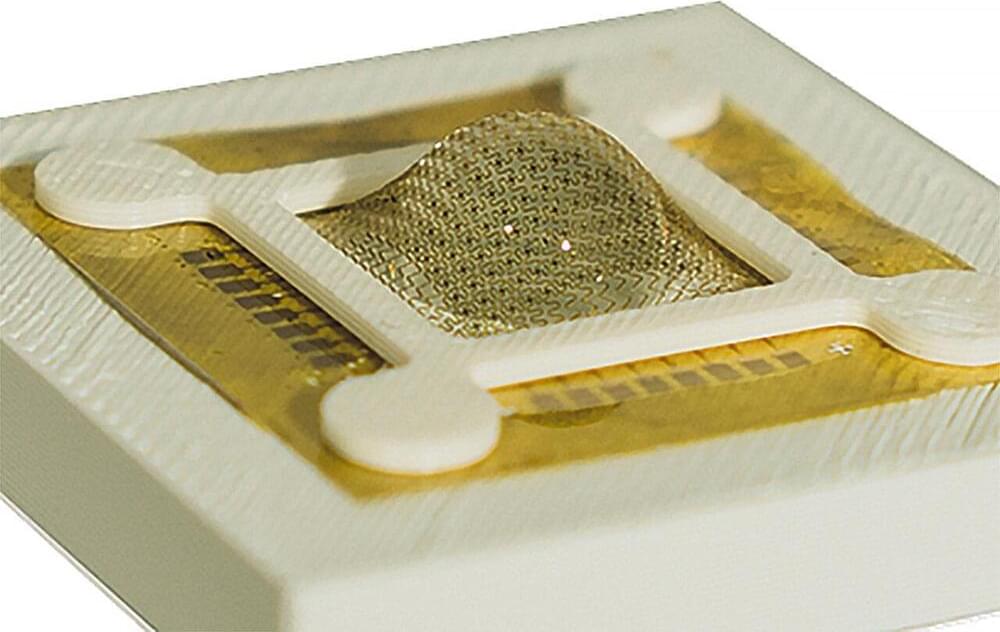
Self-driving cars occasionally crash because their visual systems can’t always process static or slow-moving objects in 3D space. In that regard, they’re like the monocular vision of many insects, whose compound eyes provide great motion-tracking and a wide field of view but poor depth perception.
Except for the praying mantis.
A praying mantis’s field of view also overlaps between its left and right eyes, creating binocular vision with depth perception in 3D space.