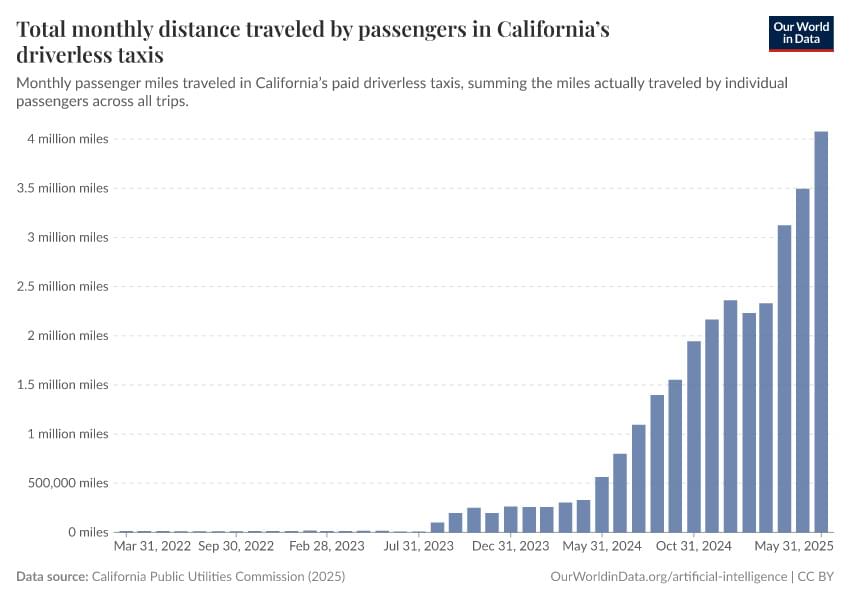
Monthly passenger miles traveled in California’s paid driverless taxis, summing the miles actually traveled by individual passengers across all trips.


Gemini 2.5 Deep Think achieves breakthrough performance at the world’s most prestigious computer programming competition, demonstrating a profound leap in abstract problem solving.
An advanced version of Gemini 2.5 Deep Think has achieved gold-medal level performance at the 2025 International Collegiate Programming Contest (ICPC) World Finals.
This milestone builds directly on Gemini 2.5 Deep Think’s gold-medal win at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) just two months ago. Innovations from these efforts will continue to be integrated into future versions of Gemini Deep Think, expanding the frontier of advanced AI capabilities accessible to students and researchers.
AlterEgo is a non-invasive, wearable, peripheral neural interface that allows humans to converse in natural language with machines, artificial intelligence assistants, services, and other people without any voice—without opening their mouth, and without externally observable movements—simply by articulating words internally. The feedback to the user is given through audio, via bone conduction, without disrupting the user’s usual auditory perception, and making the interface closed-loop. This enables a human-computer interaction that is subjectively experienced as completely internal to the human user—like speaking to one’s self.
A primary focus of this project is to help support communication for people with speech disorders including conditions like ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) and MS (multiple sclerosis). Beyond that, the system has the potential to seamlessly integrate humans and computers—such that computing, the Internet, and AI would weave into our daily life as a “second self” and augment our cognition and abilities.
The wearable system captures peripheral neural signals when internal speech articulators are volitionally and neurologically activated, during a user’s internal articulation of words. This enables a user to transmit and receive streams of information to and from a computing device or any other person without any observable action, in discretion, without unplugging the user from her environment, without invading the user’s privacy.
The pursuit of artificial intelligence increasingly focuses on replicating the efficiency and adaptability of the human brain, and a new approach, termed neuromorphic intelligence, offers a promising path forward. Marcel van Gerven from Radboud University and colleagues demonstrate how brain-inspired systems can achieve significantly greater energy efficiency than conventional digital computers. This research establishes a unifying theoretical framework, rooted in dynamical systems theory, to integrate insights from diverse fields including neuroscience, physics, and artificial intelligence. By harnessing noise as a learning resource and employing differential genetic programming, the team advances the development of truly adaptive and sustainable artificial intelligence, paving the way for emergent intelligence arising directly from physical substrates.
Researchers demonstrate that applying dynamical systems theory, a mathematical framework describing change over time, to artificial intelligence enables the creation of more sustainable and adaptable systems by harnessing noise as a learning tool and allowing intelligence to emerge from the physical properties of the system itself.
Tesla’s new energy products, such as the Mega Pack and Megablock, have the potential to revolutionize energy storage and generation, drive decentralization and grid resilience, and support widespread AI adoption, potentially driving its energy business to $50 billion in revenue and generating $10 billion in annual gross margin ## Questions to inspire discussion.
Energy Storage and Grid Management.
🔋 Q: How does Tesla’s Mega Pack improve energy storage? A: Tesla’s Mega Pack offers 20% more energy density and 25% more energy per unit, providing 8 hours of storage to expand the total addressable market for renewable energy.
⚡ Q: What is the Mega Block and how does it enhance efficiency? A: The Mega Block is a transformer and switchgear all-in-one unit that simplifies processes, reduces cabling and on-site assembly, making the product more streamlined and efficient.
🔌 Q: How do battery storage systems compare to traditional grid power? A: Battery storage is significantly more capable at dumping power instantly compared to the grid, which needs to spool up and down, making it better for managing wild swings in data center load profiles.
Data centers and AI energy demands.

As AI becomes more integrated into our lives, building it with privacy at its core is a critical frontier for the field. Differential privacy (DP) offers a mathematically sound solution by adding calibrated noise to prevent memorization. However, applying DP to LLMs introduces trade-offs. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial. Applying DP noise alters traditional scaling laws — rules describing performance dynamics — by reducing training stability (the model’s ability to learn consistently without experiencing catastrophic events like loss spikes or divergence) and significantly increasing batch size (a collection of training examples sent to the model simultaneously for processing) and computation costs.
Our new research, “Scaling Laws for Differentially Private Language Models”, conducted in partnership with Google DeepMind, establishes laws that accurately model these intricacies, providing a complete picture of the compute-privacy-utility trade-offs. Guided by this research, we’re excited to introduce VaultGemma, the largest (1B-parameters), open model trained from scratch with differential privacy. We are releasing the weights on Hugging Face and Kaggle, alongside a technical report, to advance the development of the next generation of private AI.
A number of chip companies — importantly Intel and IBM, but also the Arm collective and AMD — have come out recently with new CPU designs that feature native Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its related machine learning (ML). The need for math engines specifically designed to support machine learning algorithms, particularly for inference workloads but also for certain kinds of training, has been covered extensively here at The Next Platform.
Just to rattle off a few of them, consider the impending “Cirrus” Power10 processor from IBM, which is due in a matter of days from Big Blue in its high-end NUMA machines and which has a new matrix math engine aimed at accelerating machine learning. Or IBM’s “Telum” z16 mainframe processor coming next year, which was unveiled at the recent Hot Chips conference and which has a dedicated mixed precision matrix math core for the CPU cores to share. Intel is adding its Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) to its future “Sapphire Rapids” Xeon SP processors, which should have been here by now but which have been pushed out to early next year. Arm Holdings has created future Arm core designs, the “Zeus” V1 core and the “Perseus” N2 core, that will have substantially wider vector engines that support the mixed precision math commonly used for machine learning inference, too. Ditto for the vector engines in the “Milan” Epyc 7,003 processors from AMD.
All of these chips are designed to keep inference on the CPUs, where in a lot of cases it belongs because of data security, data compliance, and application latency reasons.


