MultiCell is a deep learning method to capture complex cell dynamics during multicellular development.


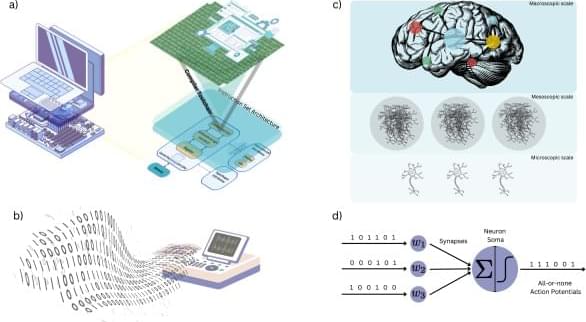
At first glance, the idea sounds implausible: a computer made not of silicon, but of living brain cells. It’s the kind of concept that seems better suited to science fiction than to a laboratory bench. And yet, in a few research labs around the world, scientists are already experimenting with computers that incorporate living human neurons. Such computers are now being trained to perform complex tasks such as play games and even drive robots.
These systems are built from brain organoids: tiny, lab-grown clusters of human neurons derived from stem cells. Though often nicknamed “mini-brains,” they are not thinking minds or conscious entities. Instead, they are simplified neural networks that can be interfaced with electronics, allowing researchers to study how living neurons process information when placed in a computational loop.
In fact, some researchers even claim that these tools are pushing the frontiers of medicine, along with those of computing. Dr. Ramon Velaquez, a neuroscientist from Arizona State University, is one such researcher.
At the same time, estimates from the US indicate that power consumption from IT applications has doubled over the past eight years, with the rise of AI. Researchers from California’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory suggest that more than half of the electricity used by data centers will be used solely for AI by 2028.
This puts the rapid advance of the digital revolution at risk as energy demand can no longer be met. Traditional silicon chips, which draw power even when idle, are becoming a critical limitation. As a result, researchers worldwide are exploring alternative microelectronic technologies that are far more energy-efficient.
To address the challenge, the team will begin developing superconducting circuits on January 1. These circuits, which were first envisioned by Hungarian-American mathematician and physicist John von Neumann in the 1950s, exploit quantum effects to transmit data using extremely short voltage pulses.
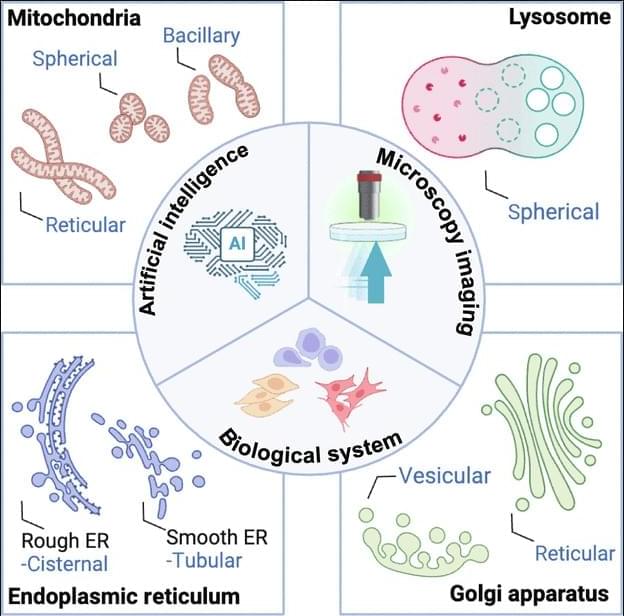
JUST PUBLISHED: artificial intelligence for organelle segmentation in live-cell imaging
Click here to read the latest free, Open Access article from Research, a Science Partner Journal.
Investigations into organelles illuminate the intricate interplay of cellular systems, uncovering how specialized structures orchestrate homeostasis, regulate metabolic pathways, and modulate signal transduction. The structural and functional integrity of organelles, including mitochondria, ER, GA, and lysosomes, is critical for cellular health. Deviations in organelle shape and behavior are frequently associated with disease development [51]. Consequently, precise characterization of organelles is crucial for advancing our understanding of cell biology and mechanisms.
Organelle image segmentation is important for extracting precise spatial and structural information, forming the foundation for subsequent quantitative analyses. Unlike whole-cell or nuclear, organelle segmentation is inherently more challenging due to the smaller size, irregular shapes, and intricate distributions of these structures. Additionally, many organelles exhibit dynamic behaviors such as fusion, fission, and trafficking, requiring accurate segmentation across both temporal and spatial dimensions. Advances in segmentation technologies have notably improved the ability to identify and characterize organelles with high-precision accuracy, opening new avenues for understanding cellular functions in health and disease.
How AI Slop is Quietly Breaking YouTubeJoin this channel to get access to perks:https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCzIJ3uWt-5H_dhYPKL1k9Ow/joinDisclaimer: This…

Generative AI and robotics are moving us ever closer to the day when we can ask for an object and have it created within a few minutes. In fact, MIT researchers have developed a speech-to-reality system, an AI-driven workflow that allows them to provide input to a robotic arm and “speak objects into existence,” creating things like furniture in as little as five minutes.
With the speech-to-reality system, a robotic arm mounted on a table is able to receive spoken input from a human, such as “I want a simple stool,” and then construct the objects out of modular components. To date, the researchers have used the system to create stools, shelves, chairs, a small table, and even decorative items such as a dog statue.
“We’re connecting natural language processing, 3D generative AI, and robotic assembly,” says Alexander Htet Kyaw, an MIT graduate student and Morningside Academy for Design (MAD) fellow. “These are rapidly advancing areas of research that haven’t been brought together before in a way that you can actually make physical objects just from a simple speech prompt.”

As the geopolitical climate shifts, we increasingly hear warmongering pronouncements that tend to resurrect popular sentiments we naïvely believed had been buried by history. Among these is the claim that Europe is weak and cowardly, unwilling to cross the threshold between adolescence and adulthood. Maturity, according to this narrative, demands rearmament and a head-on confrontation with the challenges of the present historical moment. Yet beneath this rhetoric lies a far more troubling transformation.
We are witnessing a blatant attempt to replace the prevailing moral framework—until recently ecumenically oriented toward a passive and often regressive environmentalism—with a value system founded on belligerence. This new morality defines itself against “enemies” of presumed interests, whether national, ethnic, or ideological.
Those who expected a different kind of shift—one that would abandon regressive policies in favor of an active, forward-looking environmentalism—have been rudely awakened. The self-proclaimed revolutionaries sing an old and worn-out song: war. These new “futurists” embrace a technocratic faith that goes far beyond a legitimate trust in science and technology—long maligned during the previous ideological era—and descends into open contempt for human beings themselves, now portrayed as redundant or even burdensome in the age of the supposedly unstoppable rise of artificial intelligence.

Experiments reveal that inflation not only smooths the universe but populates it with a specific distribution of initial perturbations, creating a foundation for structure formation. The team measured how quantum fluctuations during inflation are stretched and amplified, transitioning from quantum to classical behavior through a process of decoherence and coarse-graining. This process yields an emergent classical stochastic process, captured by Langevin or Fokker-Planck equations, demonstrating how classical stochastic dynamics can emerge from underlying quantum dynamics. The research highlights that the “initial conditions” for galaxy formation are not arbitrary, but constrained by the Gaussian field generated during inflation, possessing specific correlations. This framework provides a cross-scale narrative, linking microphysics and cosmology to life, brains, culture, and ultimately, artificial intelligence, demonstrating a continuous evolution of dynamics across the universe.
Universe’s Evolution, From Cosmos to Cognition
This research presents a unified, cross-scale narrative of the universe’s evolution, framing cosmology, astrophysics, biology, and artificial intelligence as successive regimes of dynamical systems. Rather than viewing these fields as separate, the work demonstrates how each builds upon the previous, connected by phase transitions, symmetry-breaking events, and attractors, ultimately tracing a continuous chain from the Big Bang to contemporary learning systems. The team illustrates how gravitational instability shapes the cosmic web, leading to star and planet formation, and how geochemical cycles establish stable, long-lived attractors, providing the foundation for life’s emergence as self-maintaining reaction networks. The study emphasizes that the universe is not simply evolving in state, but also in its capacity for description and learning, with each transition.
The rapid advances in the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have galvanised public and scientific debates over whether artificial systems might one day be conscious. Prevailing optimism is often grounded in computational functionalism: the assumption that consciousness is determined solely by the right pattern of information processing, independent of the physical substrate. Opposing this, biological naturalism insists that conscious experience is fundamentally dependent on the concrete physical processes of living systems. Despite the centrality of these positions to the artificial consciousness debate, there is currently no coherent framework that explains how biological computation differs from digital computation, and why this difference might matter for consciousness.
SpaceX is preparing for a potential IPO by buying back shares from institutional holders and allowing existing shareholders to sell shares, while its affiliate company Tesla is making progress in autonomous driving technology with plans to launch robo-taxis in multiple cities ## Questions to inspire discussion.
SpaceX Investment Access.
🔐 Q: How can individual investors access SpaceX shares before the IPO?
A: Investors must be accredited with liquid net worth over $1M (excluding home) and can access shares through special purpose vehicles (SPVs) that charge upfront fees and 10% carry on returns.
💰 Q: What is the minimum investment required to buy SpaceX shares directly?
A: Direct SpaceX share purchases require $50M-$1B investments due to SEC’s 2,000 shareholder cap for private companies, making SPVs the only option for smaller investors.