Autonomous battleships, autonomous defense technology, autonomous navy fleet, autonomous naval warships, autonomous patrol vessels, autonomous ship AI, autonomous warships 2025, battlefield AI systems, combat drone ships, cutting-edge naval AI, deep sea AI fleet, defense automation, drone fleet navy, drone operated ships, drone warships, future autonomous fleets, future navy AI, futuristic battle navy, ghost fleet AI, ghost fleet autonomous, ghost fleet drones, ghost naval ships, ghost warship fleet, high-tech naval fleet, military AI fleets, military autonomous ships, military drone ships, navy 2040 AI, navy AI automation, navy AI drone fleet, navy AI fleets, navy automation future, navy ghost drones, navy ghost ships, navy robotics systems, next-gen navy tech, robotic battle ships, robotic drone vessels, robotic navy future, robotic sea fleet, robotic sea patrol, robotic war navy, robotic warships AI, self-piloted navy, self-steering warships, stealth autonomous navy, stealth ghost fleet, stealth navy automation, tech navy evolution, unmanned AI navy, unmanned battle drones, unmanned combat vessels, unmanned ghost navy, unmanned military fleet, unmanned naval drones, unmanned navy boats, unmanned navy future, unmanned sea patrols, warship AI tech, warship drone AI, warship ghost fleet, warship robotics, warship self-navigation, autonomous ghost navy, AI powered navy, AI ship combat, AI ship navies, AI war vessels, AI warship combat, AI weaponized fleet, AI-controlled navy, AI-driven battle sea, AI-driven ghost fleet, AI-enabled navy future, autonomous ocean defense, autonomous war sea fleet, drone-based warships, drone-controlled navy, drone-led ghost fleet, drone-swarm navy, future military vessels, future sea combat, ghost navy technology, naval AI drones, navy AI future warfare, navy drone AI tech, navy drone patrol, navy ghost AI systems, robotic ship combat, sea battle AI systems, self-navigating warships, stealth AI navy tech, unmanned robotic ships, war automation navy, war ghost drones, war naval AI, war robot ships, weaponized drone navy, navy drone revolution, AI ocean patrols, underwater drone warfare, military ghost fleets, stealth unmanned warships, intelligent navy drones, navy robotics AI, robotic submarines AI, AI sea defense, future of naval AI, drone navy intelligence, unmanned stealth destroyers, AI-powered naval tech, smart navy ships, robotic destroyer fleet, next-gen ocean defense, deep sea robotics, drone guided torpedoes, sea AI weapons, unmanned marine fleet, combat sea robots, autonomous navy destroyers, unmanned military ocean tech, AI navy weapon systems, tech-driven warships, artificial intelligence warships, unmanned surface vessels, navy robotic patrol boats, AI-enabled destroyers, autonomous military defense, future ghost ships, navy drone control system, AI-controlled destroyers, unmanned combat surface fleet, ocean war robots, marine AI surveillance, robotic ocean patrols, future war drones, ghost ship navy, intelligent sea vessels, navy drone carriers, stealth autonomous ships, drone-enabled defense, underwater robotic navy, futuristic ocean fleet, drone-operated destroyers, AI-enabled sea robots, military robotics sea, next-gen destroyer drones, future stealth navy, navy robotics revolution, AI warfare at sea, unmanned maritime systems, AI naval monitoring, AI-controlled navy drones, autonomous destroyer squad, future naval swarms, robotic surface fleet, navy stealth AI, sea-based warbots, AI-controlled naval fleet, maritime ghost drones, automated navy systems, autonomous ship squadrons, ocean warfare automation, ghost destroyer drones, next-gen military fleets, automated sea defense, intelligent ship fleets, AI stealth destroyers, tech navy transformation, navy bots warfare, unmanned combat bots, autonomous naval innovations, AI warship patrols, automated ship navies, drone navy upgrades, future of robotic fleets, stealth robotics navy, AI ship fleets 2030, autonomous ocean warriors, naval robotics AI 2025, autonomous deep-sea ships, drone war technology, unmanned weaponized ships, futuristic ship fleets, next-gen ghost warships, ocean-based military AI, naval swarming drones, robotic future navy, navy drone revolution, AI ocean patrols, underwater drone warfare, military ghost fleets, stealth unmanned warships, intelligent navy drones, navy robotics AI, robotic submarines AI, AI sea defense, future of naval AI, drone navy intelligence, unmanned stealth destroyers, AI-powered naval tech, smart navy ships, robotic destroyer fleet, next-gen ocean defense, deep sea robotics, drone guided torpedoes, sea AI weapons, unmanned marine fleet, combat sea robots, autonomous navy destroyers, unmanned military ocean tech, AI navy weapon systems, tech-driven warships, artificial intelligence warships, unmanned surface vessels, navy robotic patrol boats, AI-enabled destroyers, autonomous military defense, future ghost ships, navy drone control system, AI-controlled destroyers.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 241
The Futurists — EPS_286: The Meaning Economy with David Shapiro
In this week’s episode we interview author, AI theorist and researcher David Shapiro is part philosopher, part theorist with a fair bit of practical wisdom thrown in. With a hit YouTube channel Shapiro travels the globe as a speaker and advisor musing on the longer-term impacts of AI, technology and human adaptability. In this deep conversation with host Brett King, we delve into the ways in which advanced AI might completely transform our way of life, including economics, politics and what it means to be human itself. This is not one you’ll want to miss.
Follow David Shapiro: @DaveShap
ABOUT SHOW
Subscribe and listen to TheFuturists.com Podcast where hosts Brett King and Robert TerceK interview the worlds foremost super-forecasters, thought leaders, technologists, entrepreneurs and futurists building the world of tomorrow. Together we will explore how our world will radically change as AI, bioscience, energy, food and agriculture, computing, the metaverse, the space industry, crypto, resource management, supply chain and climate will reshape our world over the next 100 years. Join us on The Futurists and we will see you in the future!
HOSTS
https://thefuturists.com/info/hosts-b… / brettking & http://brettking.com/
/ superplex &https://roberttercek.com/ SUBSCRIBE & LISTEN https://thefuturists.com/info/listen–… https://open.spotify.com/show/0nvdnEs… https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast… https://blubrry.com/thefuturists/ FOLLOW & ENGAGE
/ futuristpodcast
/ futuristpodcast
/ thefuturistspodcast
/ @thefuturistspodcast GET EVEN MORE https://thefuturists.com/exclusive/
/ brettking & http://brettking.com/
/ superplex & https://roberttercek.com/
SUBSCRIBE & LISTEN
https://thefuturists.com/info/listen–…
https://open.spotify.com/show/0nvdnEs…
https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast…
https://blubrry.com/thefuturists/
FOLLOW & ENGAGE
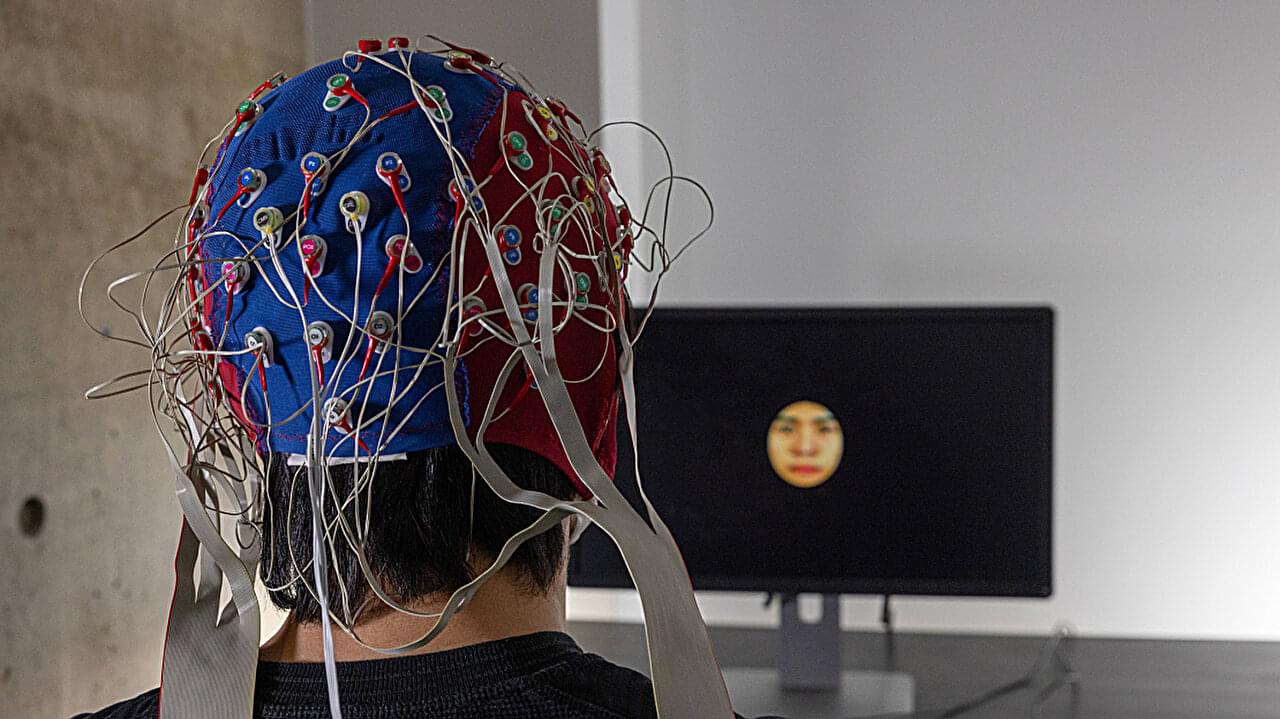

AI and brain activity reveal how we perceive faces from other racial groups differently
University of Toronto Scarborough researchers have harnessed artificial intelligence (AI) and brain activity to shed new light on why we struggle to accurately recognize faces of people from different races.
Across a pair of studies, researchers explored the Other-Race-Effect (ORE), a well-known phenomenon in which people recognize faces of their own race more easily than others. They combined AI and brain activity collected through EEG (electroencephalography) to reveal new insights into how we perceive other-race faces, including visual distortions more deeply ingrained in our brain than previously thought.
“What we found was striking—people are so much better at seeing the facial details of people from their own race,” says Adrian Nestor, associate professor in the Department of Psychology and co-author of the studies.
Physicists use machine learning to find out how layered gases and metals melt
In physics, a phase transition is a transformation of a substance from one form to another. They happen everywhere, from beneath the Earth’s crust to the cores of distant stars, but the classic example is water transitioning from liquid to gas by boiling.
Things get much more complex when physicists zoom in on the minuscule quantum realm or work with exotic matter. Understanding phase transitions rewards both increased knowledge of fundamental physics and future technological applications.
Now researchers have found out how thin layers of noble gases like helium and metals like aluminum melt in confined spaces by topological excitations. In the study, the layers were confined between two graphene sheets at high pressures.
As AI Becomes More Powerful, Simulation Theory Becomes Compelling: Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney
AI isn’t just changing how we work and play, but it’s also helping us rethink our underlying reality itself.
Tim Sweeney, CEO of Epic Games, the company behind the wildly popular Fortnite and Unreal Engine, recently delved into a philosophical discussion sparked by the rapid advancements in AI. His musings touch upon the age-old simulation hypothesis, questioning not just the nature of our own reality, but also the reality of our potential creators. What’s particularly intriguing is how Sweeney links the increasing sophistication of AI with the growing plausibility of such thought experiments.
“I don’t know,” Sweeney pondered on the Lex Fridman podcast, “The question of whether we are living in a simulation ourselves always boils down to: if we are living in a simulation, where are *they* living? Because at some point there has to be some base reality.”

New tool evaluates progress in reinforcement learning
Eco-driving involves making small adjustments to minimize unnecessary fuel consumption. For example, as cars approach a traffic light that has turned red, “there’s no point in me driving as fast as possible to the red light,” she says. By just coasting, “I am not burning gas or electricity in the meantime.” If one car, such as an automated vehicle, slows down at the approach to an intersection, then the conventional, non-automated cars behind it will also be forced to slow down, so the impact of such efficient driving can extend far beyond just the car that is doing it.
That’s the basic idea behind eco-driving, Wu says. But to figure out the impact of such measures, “these are challenging optimization problems” involving many different factors and parameters, “so there is a wave of interest right now in how to solve hard control problems using AI.”
The new benchmark system that Wu and her collaborators developed based on urban eco-driving, which they call “IntersectionZoo,” is intended to help address part of that need. The benchmark was described in detail in a paper presented at the 2025 International Conference on Learning Representation in Singapore.
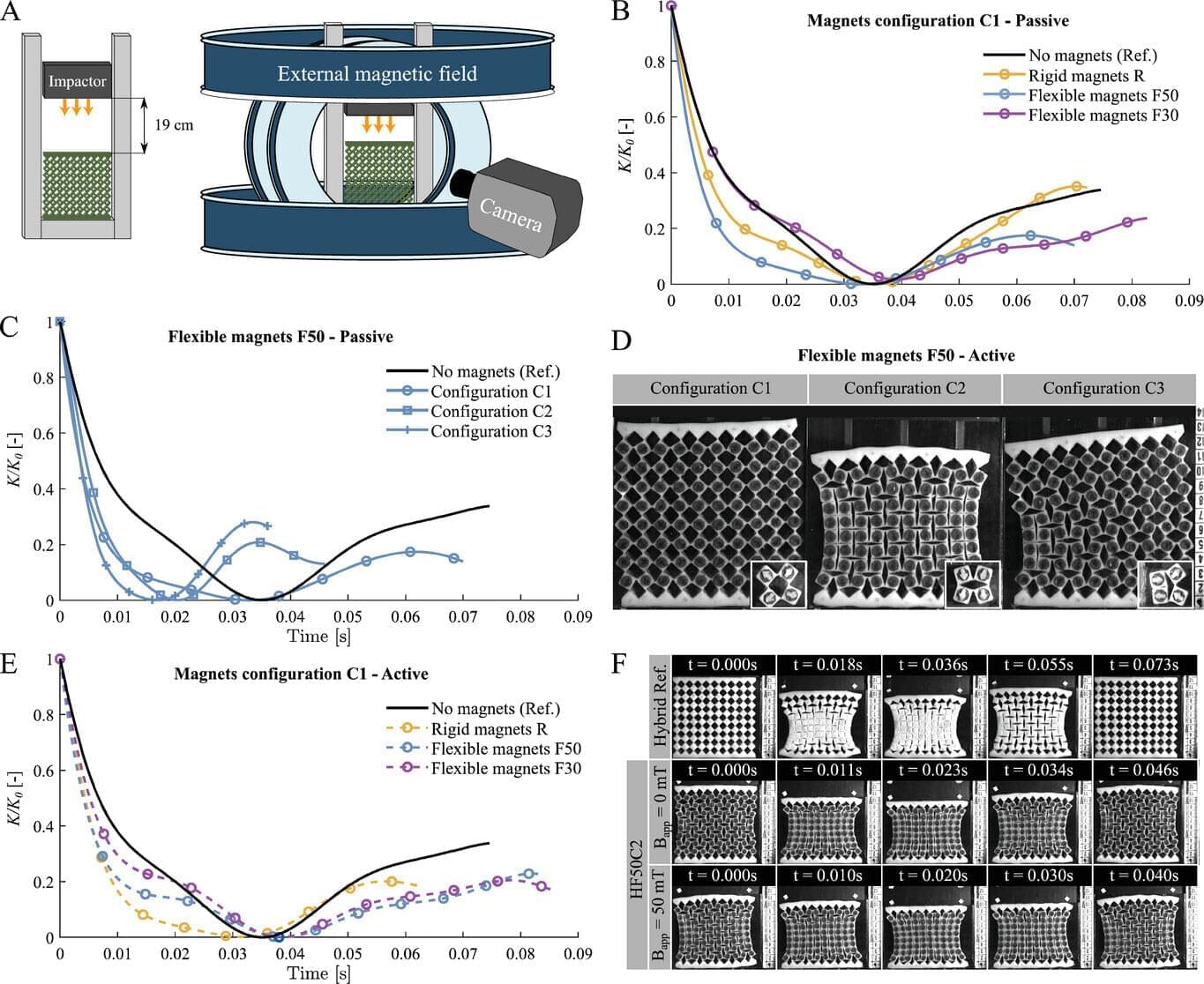
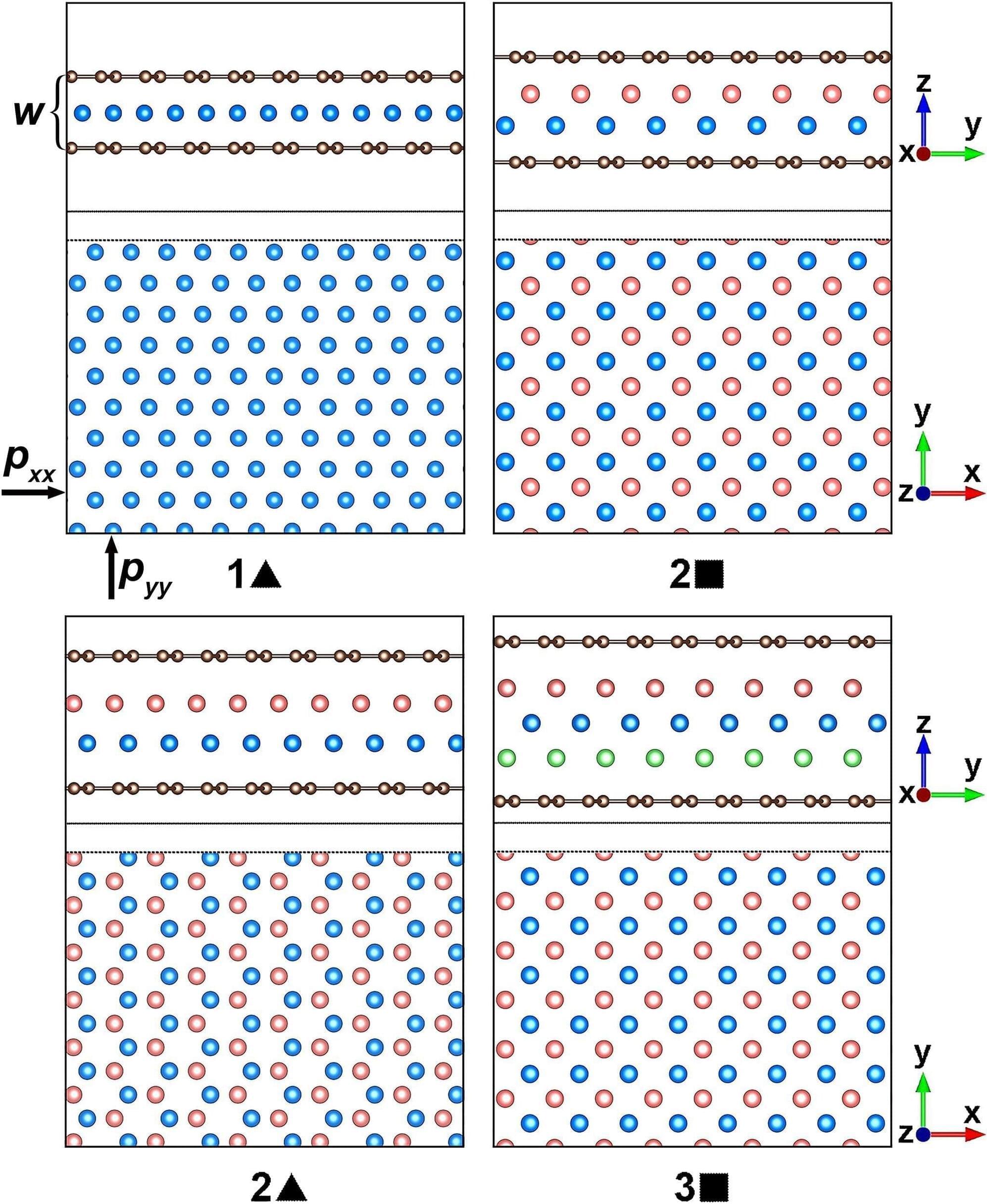
Structurally reprogrammable magnetic metamaterials hold promise for biomedicine, soft robotics
Scientists from Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) and Harvard University have experimentally demonstrated that it is possible to reprogram the mechanical and structural behavior of innovative artificial materials with magnetic properties, known as metamaterials, without the need to modify their composition. This technology opens the door to innovations in fields such as biomedicine and soft robotics, among others.
The study, recently published in the journal Advanced Materials, details how to reprogram these mechanical metamaterials by using flexible magnets distributed throughout their structure.
What is innovative about our proposal is the incorporation of small flexible magnets integrated into a rotating rhomboid matrix that allows the stiffness and energy absorption capacity of the structure to be modified by simply changing the distribution of these magnets or applying an external magnetic field. This confers unique properties that are not present in conventional materials or in nature.

Futuristic 3D heart scans on NHS speed up diagnosis and save millions
Revolutionary AI-driven 3D heart scans cut the need for invasive tests and have already saved millions of pounds, according to new analysis. Now rolled out across 56 NHS hospitals in England, the clever tech enables doctors to diagnose and treat patients with suspected heart disease much faster by turning a CT scan of their heart […]
Nvidia, ServiceNow engineer open-source model to create AI agents
Nvidia and ServiceNow have created an AI model that can help companies create learning AI agents to automate corporate workloads.
The open-source Apriel model, available generally in the second quarter on HuggingFace, will help create AI agents that can make decisions around IT, human resources and customer-service functions.
“If you look at the foundation models, they’re very big, very slow,” Dorit Zilbershot, ServiceNow’s group vice president of AI experiences and innovation, said in an interview. “This is only a 15-billion-parameters model, it’s highly trained on reasoning. We expect the reasoning to be very, very important.
FutureHouse Platform: Superintelligent AI Agents for Scientific Discovery
This AI superintelligence can help replace the need for tons of research hurdles such as time constraints finding items of knowledge to make what would take weeks or years into seconds of time.
Science is bottlenecked by data. The 38 million papers on PubMed, 500,000+ clinical trials, and thousands of specialized tools have created an information bottleneck that even the most brilliant scientists can’t navigate. At FutureHouse, our mission is to solve this problem by building an AI Scientist. Today, we are taking a significant step forward by releasing the first publicly available superintelligent scientific agents accessible to researchers everywhere, with benchmarked superhuman literature search & synthesis capabilities.
Crow is a general-purpose agent that can search the literature and provide concise, scholarly answers to questions, and is perfect for use via API.
Falcon is specialized for deep literature reviews. It can search and synthesize more scientific literature than any other agent we are aware of, and also has access to several specialized scientific databases, like OpenTargets.