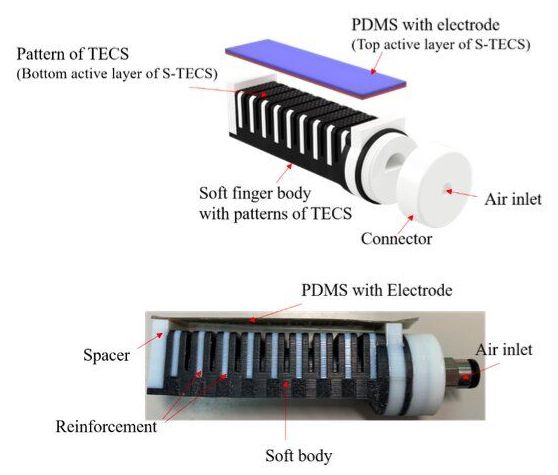
Researchers at Zhejiang University of Technology, Tianjin University, Nanjing Institute of Technology and Ritsumeikan University have recently created a soft robotic finger that integrates a self-powered curvature sensor using multi-material 3D printing technology. The new robotic finger, presented in a paper published in Elsevier’s Nano Energy journal, is made of several materials, including a stretchable electrode, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), AgilusBlack, VeroWhite and FLX9060.
“Soft robots have the potential to bridge the gap between machines and humans, but it is important for them to ensure a safe interaction between humans, objects and the environment,” Mengying Xie, co-author of the paper, told TechXplore. “Embedded soft sensors are critical for the development of controllable soft robots that can fulfill their full potential in practical applications.”
In their previous research, part of the research team working at Ritsumeikan University developed a fully multi-material 3D printed gripper with variable stiffness that could achieve robust grasping of objects. In this new study, Xie, Zhu and their colleagues drew inspiration from this previous work and set out to create a 3D-printed soft finger with sensing capabilities that could monitor its bending movements.