In her new column covering neuromorphic engineering, intelligent robotics, and AI hardware, Sunny Bains looks at attempts to increase connectivity by creating three dimensional systems.
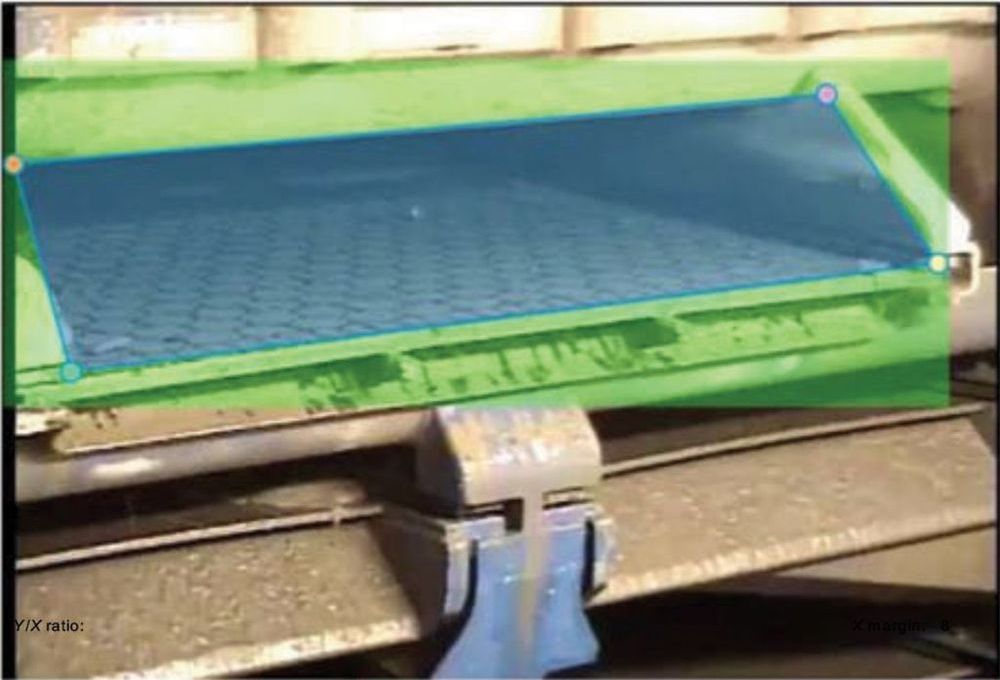


A real-time deep-learning model is proposed to classify the volume of cuttings from a shale shaker on an offshore drilling rig by analyzing the real-time monitoring video stream. As opposed to the traditional, time-consuming video-analytics method, the proposed model can implement a real-time classification and achieve remarkable accuracy. The approach is composed of three modules. Compared with results manually labeled by engineers, the model can achieve highly accurate results in real time without dropping frames.
Introduction
A complete work flow already exists to guide the maintenance and cleaning of the borehole for many oil and gas companies. A well-formulated work flow helps support well integrity and reduce drilling risks and costs. One traditional method needs human observation of cuttings at the shale shaker and a hydraulic and torque-and-drag model; the operation includes a number of cleanup cycles. This continuous manual monitoring of the cuttings volume at the shale shaker becomes the bottleneck of the traditional work flow and is unable to provide a consistent evaluation of the hole-cleaning condition because the human labor cannot be available consistently, and the torque-and-drag operation is discrete, containing a break between two cycles.
This study also analyzes the market status, market share, growth rate, future trends, market drivers, opportunities and challenges, risks and entry barriers, sales channels, distributors and Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. Neural Network Software market report all-inclusively estimates general market conditions, the growth prospects in the market, possible restrictions, significant industry trends, market size, market share, sales volume and future trends. The report starts by an introduction about the company profiling and a comprehensive review about the future events, sales strategies, Investments, business marketing strategy, future products, new geographical markets, customer actions or behaviors with the help of 100+ market data Tables, Pie Charts, Graphs & Figures spread through Pages for easy understanding. Neural Network Software market report has been designed by keeping in mind the customer requirements which assist them in increasing their return on investment (ROI and this research also provides a deep insight into the activities of key players such as Starmind, NeuralWare, Slagkryssaren AB, AND Corporation, Slashdot Media, XENON Systems Pty Ltd, Xilinx Inc and others. and others.
Get Full PDF Sample Copy of Report (Including Full TOC, List of Tables & Figures, Chart) at @ https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/request-a-sample/?d…are-market
Global neural network software market is set to witness a healthy CAGR of 35.70% in the forecast period of 2019 to 2026.
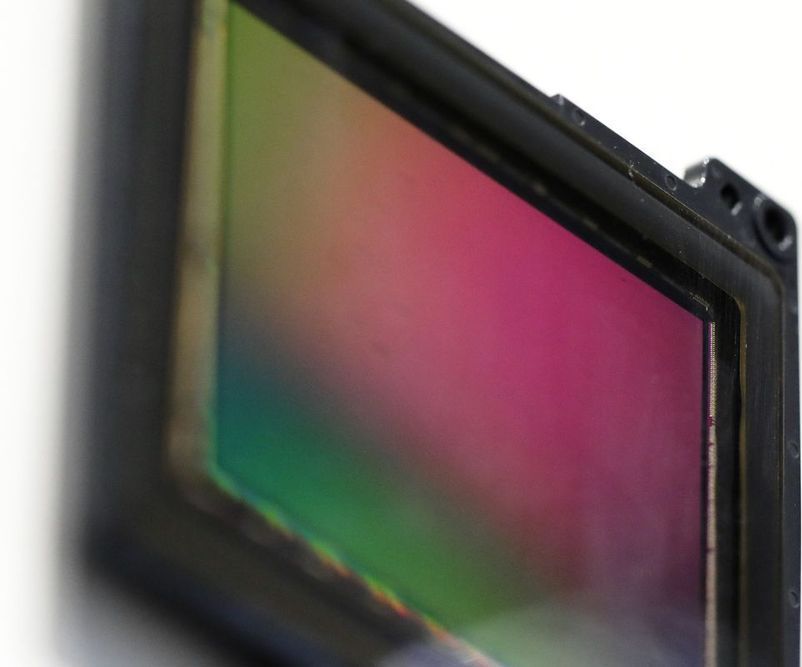


The new module’s big advantage is that it has its own processor and memory built in, which allows it to analyze video using AI tech like Microsoft’s Azure, but in a self-contained system that’s faster, simpler and more secure to operate than existing methods.
Sony Corp. and Microsoft Corp. have partnered to embed artificial intelligence capabilities into the Japanese company’s latest imaging chip, a big boost for a camera product the electronics giant describes as a world-first for commercial customers.

The contracting giant will provide the JAIC with “data labeling, data management, data conditioning, AI product development, and the transition of AI products into new and existing fielded programs,” according to the GSA news release.
“The delivered AI products will leverage the power of DoD data to enable a transformational shift across the Department that will give the U.S. a definitive information advantage to prepare for future warfare operations,” the release said.
The contract will support the JAIC’s new joint warfighting mission initiative, launched earlier this year. The initiative includes “Joint All-Domain Command and Control; autonomous ground reconnaissance and surveillance; accelerated sensor-to-shooter timelines; operations center workflows; and deliberate and dynamic targeting solutions,” said JAIC spokesperson Arlo Abrahamson told C4ISRNET in January.
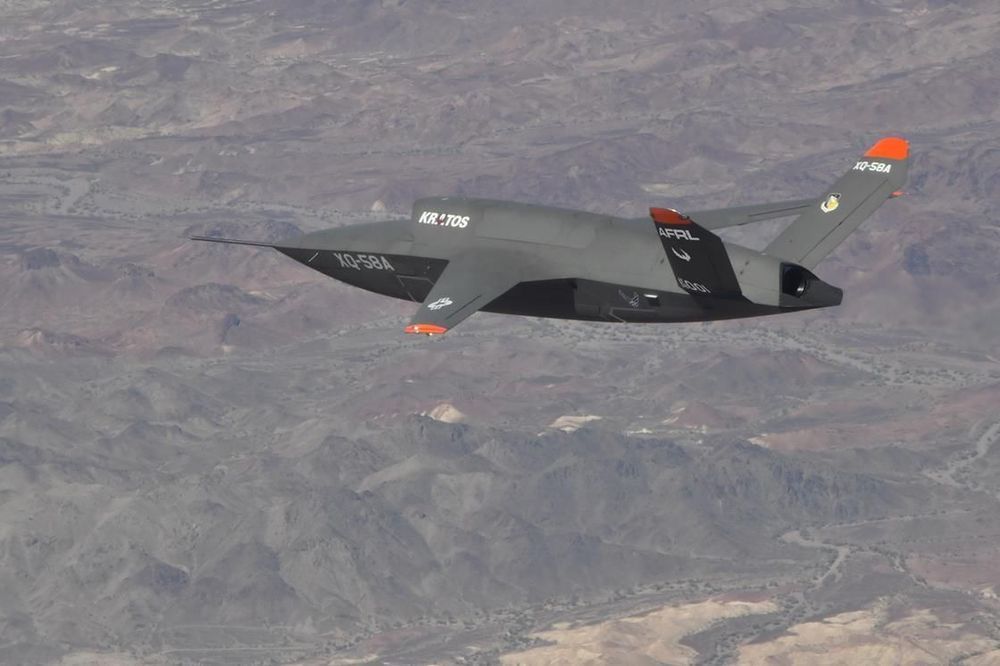

The US Air Force (USAF) has launched a competition to design the artificially intelligent software, called Skyborg, that would control its planned fleet of loyal wingman unmanned air vehicles (UAV).
The service intends to grant indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity contracts worth $400 million per awardee to develop the software and related hardware, it says in a request for proposals released on 15 May. The USAF is looking for technical and cost proposals from companies by 15 June 2020 and intends to award multiple companies contracts, though it may award just one contract or no contracts, based on proposals.
Circa 2010 what someday we could use crispr to develop a biology singularity to find the epigenetics to evolve at lightning speed.
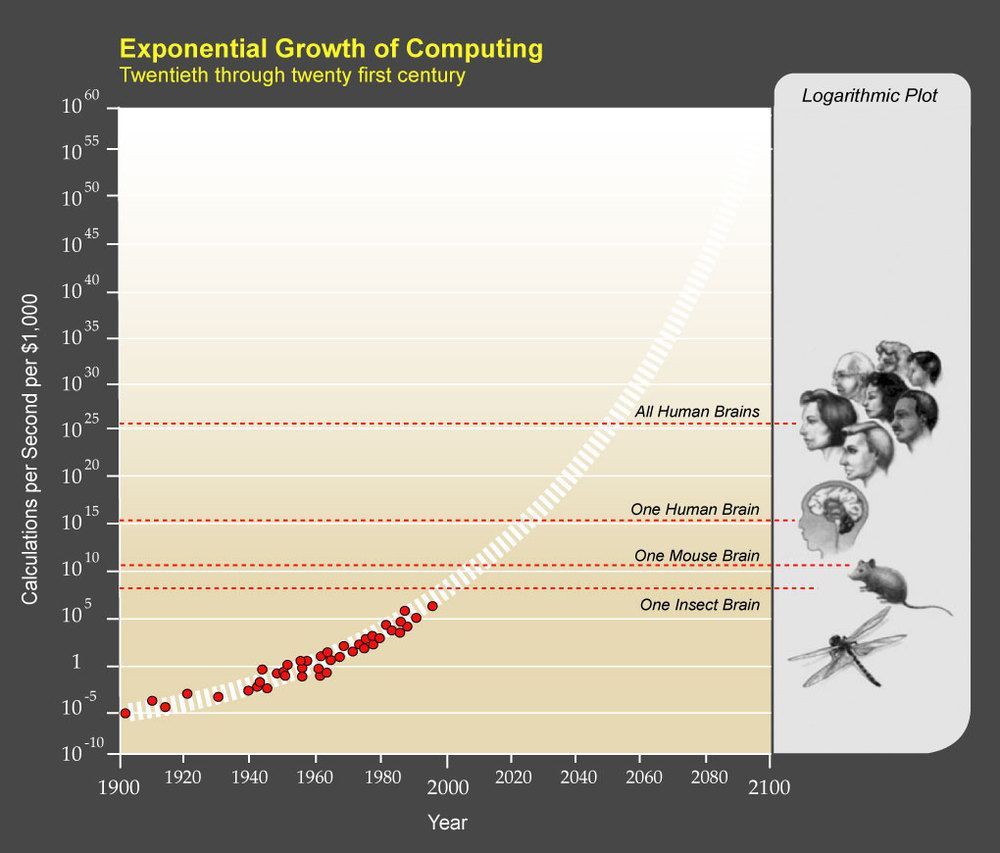
If you’re a sci-fi reader, you are probably familiar with the idea of the “technological singularity”. For the uninitiated, the Singularity is the idea that computational power is increasing so rapidly that soon there will be genuine artificial intelligence that will far surpass humans. Essentially, once you have smarter-than-human computers, they will drive their own advancement and we will no longer be able to comprehend the technology.
We can debate whether the singularity will or will not happen, and what the consequences might be, for a long time, but that’s not the point of this post. This post was inspired by the final chapter in Denialism by Michael Specter. In that chapter, Specter talks about the rapid advancement in biotechnology. Specifically, he points to the rapid increase in computational power and the resulting rapid increase in the speed of genome processing.
You might like this interview I did with futurist writer Nikola Danaylov, who runs the Singularity Weblog and wrote ‘Conversations with the Future: 21 Visions for the 21st century’, on how advances in AI could utterly transform human society and the health of the global transhumanist movement.
I’m trying to grow my futurism YouTube channel (transhumanism, AI, space colonisation etr) so if this is of interest to you I’d be very grateful for any subscribers.
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCnVLqMgLDwO-aSk5YcYo1dA…
I interview Nikola Danaylov (@singularityblog), founder of the Singularity Weblog and author of Conversations with the Future: 21 Visions for the 21st Century. We discuss advances in AI, the singularity, whether western political leaders appreciate how fast technology is evolving and the global transhumanist movement.
You can buy Danaylov’s book here: https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B01N4QF7GU/ref=as_li_qf_sp…5f50cf0e90