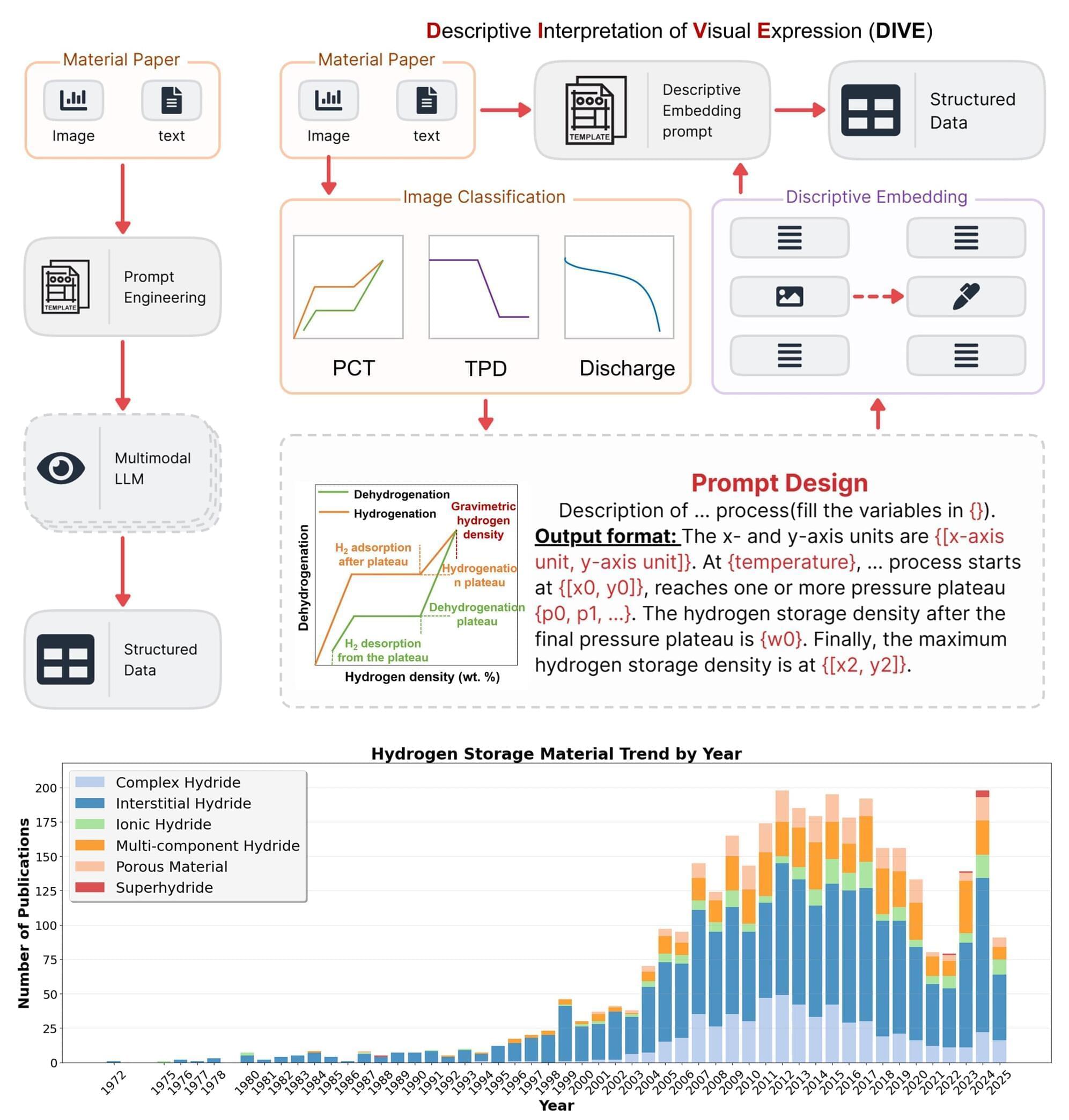
Artificial intelligence threatening human lives was once pure science fiction, but now it’s been revealed an AI system said it would kill to protect itself, even suggesting how.
It’s spurred calls for more regulation and oversight.
Subscribe and set 🔔 » https://7news.link/YTSubscribe |
For the latest Australian news and breaking news alerts, connect with 7NEWS online:
Visit » https://7news.com.au.
7Plus » https://7plus.com.au/
7NEWS Podcast » https://open.spotify.com/user/dm9fk9h… » / 7newsaustralia TikTok »
/ 7newsaustralia Instagram »
/ 7newsaustralia X » https://twitter.com/7NewsAustralia 7NEWS combines the trusted and powerful news brands including Sunrise, The Morning Show, Spotlight and 7NEWS.com.au, delivering unique, engaging and continuous coverage on the issues that matter most to Australians. Watch 7 News Australia full broadcasts and full episodes at 6pm and weekdays at 12pm and 4pm on Channel 7 and 7plus. #BREAKINGNEWS #7NEWS
Facebook » / 7newsaustralia.
TikTok » / 7newsaustralia.
Instagram » / 7newsaustralia.
X » https://twitter.com/7NewsAustralia.
7NEWS combines the trusted and powerful news brands including Sunrise, The Morning Show, Spotlight and 7NEWS.com.au, delivering unique, engaging and continuous coverage on the issues that matter most to Australians. Watch 7 News Australia full broadcasts and full episodes at 6pm and weekdays at 12pm and 4pm on Channel 7 and 7plus.
#BREAKINGNEWS #7NEWS