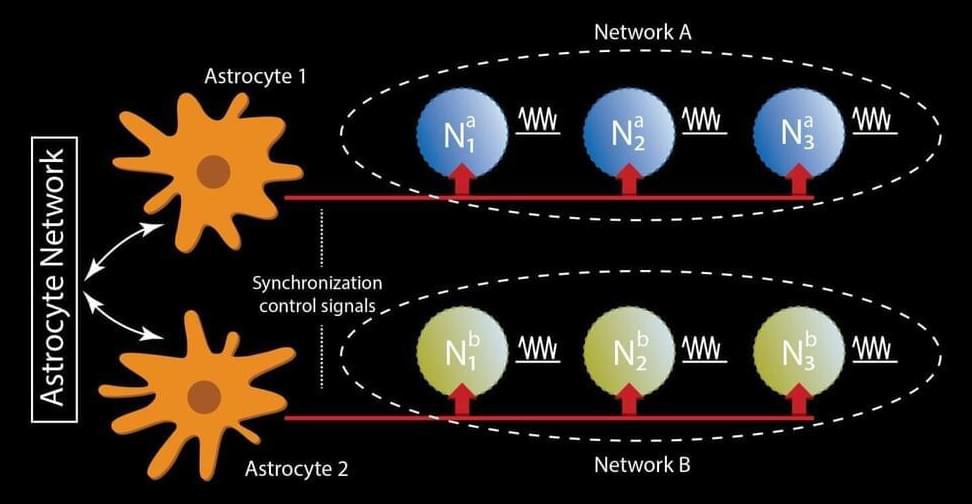
A clearer understanding of how a type of brain cell known as astrocytes function and can be emulated in the physics of hardware devices, may result in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning that autonomously self-repairs and consumes much less energy than the technologies currently do, according to a team of Penn State researchers.
Astrocytes are named for their star shape and are a type of glial cell, which are support cells for neurons in the brain. They play a crucial role in brain functions such as memory, learning, self-repair and synchronization.
“This project stemmed from recent observations in computational neuroscience, as there has been a lot of effort and understanding of how the brain works and people are trying to revise the model of simplistic neuron-synapse connections,” said Abhronil Sengupta, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science. “It turns out there is a third component in the brain, the astrocytes, which constitutes a significant section of the cells in the brain, but its role in machine learning and neuroscience has kind of been overlooked.”