Feat : hessid · zetno creato.
This is generated using Stable diffusion’s deforun model.
This is made purely for educational purpose alone.
Feat : hessid · zetno creato.
This is generated using Stable diffusion’s deforun model.
This is made purely for educational purpose alone.

Year 2020 o.o!
Explorations into the nature of reality have been undertaken across the ages, and in the contemporary world, disparate tools, from gedanken experiments [1–4], experimental consistency checks [5,6] to machine learning and artificial intelligence are being used to illuminate the fundamental layers of reality [7]. A theory of everything, a grand unified theory of physics and nature, has been elusive for the world of Physics. While unifying various forces and interactions in nature, starting from the unification of electricity and magnetism in James Clerk Maxwell’s seminal work A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism [8] to the electroweak unification by Weinberg-Salam-Glashow [9–11] and research in the direction of establishing the Standard Model including the QCD sector by Murray Gell-Mann and Richard Feynman [12,13], has seen developments in a slow but surefooted manner, we now have a few candidate theories of everything, primary among which is String Theory [14]. Unfortunately, we are still some way off from establishing various areas of the theory in an empirical manner. Chief among this is the concept of supersymmetry [15], which is an important part of String Theory. There were no evidences found for supersymmetry in the first run of the Large Hadron Collider [16]. When the Large Hadron Collider discovered the Higgs Boson in 2011-12 [17–19], there were results that were problematic for the Minimum Supersymmetric Model (MSSM), since the value of the mass of the Higgs Boson at 125 GeV is relatively large for the model and could only be attained with large radiative loop corrections from top squarks that many theoreticians considered to be ‘unnatural’ [20]. In the absence of experiments that can test certain frontiers of Physics, particularly due to energy constraints particularly at the smallest of scales, the importance of simulations and computational research cannot be underplayed. Gone are the days when Isaac Newton purportedly could sit below an apple tree and infer the concept of classical gravity from an apple that had fallen on his head. In today’s age, we have increasing levels of computational inputs and power that factor in when considering avenues of new research in Physics. For instance, M-Theory, introduced by Edward Witten in 1995 [21], is a promising approach to a unified model of Physics that includes quantum gravity. It extends the formalism of String Theory. There have been computational tools relating to machine learning that have lately been used for solving M-Theory geometries [22]. TensorFlow, a computing platform normally used for machine learning, helped in finding 194 equilibrium solutions for one particular type of M-Theory spacetime geometries [23–25].
Artificial intelligence has been one of the primary areas of interest in computational pursuits around Physics research. In 2020, Matsubara Takashi (Osaka University) and Yaguchi Takaharu (Kobe University), along with their research group, were successful in developing technology that could simulate phenomena for which we do not have the detailed formula or mechanism, using artificial intelligence [26]. The underlying step here is the creation of a model from observational data, constrained by the model being consistent and faithful to the laws of Physics. In this pursuit, the researchers utilized digital calculus as well as geometrical approach, such as those of Riemannian geometry and symplectic geometry.

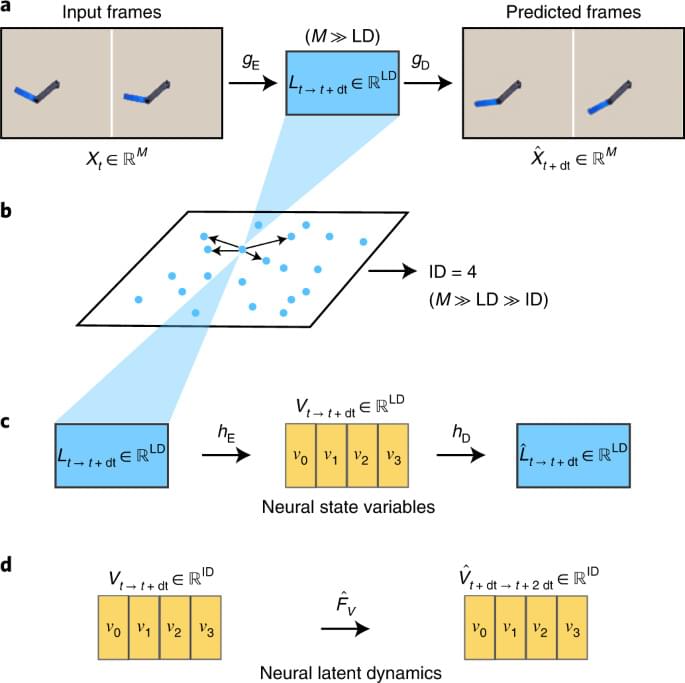
Year 2022 What they find is a new type of physics generated by their artificial intelligence.
The determination of state variables to describe physical systems is a challenging task. A data-driven approach is proposed to automatically identify state variables for unknown systems from high-dimensional observational data.


While “protein” often evokes pictures of chicken breasts, these molecules are more similar to an intricate Lego puzzle. Building a protein starts with a string of amino acids—think a myriad of Christmas lights on a string— which then fold into 3D structures (like rumpling them up for storage).
DeepMind and Baker both made waves when they each developed algorithms to predict the structure of any protein based on their amino acid sequence. It was no simple endeavor; the predictions were mapped at the atomic level.
Designing new proteins raises the complexity to another level. This year Baker’s lab took a stab at it, with one effort using good old screening techniques and another relying on deep learning hallucinations. Both algorithms are extremely powerful for demystifying natural proteins and generating new ones, but they were hard to scale up.

Since OpenAI released ChatGPT, there has been a lot of speculation about what its killer app will be. And perhaps topping the list is online search. According to The New York Times, Google’s management has declared a “code red” and is scrambling to protect its online search monopoly against the disruption that ChatGPT will bring.
ChatGPT is a wonderful technology, one that has a great chance of redefining the way we create and interact with digital information. It can have many interesting applications, including for online search.
But it might be a bit of a stretch to claim that it will dethrone Google—at least from what we have seen so far. For the moment, large language models (LLM) have many problems that need to be fixed before they can possibly challenge search engines. And even when the technology matures, Google Search might be positioned to gain the most from LLMs.

Timetable.
0:00 — AI in our society.
0:46 — Defining Algocracy.
1:00 — Current AI algorithms.
2:20 — Future of AI decision-making.
5:59 — AI governance scenarios.
7:43 — Poll on our opinions of AI
8:35 — What actually worries experts.
10:02 — What now?
Subscribe for more insight on the future of AI in our society.
Written Sources:
Civil society calls on the EU to prohibit predictive and profiling AI systems in law enforcement and criminal justice.
https://www.statewatch.org/news/2022/march/civil-society-cal…l-justice/
Toward a Theory of Justice for Artificial Intelligence, Gabriel.
https://direct.mit.edu/daed/article/151/2/218/110610/Toward-…Artificial.
EUROPEAN TECH INSIGHTS 2021 PART II, IE Center For The Governance Of Change.
https://www.ie.edu/cgc/research/european-tech-insights/?subm…wnload-cgc.
Noble, Safiya Umoja (20 February 2018). Algorithms of Oppression: How Search Engines Reinforce Racism. New York: NYU Press. ISBN 978–1479837243.