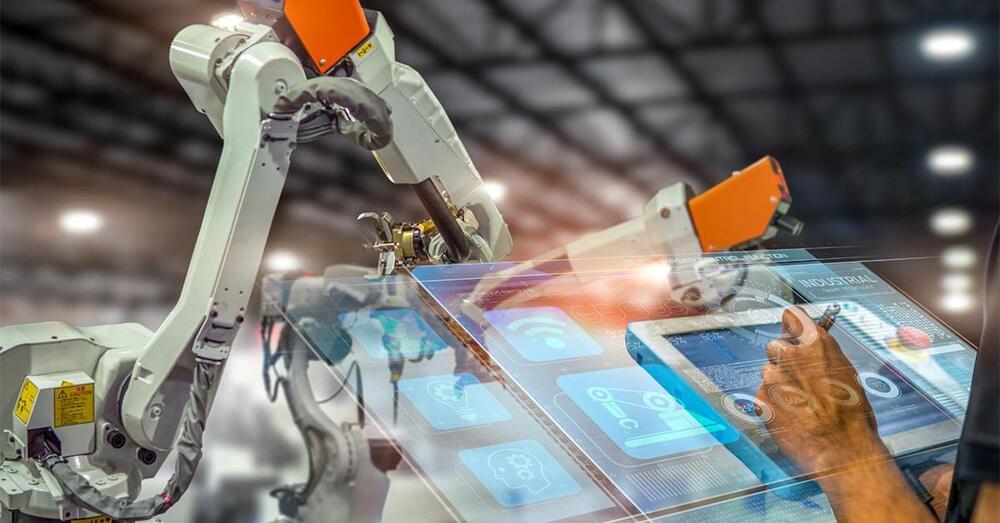
An intuitive UI/UX design is critical for optimizing the user experience. Discover the importance of consistent UI/UX design patterns, feedback, and responsiveness in industrial automation.




Possibly a move to freeze and stall the tec, like the bio ethics clowns who were able to freeze bio tec. But, China wouldnt sign on to any freeze, thankfully. And the tec has already spread across 3rd world countries.
WASHINGTON, June 6 (Reuters) — Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer said on Tuesday he has scheduled three briefings for senators on artificial intelligence, including the first classified briefing on the topic.
In a letter to colleagues on Tuesday, the Democratic leader said senators need to deepen their understanding of artificial intelligence.
“AI is already changing our world, and experts have repeatedly told us that it will have a profound impact on everything from our national security to our classrooms to our workforce, including potentially significant job displacement,” Schumer said.

There was once a stigma attached to online dating: Less than a decade ago, many couples who had met online would make up stories for how they met rather than admit that they had done so via an app.
Not so anymore. Online dating is so mainstream that you’re an outlier if you haven’t met your partner on Tinder, Grindr or Hinge.
We bring up online dating to show just how quickly conventions around romance can change. With rapid advances in AI technology over the past few years, these norms may well evolve to include sex, love and friendships with AI-equipped machines.
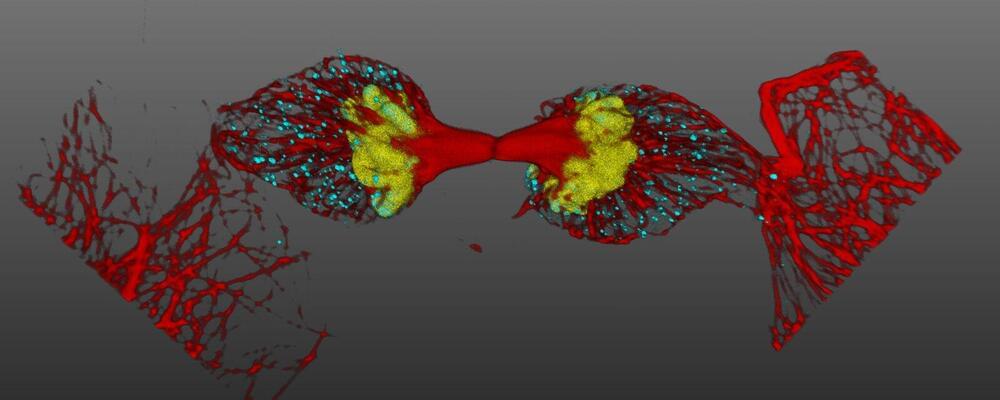
Autonomous Microscopy powered by Aivia enables scientists to discover more by extracting the most relevant data from their experiments.
06 June 2023, Wetzlar, Germany - Leica Microsystems, a leader in microscopy and scientific instrumentation, has launched Autonomous Microscopy powered by Aivia. This new AI-based detection workflow for confocal microscopy automates the detection of rare events. It follows what the user has defined as the objects of interest that will trigger the rare event scan. Users benefit from the potential to discover more by automatically detecting up to 90% of rare events during an experiment. By focusing on the data that matter during the acquisition process itself, time to result can be reduced by up to 70%. The Aivia-powered workflow reduces time spent at the microscope by up to 75%, leading to increased productivity to do more.
“Autonomous Microscopy powered by Aivia brings the power of Artificial Intelligence to everyday experimental environments in an easy-to-use way,” says James O’Brien, Vice President of Life Sciences and Applied Microscopy at Leica Microsystems. “Researchers can now establish confocal microscopy workflows that address advanced experiments and biological questions that would be impossible or very laborious without automated procedures. This solution gives them outstanding new options to obtain results that answer their research questions.”

By Marc Andreessen
The industry standard for dangerous and routine autonomous inspections, now with a brand new set of features and hardware.
#BostonDynamics

Hallucination!
Can “hallucinations” generate an alternate world, prophesying falsehood?
As I write this article, NVIDIA(• is surpassing Wall Street’s expectations. The company, headquartered in Santa Clara, California, has just joined the exclusive club of only five companies in the world valued at over a trillion dollars [Apple (2.7T), Microsoft (2.4T), Saudi Aramco (2T), Alphabet/Google (1.5T), and Amazon (1.2T)], as its shares rose nearly 25% in a single day! A clear sign of how the widespread use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) can dramatically reshape the technology sector.
Intel has announced an ambitious plan to develop scientific generative AIs designed with one trillion parameters. These models will be trained on various types of data, including general texts, code, and scientific information. In comparison, OpenAI’s GPT-3 has 175 billion parameters (the size of GPT-4 has not yet been disclosed by OpenAI). The semiconductor company’s main focus is to apply these AIs in the study of areas such as biology, medicine, climate, cosmology, chemistry, and the development of new materials. To achieve this goal, Intel plans to launch a new supercomputer called Aurora, with processing capacity exceeding two EXAFLOPS(*•, later this year.

On his appointment, he said, It is really a great honour and privilege to be part of the Board of the Data Lab Scotland’s Artificial Intelligence and data to help contribute and provide strategic direction to the leadership of the Lab.
I am deeply humbled for this opportunity to contribute and help unlock the rich opportunities for AI and data, not just in Scotland, UK and across the world, by bringing industry, academia and public sector to harness opportunities, connect people and ideas, develop knowledge and expertise for the good of humanity and society-creating a better and sustainable economy and society.
The Nigerian-British man stressed his love for data and AI, saying, I am deeply passionate and intentional about data, AI, transformation, innovation, education, technology, inclusion, social and global mobility.