The fascinating collective behaviors of biological systems have inspired extensive studies on shape assembly of robot swarms6,7,8,9. One class of strategies widely studied in the literature are based on goal assignment in either centralized or distributed ways10,11,12. Once a swarm of robots are assigned unique goal locations in a desired shape, the consequent task is simply to plan collision-free trajectories for the robots to reach their goal locations10 or conduct distributed formation control based on locally sensed information6,13,14. It is notable that centralized goal assignment is inefficient to support large-scale swarms since the computational complexity increases rapidly as the number of robots increases15,16. Moreover, when robots fail to function normally, additional algorithms for fault-tolerant detection and goal re-assignment are required to handle such situations17. As a comparison, distributed goal assignment can support large-scale swarms by decomposing the centralized assignment into multiple local ones11,12. It also exhibits better robustness to robot faults. However, since distributed goal assignments are based on locally sensed information, conflicts among local assignments are inevitable and must be resolved by sophisticated algorithms such as local task swapping11,12.
Another class of strategies for shape assembly that have also attracted extensive research attention are free of goal assignment18,19,20,21. For instance, the method proposed in ref. 18 can assemble complex shapes using thousands of homogeneous robots. An interesting feature of this method is that it does not rely on external global positioning systems. Instead, it establishes a local positioning system based on a small number of pre-localized seed robots. As a consequence of the local positioning system, the proposed edge-following control method requires that only the robots on the edge of a swarm can move while those inside must stay stationary. The method in ref. 19 can generate swarm shapes spontaneously from a reaction-diffusion network similar to embryogenesis in nature. However, this method is not able to generate user-specified shapes precisely. The method in ref. 21 can aggregate robots on the frontier of shapes based on saliency detection. The user-defined shape is specified by a digital light projector. An interesting feature of this method is that it does not require centralized edge detectors. Instead, edge detection is realized in a distributed manner by fusing the beliefs of a robot with its neighbors. However, since the robots cannot self-localize themselves relative to the desired shape, they make use of random walks to search for the edges, which would lead to random trajectories. Another class of methods that do not require goal assignment is based on artificial potential fields22,23,24,25. One limitation of this class of methods is that robots may easily get trapped in local minima, making it difficult to assemble nonconvex complex shapes.
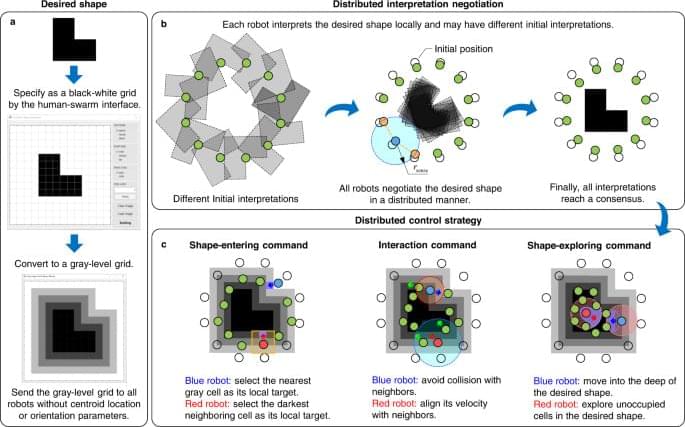
Here, we propose a strategy for shape assembly of robot swarms based on the idea of mean-shift exploration: when a robot is surrounded by neighboring robots and unoccupied locations, it would actively give up its current location by exploring the highest density of nearby unoccupied locations in the desired shape. This idea does not rely on goal assignment. It is realized by adapting the mean-shift algorithm26,27,28, which is an optimization technique widely used in machine learning for locating the maxima of a density function. Moreover, a distributed negotiation mechanism is designed to allow robots to negotiate the final desired shape with their neighbors in a distributed manner. This negotiation mechanism enables the swarm to maneuver while maintaining a desired shape based on a small number of informed robots. The proposed strategy empowers robot swarms to assemble nonconvex complex shapes with strong adaptability and high efficiency, as verified by numerical simulation results and real-world experiments with swarms of 50 ground robots. The strategy can be adapted to generate interesting behaviors including shape regeneration, cooperative cargo transportation, and complex environment exploration.