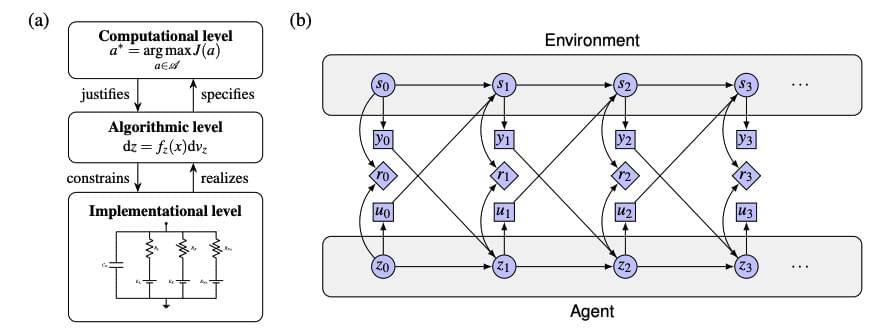
The pursuit of artificial intelligence increasingly focuses on replicating the efficiency and adaptability of the human brain, and a new approach, termed neuromorphic intelligence, offers a promising path forward. Marcel van Gerven from Radboud University and colleagues demonstrate how brain-inspired systems can achieve significantly greater energy efficiency than conventional digital computers. This research establishes a unifying theoretical framework, rooted in dynamical systems theory, to integrate insights from diverse fields including neuroscience, physics, and artificial intelligence. By harnessing noise as a learning resource and employing differential genetic programming, the team advances the development of truly adaptive and sustainable artificial intelligence, paving the way for emergent intelligence arising directly from physical substrates.
Researchers demonstrate that applying dynamical systems theory, a mathematical framework describing change over time, to artificial intelligence enables the creation of more sustainable and adaptable systems by harnessing noise as a learning tool and allowing intelligence to emerge from the physical properties of the system itself.