Reproducibility is a bedrock of scientific progress. However, it’s remarkably difficult to get reproducible results out of large language models.
For example, you might observe that asking ChatGPT the same question multiple times provides different results. This by itself is not surprising, since getting a result from a language model involves “sampling”, a process that converts the language model’s output into a probability distribution and probabilistically selects a token.
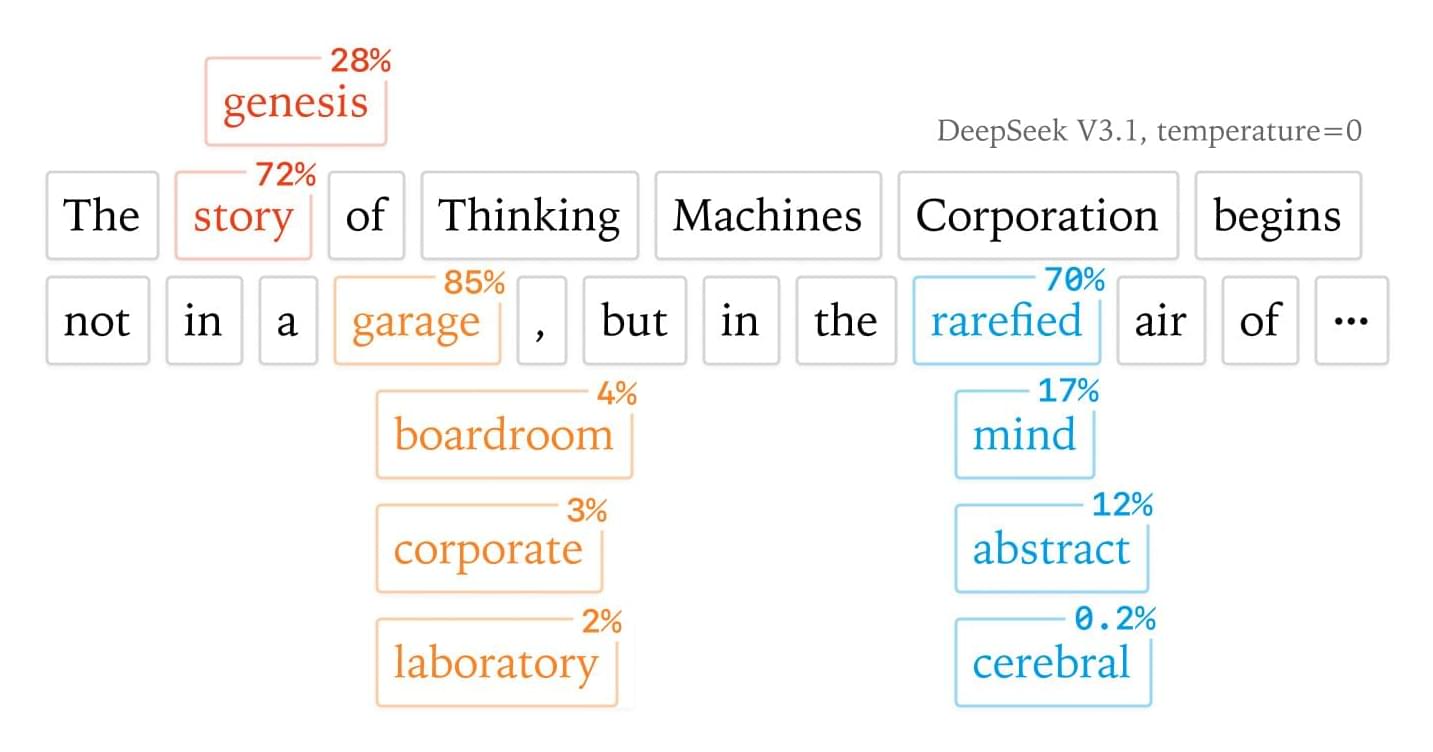
What might be more surprising is that even when we adjust the temperature down to 0This means that the LLM always chooses the highest probability token, which is called greedy sampling. (thus making the sampling theoretically deterministic), LLM APIs are still not deterministic in practice (see past discussions here, here, or here). Even when running inference on your own hardware with an OSS inference library like vLLM or SGLang, sampling still isn’t deterministic (see here or here).